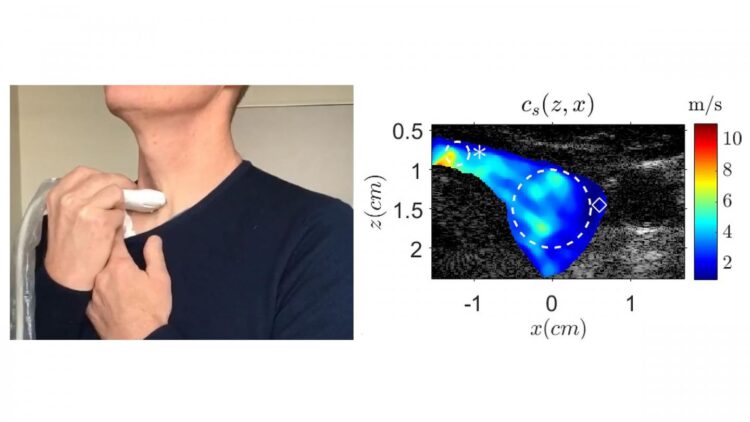
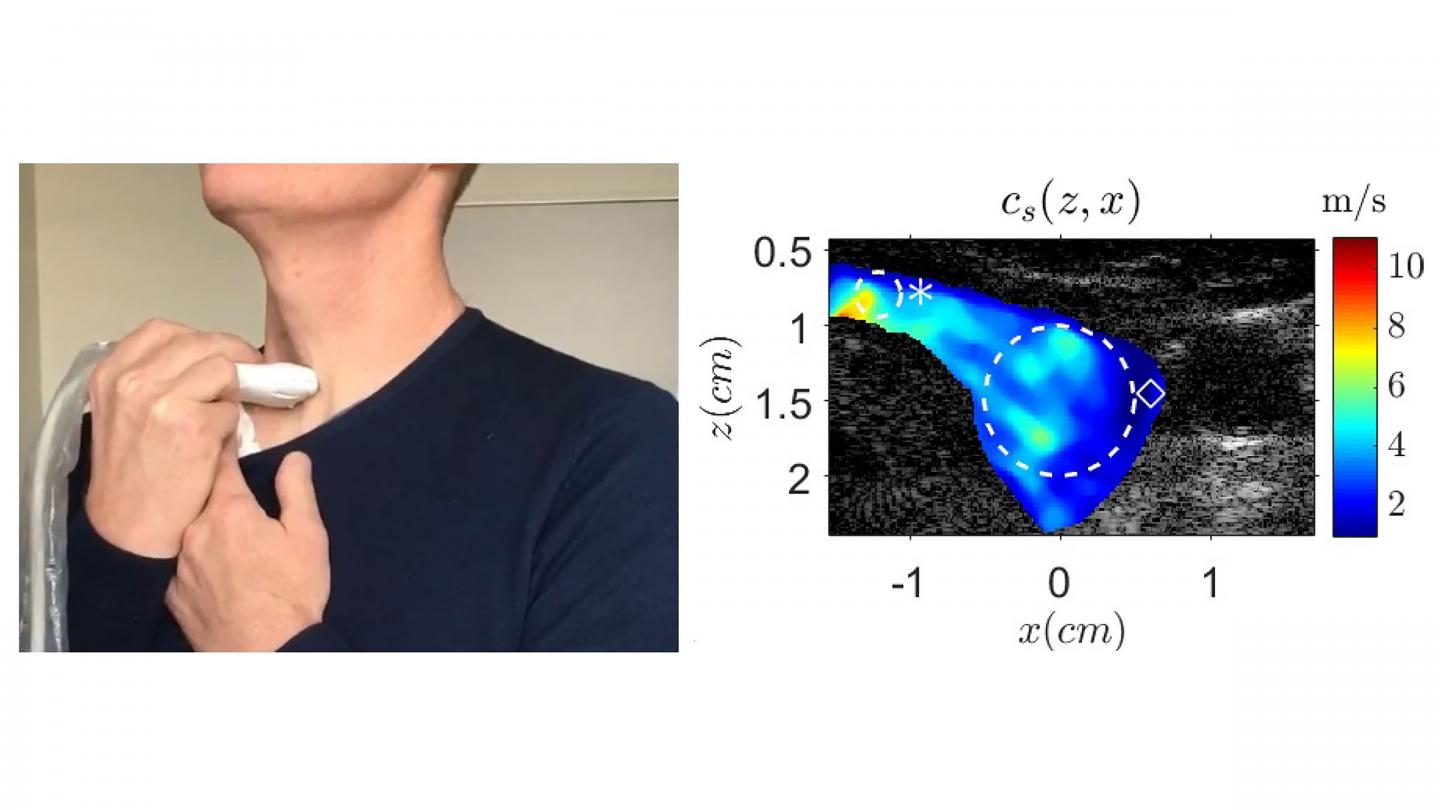
Monitoring the stiffness of the tissue near a patient’s thyroid while they sing a note can allow medical professionals to determine the presence of a tumor.
Credit: Steve Beuve
WASHINGTON, January 12, 2021 — Singing may be the next-generation, noninvasive approach to determining the health of a patient’s thyroid.
Typically, a fine needle is used to detect the presence of a tumor in the thyroid, which most commonly affects children and younger women. However, this method can only detect about 5% of thyroid cancers.
Researchers from Université de Tours, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Dijon-Bourgogne, and Université Bourgogne Franche-Comté suggest a simpler approach: singing. They demonstrate the technique in the journal Applied Physics Letters, from AIP Publishing.
“Developing noninvasive methods would reduce the stress of patients during their medical exams,” said Steve Beuve, one of the authors. “Having to sing during a medical exam can perhaps help release some of the nervous tension even more.”
When a person sings, the vibrations from their voice create waves in the tissue near the vocal tract called shear waves. If a tumor is present in the thyroid, the elasticity of its surrounding tissue increases, stiffening, and causing the shear waves to accelerate.
Using ultrasound imaging to measure the speed of these waves, the researchers can determine the elasticity of the thyroid tissue. This method, which the authors call vocal passive elastography, is an extension of passive elastography, a shear wave propagation tracking technique used in seismology.
“The propagation of shear waves gives us information about mechanical properties of soft tissues,” Beuve said.
Because the elasticity of biological tissues depends on the speed of the shear waves, by asking a volunteer to sing and maintain an “eeee” sound at 150 hertz, approximately the frequency of D3, the group was able to characterize the thyroid and find any abnormally stiff areas.
A key benefit of V-PE is how quick and easy it is. It requires no specialized or complex equipment added to the ultrasound scanner and only needs about one second of data acquisition to complete. Analyzing the data is the longest step, but a computer program that the team developed does the computation automatically.
The group is working on improving the user friendliness of the computer interface and potentially expanding V-PE to include other areas near the vocal tract, such as the brain.
“We want to cooperate with physicians to propose protocols to verify the relevance of elasticity as a biomarker of pathogens,” Beuve said.
###
The article “Natural shear wave imaging using vocal tract vibrations: introducing vocal passive elastography (V-PE) to thyroid elasticity mapping” is authored by Steve Beuve, Samuel Callé, Elise Khoury, Emmanuel Simon, and Jean Pierre Remenieras. The article will appear in Applied Physics Letters on Jan. 12, 2021 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0031169). After that date, it can be accessed at
https:/
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Applied Physics Letters features rapid reports on significant discoveries in applied physics. The journal covers new experimental and theoretical research on applications of physics phenomena related to all branches of science, engineering, and modern technology. See https:/
Media Contact
Larry Frum
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.