New experimental technique with Goethe University’s reaction microscope allows ‘X-ray’ of individual molecules
Credit: Till Jahnke, Goethe University Frankfurt
“The smaller the particle, the bigger the hammer.” This rule from particle physics, which looks inside the interior of atomic nuclei using gigantic accelerators, also applies to this research. In order to “X-ray” a two-atom molecule such as oxygen, an extremely powerful and ultra-short X-ray pulse is required. This was provided by the European XFEL which started operations in 2017 and is one of the the strongest X-ray source in the world
In order to expose individual molecules, a new X-ray technique is also needed: with the aid of the extremely powerful laser pulse the molecule is quickly robbed of two firmly bound electrons. This leads to the creation of two positively charged ions that fly apart from each other abruptly due to the electrical repulsion. Simultaneously, the fact that electrons also behave like waves is used to advantage. “You can think of it like a sonar,” explains project manager Professor Till Jahnke from the Institute for Nuclear Physics. “The electron wave is scattered by the molecular structure during the explosion, and we recorded the resulting diffraction pattern. We were therefore able to essentially X-ray the molecule from within, and observe it in several steps during its break-up.”
For this technique, known as “electron diffraction imaging”, physicists at the Institute for Nuclear Physics spent several years further developing the COLTRIMS technique, which was conceived there (and is often referred to as a “reaction microscope”). Under the supervision of Dr Markus Schöffler, a corresponding apparatus was modified for the requirements of the European XFEL in advance, and designed and realised in the course of a doctoral thesis by Gregor Kastirke. No simple task, as Till Jahnke observes: “If I had to design a spaceship in order to safely fly to the moon and back, I would definitely want Gregor in my team. I am very impressed by what he accomplished here.”
The result, which was published in the current issue of the renowned Physical Review X, provides the first evidence that this experimental method works. In the future, photochemical reactions of individual molecules can be studied using these images with their high temporal resolution. For example, it should be possible to observe the reaction of a medium-sized molecule to UV rays in real time. In addition, these are the first measurement results to be published since the start of operations of the Small Quantum Systems (SQS) experiment station at the European XFEL at the end of 2018.
###
Publication: Photoelectron diffraction imaging of a molecular breakup using an X-ray free-electron laser.
Gregor Kastirke et al. Phys. Rev. X 10, 021052 https:/
Images may be downloaded at this link: http://www.
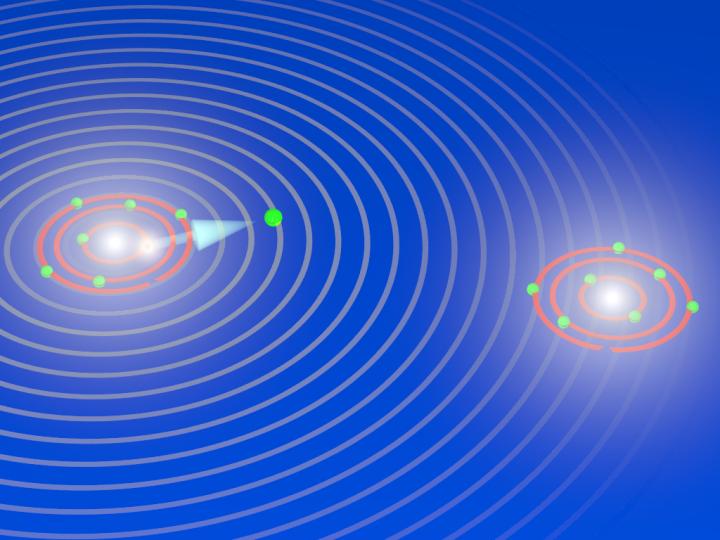
Caption: During the explosion of an oxygen molecule: the X-ray laser XFEL knocks electrons out of the two atoms of the oxygen molecule and initiates its breakup. During the fragmentation, the X-ray laser releases another electron out of an inner shell from one of the two oxygen atoms that are now charged (ions). The electron has particle and wave characteristics, and the waves are scattered by the other oxygen ion. The diffraction pattern are used to image the breakup of the oxygen molecules and to take snapshots of the fragmentation process (electron diffraction imaging). Credit: Till Jahnke, Goethe University Frankfurt
Further information:
Professor Till Jahnke
Institute for Nuclear Physics
Goethe University Frankfurt
Tel.: +49 69 798-47025
E-Mail: [email protected].
Current news about science, teaching, and society can be found on GOETHE-UNI online (http://www.
Goethe University is a research-oriented university in the European financial centre Frankfurt am Main. The university was founded in 1914 through private funding, primarily from Jewish sponsors, and has since produced pioneering achievements in the areas of social sciences, sociology and economics, medicine, quantum physics, brain research, and labour law. It gained a unique level of autonomy on 1 January 2008 by returning to its historic roots as a “foundation university”. Today, it is one of the three largest universities in Germany. Together with the Technical University of Darmstadt and the University of Mainz, it is a partner in the inter-state strategic Rhine-Main University Alliance. Internet: http://www.
Publisher: The President of Goethe University Editor: Dr. Markus Bernards, Science Editor, PR & Communication Department, Theodor-W.-Adorno-Platz 1, 60323 Frankfurt am Main, Tel: -49 (0) 69 798-12498, Fax: +49 (0) 69 798-763 12531, [email protected].
Media Contact
Till Jahnke
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




