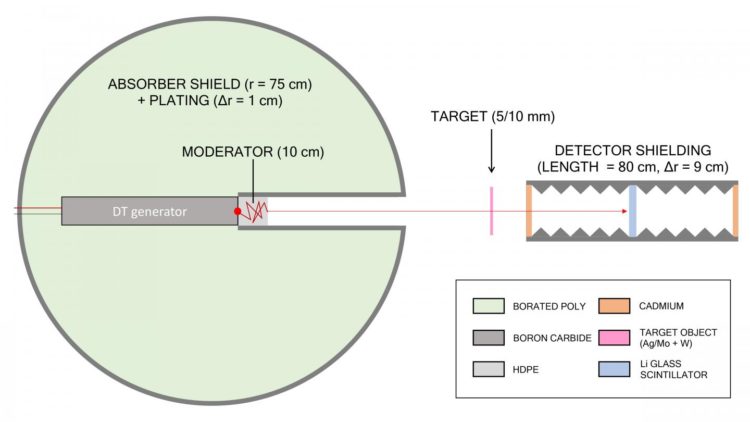
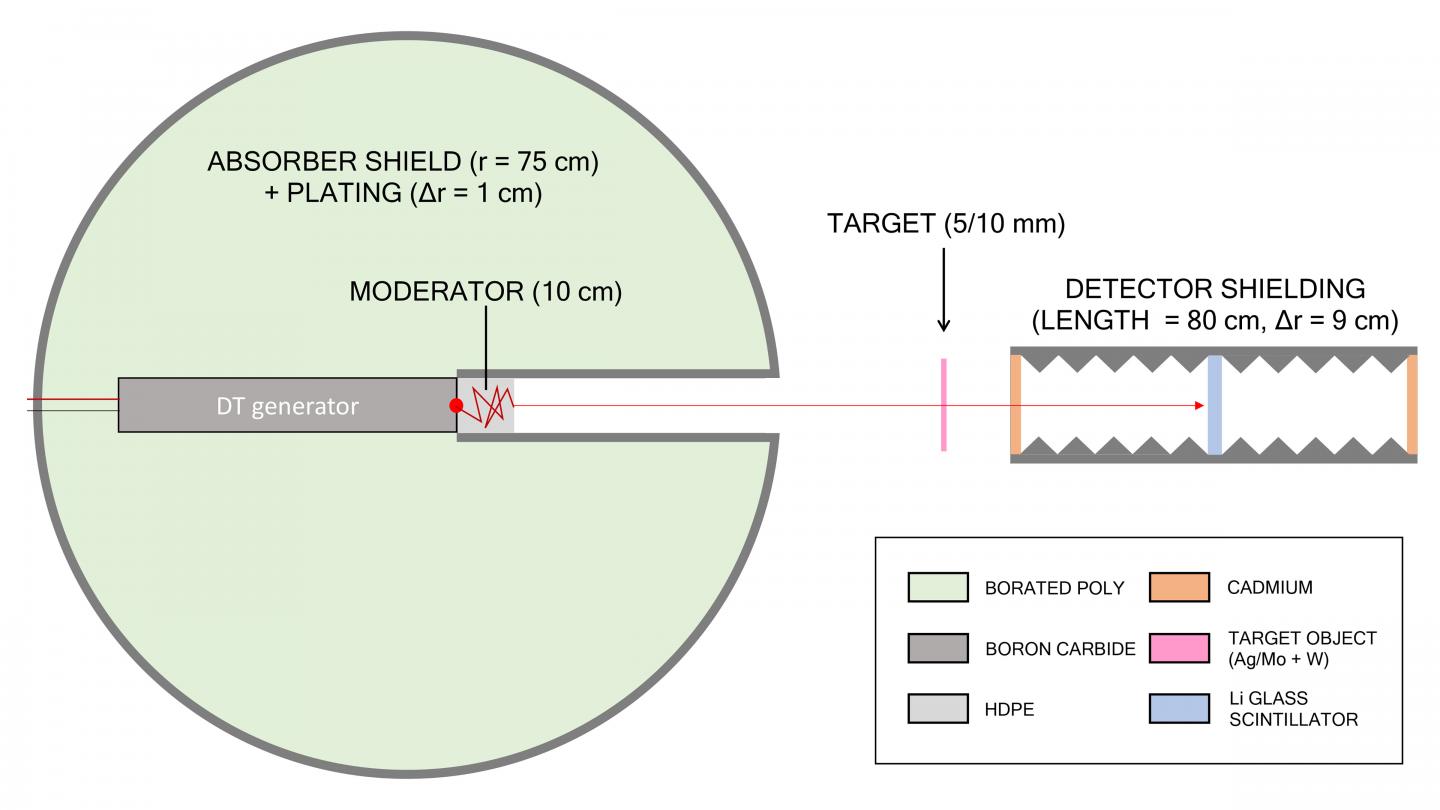
This compact neutron resonance transmission analysis device can detect nuclear material in one minute and makes possible in 5 meters what normally requires a kilometer-scale neutron beam.
