Credit: Insilico Medicine
Summary:
- Cetuximab, an anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody and the only FDA-approved targeted therapy against advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), has limited efficacy due to development of resistance.
- In a bid to identify new therapeutic strategies to circumvent the de novo or acquired cetuximab resistance in HNSCC tumors, researchers studied the clinical relevance of SMAD4 loss on cetuximab response in HPV-negative HNSCC patients.
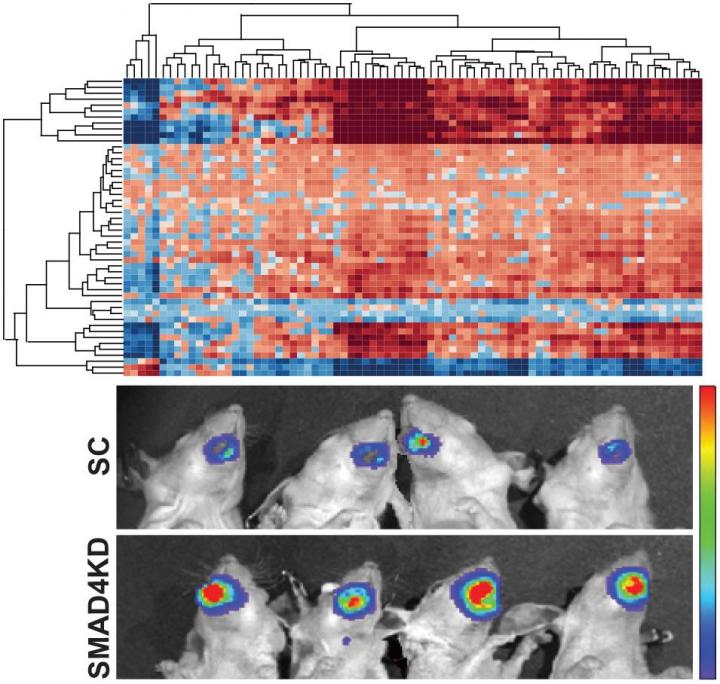
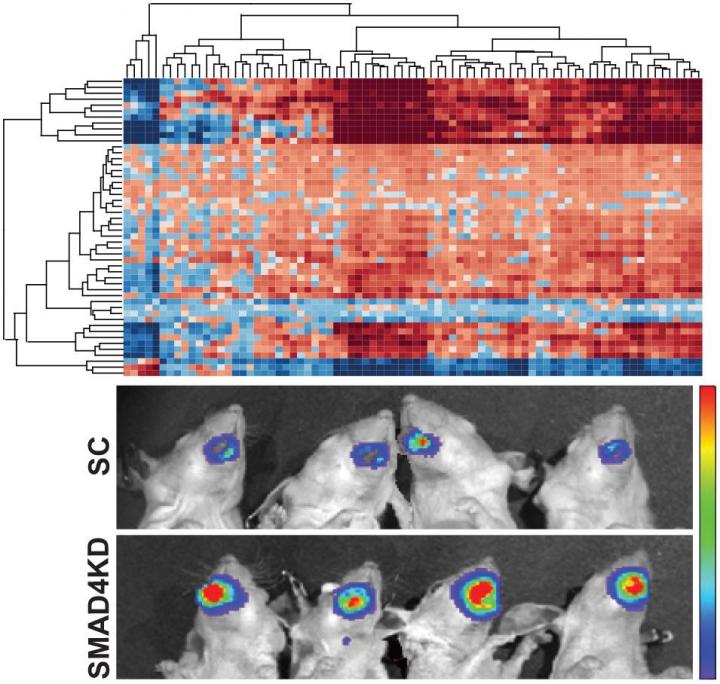
- The researchers identified that SMAD4 loss results in cetuximab resistance in vitro and poor survival in HPV-negative HNSCC patients and in vivo models. Using OncoFinder (an innovative bioinformatic tool currently rebranded as iPANDA), they revealed a signature of pro-survival and anti-apoptotic pathways specifically dysregulated in SMAD4-low HNSCCs and indicate JNK and MAPK activation as potential mediators of cetuximab resistance.
