A KAIST team’s mathematical sampling model shows that retino-cortical mapping is a prime determinant in the topography of cortical organization
Credit: Professor Se-Bum Paik, KAIST.
Researchers have explained how visual cortexes develop uniquely across the brains of different mammalian species. A KAIST research team led by Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has identified a single biological factor, the retino-cortical mapping ratio, that predicts distinct cortical organizations across mammalian species.
This new finding has resolved a long-standing puzzle in understanding visual neuroscience regarding the origin of functional architectures in the visual cortex. The study published in Cell Reports on March 10 demonstrates that the evolutionary variation of biological parameters may induce the development of distinct functional circuits in the visual cortex, even without species-specific developmental mechanisms.
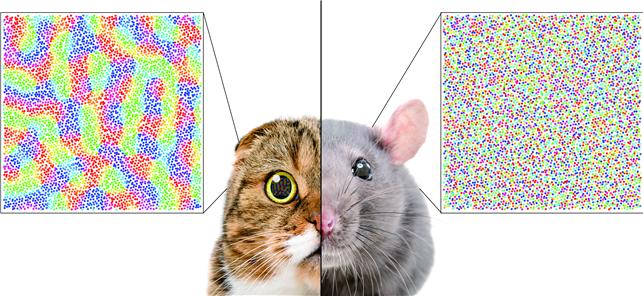
In the primary visual cortex (V1) of mammals, neural tuning to visual stimulus orientation is organized into one of two distinct topographic patterns across species. While primates have columnar orientation maps, a salt-and-pepper type organization is observed in rodents.
For decades, this sharp contrast between cortical organizations has spawned fundamental questions about the origin of functional architectures in the V1. However, it remained unknown whether these patterns reflect disparate developmental mechanisms across mammalian taxa, or simply originate from variations in biological parameters under a universal development process.
To identify a determinant predicting distinct cortical organizations, Professor Paik and his researchers Jaeson Jang and Min Song examined the exact condition that generates columnar and salt-and-pepper organizations, respectively. Next, they applied a mathematical model to investigate how the topographic information of the underlying retinal mosaics pattern could be differently mapped onto a cortical space, depending on the mapping condition.
The research team proved that the retino-cortical feedforwarding mapping ratio appeared to be correlated to the cortical organization of each species. In the model simulations, the team found that distinct cortical circuitries can arise from different V1 areas and retinal ganglion cell (RGC) mosaic sizes. The team’s mathematical sampling model shows that retino-cortical mapping is a prime determinant in the topography of cortical organization, and this prediction was confirmed by neural parameter analysis of the data from eight phylogenetically distinct mammalian species.
Furthermore, the researchers proved that the Nyquist sampling theorem explains this parametric division of cortical organization with high accuracy. They showed that a mathematical model predicts that the organization of cortical orientation tuning makes a sharp transition around the Nyquist sampling frequency, explaining why cortical organizations can be observed in either columnar or salt-and-pepper organizations, but not in intermediates between these two stages.
Professor Paik said, “Our findings make a significant impact for understanding the origin of functional architectures in the visual cortex of the brain, and will provide a broad conceptual advancement as well as advanced insights into the mechanism underlying neural development in evolutionarily divergent species.”
He continued, “We believe that our findings will be of great interest to scientists working in a wide range of fields such as neuroscience, vision science, and developmental biology.”
###
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF).
Media Contact
Younghye Cho
[email protected]
82-423-502-294
Original Source
http://news.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