Credit: Ezra M. Engel and Ethan A. Klein, MIT
WASHINGTON, January 29, 2020 — Most nuclear data measurements are performed at accelerators large enough to occupy a geologic formation a kilometer wide, like the Los Alamos Neutron Science Center located on a mesa in the desert. But a portable device that can reveal the composition of materials quickly on-site would greatly benefit cases such as in archaeology and nuclear arms treaty verification.
Research published this week in AIP Advances, from AIP Publishing, used computational simulations to show that with the right geometric adjustments, it is possible to perform accurate neutron resonance transmission analysis in a device just 5 meters long.
“We expected massive backgrounds to dilute and contaminate our signal, and early simulation work confirmed that the scale of these effects would make the technique entirely impossible,” author Areg Danagoulian said. “However, careful optimization of the geometries allowed us to almost completely suppress these effects, giving us a near-perfect signal.”
Using a model of a pulsed deuterium-tritium neutron source in a polycone layout, the researchers performed a series of tests to optimize the moderation, shielding and collimation of the device and probe the configuration for uncertainties introduced by these adjustments. To confirm the device’s accuracy, they compared spectral reconstructions and tested the isotopic sensitivity of the device.
“Depending on the goal of the application, one can use spectroscopic radiography to determine the absolute abundances and densities of individual isotopes,” Danagoulian said. “It can also be used in treaty verification exercises, where an authentic nuclear weapon component is compared to that from a candidate warhead.”
While the tests used silver, tungsten and molybdenum, the method could be used to identify isotopes of plutonium or uranium in nuclear warheads or enriched fuel, as well as tin, silver or gold in archaeological sites. Their work could also be used to similarly reduce the lengths of thermal neutron beamlines.
Their work uses time-of-flight reconstructions of the energies of pulsed neutrons in order to determine the composition of target materials. These reconstructions allow analysis of the spectrum transmitted and nuclear resonances present in different isotopes to identify the isotopic makeup of the material in the target.
Their results show the device was successful. It was able to precisely differentiate various isotopes and was sensitive to variations in isotopic concentrations.
The authors plan to perform experimental validations of the above technique using various pulsed neutrons sources and neutron detectors.
###
The article, “Feasibility study of a compact neutron resonance transmission analysis instrument,” is authored by Ezra M. Engel, Ethan A. Klein and Areg Danagoulian. The article appears in AIP Advances (DOI: 10.1063/1.5129961) and can be accessed at https:/
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
AIP Advances is an open access journal publishing in all areas of physical sciences — applied, theoretical, and experimental. The inclusive scope of AIP Advances makes it an essential outlet for scientists across the physical sciences. See https:/
Media Contact
Larry Frum
[email protected]
301-209-3090
Related Journal Article
http://dx.