Credit: Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (SMART)
Singapore, 19 April, 2021 – Researchers at the Future Urban Mobility (FM) Interdisciplinary Research Group (IRG) at Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (SMART), MIT’s research enterprise in Singapore, have created a synthetic framework known as theory-based residual neural network (TB-ResNet), which combines discrete choice models (DCMs) and deep neural networks (DNNs), also known as deep learning, to improve individual decision-making analysis used in travel behaviour research.
In this research paper, Theory-based residual neural networks: A synergy of discrete choice models and deep neural networks, recently published in established transportation science journal Transportation Research: Part B, SMART researchers explain their developed TB-ResNet framework and demonstrate the strength of combining the DCMs and DNNs methods, proving that they are highly complementary.
As machine learning is increasingly used in the field of transportation, the two disparate research concepts, DCMs and DNNs, have long been viewed as conflicting methods of research.
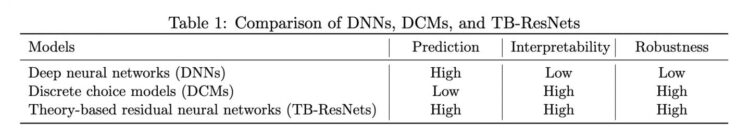
By synergising these two important research paradigms, TB-ResNet takes advantage of DCMs’ simplicity and DNNs’ expressive power to generate richer findings and more accurate predictions for individual decision-making analysis, which is important for improved travel behaviour research. The developed TB-ResNet framework is more predictive, interpretable, and robust as compared to DCMs and DNNs, with findings consistent over a wide range of data sets.
Accurate and efficient analysis of individual decision-making in the everyday context is critical for mobility companies, governments and policy makers seeking to optimise transport networks and tackle transport challenges, especially in urban cities. TB-ResNet will eliminate existing difficulties faced in DCMs and DNNs, and allow stakeholders to take a holistic, unified view towards transport planning.
Postdoctoral Associate at MIT Urban Mobility Lab and lead author of the paper, Shenhao Wang, said, “Improved insights to how travellers make decisions about travel mode, destination, departure time, and planning of activities are crucial to urban transport planning for governments and transport companies worldwide. I look forward to further developing TB-ResNet and its applications for transport planning now that it has been acknowledged by the transport research community.”
SMART FM Lead Principal Investigator and Associate Professor at MIT Department of Urban Studies and Planning, Jinhua Zhao, said, “Our Future Urban Mobility research team focuses on developing new paradigms and innovating future urban mobility systems in and beyond Singapore. This new TB-ResNet framework is an important milestone that could enrich our investigations for impacts of decision-making models for urban development.”
The TB-ResNet can also be widely applied to understand individual decision-making cases as illustrated in this research, whether it is about travels, consumption, voting, among many others.
The TB-ResNet framework was tested in three instances in this study. Firstly, researchers used it to predict travel mode decisions between transit, driving, autonomous vehicles, walking, and cycling, which are major travel modes in an urban setting. Secondly, they evaluated risk alternatives and preferences when monetary payoffs with uncertainty are involved. Examples of such situations include insurance, financial investment, and voting decisions.
Lastly, they examined temporal alternatives, measuring the trade-off between current and future money payoffs. A typical example of when such decisions are made would be in transport development where shareholders analyse infrastructure investment with large down payment and long-term benefits.
###
This research is carried out by SMART and supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) Singapore under its Campus for Research Excellence And Technological Enterprise (CREATE) programme.
About the Future Urban Mobility (FM) Interdisciplinary Research Group (IRG)
The Future Urban Mobility (FM) Interdisciplinary Research Group (IRG) is one of five IRGs in the Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology Centre (SMART). FM harnesses new technological and institutional innovations to create the next generation of urban mobility systems to increase accessibility, equity, safety and environmental performance for the citizens and businesses of Singapore and other metropolitan areas, worldwide. SMART-FM is supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) Singapore and situated in the Campus for Research Excellence and Technological Enterprise (CREATE).
For more information, please log on to: https:/
About Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (SMART)
Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (SMART) is MIT’s Research Enterprise in Singapore, established by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in partnership with the National Research Foundation of Singapore (NRF) since 2007. SMART is the first entity in the Campus for Research Excellence and Technological Enterprise (CREATE) developed by NRF. SMART serves as an intellectual and innovation hub for research interactions between MIT and Singapore. Cutting-edge research projects in areas of interest to both Singapore and MIT are undertaken at SMART. SMART currently comprises an Innovation Centre and five Interdisciplinary Research Groups (IRGs): Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR), Critical Analytics for Manufacturing Personalized-Medicine (CAMP), Disruptive & Sustainable Technologies for Agricultural Precision (DiSTAP), Future Urban Mobility (FM) and Low Energy Electronic Systems (LEES).
SMART research is funded by the National Research Foundation Singapore under the CREATE programme.
For more information, please visit http://smart.
For media queries, please contact:
Glenn Tan
[email protected]
+65 9658 5749
Media Contact
Glenn Tan
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.