WASHINGTON, March 14, 2023 – Burn wounds are notoriously prone to bacterial infection and typically lead to a larger amount of scar tissue than laceration wounds.
Credit: Jeroen Eyckmans and Anish Vasan
WASHINGTON, March 14, 2023 – Burn wounds are notoriously prone to bacterial infection and typically lead to a larger amount of scar tissue than laceration wounds.
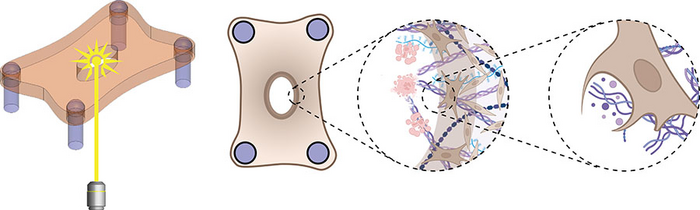
In APL Bioengineering, by AIP publishing, researchers from Boston University and Harvard University created a biomimetic model to study wound healing in burn and laceration wounds. They discovered that fibroblasts – normally considered building cells that give shape and strength to tissues and organs – clear away damaged tissue before depositing new material. This part of the healing process is slower in burn wounds, where more tissue damage is present.
Cell biologists identify four phases of wound healing: bleeding stoppage, inflammation, new tissue formation, and tissue strengthening. During the inflammation and formation stages, immune cells are thought to clear bacteria and dead cells from the wound. They also activate fibroblasts and blood vessels to begin repairs.
“Depending on the injury, the extent and duration of these four phases can wildly vary across different wound types,” said author Jeroen Eyckmans. “Given that laceration wounds are well perfused with blood, they tend to heal well. However, in burns, the blood vessels are cauterized, preventing blood from entering the wound bed and slowing down the healing process. Severe burn wounds also have large amounts of dead tissue that physically block new tissue formation.”
To study how the mode of injury impacts the healing rate of wounds, the team designed an in vitro model system made of fibroblasts embedded in a collagen hydrogel. Wounds were created in this microtissue using a microdissection knife to mimic laceration or a high-energy laser to simulate a burn.
Although both wound types were equal in size, laser ablation caused more cell death and tissue damage next to the wound margins compared to knife wounds.
“During healing, we found that the fibroblasts first cleared the damaged material from the wound before depositing new material,” said Eyckmans. “This was a surprising finding because removal of dead tissue has been attributed to specialized immune cells such as macrophages, and fibroblasts have been considered to be tissue-building cells, not tissue-removal cells.”
Given that there was more tissue damage in the laser ablation wounds, it took fibroblasts more time to remove the damage, ultimately delaying tissue healing.
Based on these findings, therapies that promote wound clearance could accelerate healing. Genetically engineered white blood cells, designed to remove dead tissue, could be particularly useful for reaching injured organs and tissues deep in the body.
###
The article “Fibroblast clearance of damaged tissue following laser ablation in engineered microtissues” is authored by Megan Elizabeth Griebel, Anish Vasan, Christopher S. Chen, and Jeroen Eyckmans. It will appear in APL Bioengineering on March 14, 2023 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0133478). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0133478.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
APL Bioengineering is an open access journal publishing significant discoveries specific to the understanding and advancement of physics and engineering of biological systems. See http://aip.scitation.org/journal/apb.
###
Journal
APL Bioengineering
DOI
10.1063/5.0133478
Article Title
Fibroblast clearance of damaged tissue following laser ablation in engineered microtissues
Article Publication Date
14-Mar-2023