July 7th, 2017, BALTIMORE, MD. A team of Moffitt Cancer Center and Johns Hopkins scientists alongside collaborators from Insilico Medicine, Inc, has identified JNK and MAPK activation as mediators of cetuximab resistance in HNSCC tumors with loss of SMAD4 expression. In a report on these findings, published online May 16 in Clinical Cancer Research , the team says that HPV-negative HNSCC patients with low expression of SMAD4 protein (a key downstream mediator of TGFβ signaling) may have poor cetuximab response.
"This work contributes to advancing our knowledge of head and neck cancer because mechanisms of cetuximab resistance can be targeted with combination therapy. We indicated JNK and MAPK activation as potential mediators of cetuximab resistance. Our study proposes concurrent EGFR and JNK/MAPK inhibition as a novel strategy for overcoming cetuximab resistance in tumors with loss of SMAD4 expression." says Christine Chung, M.D., Chair of Department of Head and Neck-Endocrine Oncology at the Moffitt Cancer Center. Chung cautions that the findings are preliminary and further confirmatory studies are planned in a wider range of cell lines and more cancer patients. But the knowledge is invaluable, she says, for both understanding the molecular biology underlying SMAD4 — associated HNSCC tumorigenesis and how to use the findings in clinical applications.
Alex Zhavoronkov, PhD, CEO of Insilico Medicine Inc, a Baltimore-based company focusing on big data analysis, says — "Through its focus on aging research and drug discovery, InSilico Medicine is actively engaged in providing innovative computational technology to academia and pharmaceutical industry. Using OncoFinder (now rebranded as iPANDA), a bioinformatics approach for analyzing high-throughput transcriptomic datasets, we uncovered a signature of pro-survival and anti-apoptotic pathways specifically dysregulated in SMAD4-low cases. These data indicates that SMAD4 may regulate genes associated with key cancer pathways and further support the role of SMAD4 as a potent tumor suppressor in head and neck cancers."
"Our team has previously reported a link between somatic inactivation of SMAD4 and cetuximab resistance in HNSCC. In this study, we were able to detect pro-survival signaling axes in tumors with low SMAD4 expression that may contribute to survival and promotion of cetuximab resistance via inhibition of apoptosis and induction of cell proliferation" – Says Ruchira Ranaweera, Ph.D, one of the lead authors of the manuscript.
Evgeny Izumchenko, an Assistant Professor at Johns Hopkins University, adds – "In particular, our data suggest that SMAD4 expression may act as a determinant of sensitivity/resistance to EGFR/MAPK or EGFR/JNK inhibition in HPV-negative tumors. But it is only the beginning to fully determine the ability of SMAD4 to stratify the subset of patients whose tumors could respond and who would clinically benefit from the combination therapy."
###
Other authors on the paper are Hiroyuki Ozawa, Elana Fertig, Jason Howard, Ana Markovic, Atul Bedi, Rajani Ravi, Jimena Perez, Hao Wang, Hyunseok Kang, Harry Quon and David Sidransky of the Johns Hopkins University, Quynh-Thu Le and Christina S. Kong of Stanford University, Richard Jordan of University of California, San Francisco and Eugene Makarev of InSilico Medicine Inc.
About Insilico Medicine, Inc
Insilico Medicine, Inc. is an artificial intelligence company located at the Emerging Technology Centers at the Johns Hopkins University Eastern campus in Baltimore with R&D resources in Belgium, Russia, and the UK hiring talent through hackathons and competitions. It utilizes advances in genomics, big data analysis and deep learning for in silico drug discovery and drug repurposing for aging and age-related diseases. The company pursues internal drug discovery programs in cancer, Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, ALS, diabetes, sarcopenia and geroprotector discovery. Through its Pharma.AI division, the company provides advanced machine learning services to biotechnology, pharmaceutical, and skin care companies. In 2017 NVIDIA selected Insilico as the top 5 AI companies for social impact.
Brief company video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=l62jlwgL3v8
http://www.insilicomedicine.com
Media Contact
Qingsong Zhu
[email protected]
443-451-7212
@InSilicoMeds
http://www.insilicomedicine.com
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1686