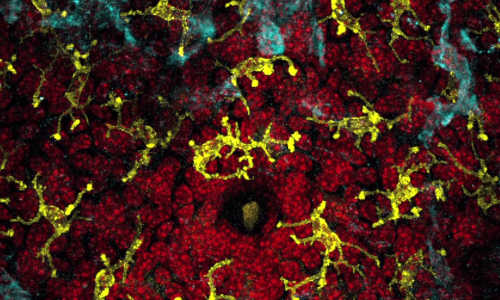
New research in mice shows that the immune system in the skin develops distinct responses to the various microbes that naturally colonize the skin, referred to as commensals. A team led by scientists at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, found that each type of microbe triggers unique aspects of the immune system, suggesting that immune cells found in the skin can rapidly sense and respond to changes in microbial communities. These findings help clarify the protective role of skin commensals and may help explain how variation in the microbes at different skin sites contributes to skin disorders.
Scientists at three NIH institutes collaborate to study the role of “good” skin bacteria in health and disease.
The skin is home to diverse microbial communities that can change over time. In the current study, investigators found that colonizing mice with different commensals leads to production of commensal-specific immune cells. They describe in detail how the common skin commensal Staphylococcus epidermidis enhances immune responses against pathogens without causing inflammation. Colonizing the skin of mice with S. epidermidis increased the number of CD8+ T immune cells, which produced the chemical messenger IL-17A. Dendritic cells, another type of immune cell, played a key role in generating this specific, non-inflammatory response. Mice colonized with S. epidermidis were protected against infection with a disease-causing fungus. Depleting CD8+ T cells or neutralizing IL-17A removed this protective effect.
The ability of different microbes to trigger distinct aspects of the immune system without causing inflammation opens the possibility of discovering new adjuvants—immune-boosting substances that may be added to vaccines or medications. Future research will focus on identifying specific chemical messengers and understanding how they stimulate the immune system.
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by NIH/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.