Whole-genome sequencing instead of biomarker testing may streamline selection of appropriate therapy, investigators report in the Journal of Molecular Diagnostics

Credit: van de Ven, Michiel, et al.
Philadelphia, March 15, 2021 – Biomarker testing surveys specific disease-associated molecules to predict treatment response and disease progression; however its use has complicated the diagnosis of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In a new study in The Journal of Molecular Diagnosis, published by Elsevier, investigators provide for the first time a complete overview of biomarker testing, spanning multiple treatment lines, in a single cohort of patients.
Using exploratory data analysis and process-mining techniques in a real-world setting, investigators identified significant variation in test utilization and treatment. They also found that while whole-genome sequencing, in which a patient’s unique DNA is mapped at once, may not be a cost saving alternative to biomarker testing, as some have suggested, it may have other benefits for patients, such as decreasing the time between testing and therapy.
“While there is a lot of interest in the use of real-world data to analyze treatment variation and outcomes, this study demonstrates the importance of identifying variation in the use of molecular tests as the gateway to most cancer treatments,” explains lead investigator Professor Maarten IJzerman, Health Technology and Services Research, TechMed Center, University of Twente, Enschede, the Netherlands; and the University of Melbourne Centre for Cancer Research in Melbourne, Australia.
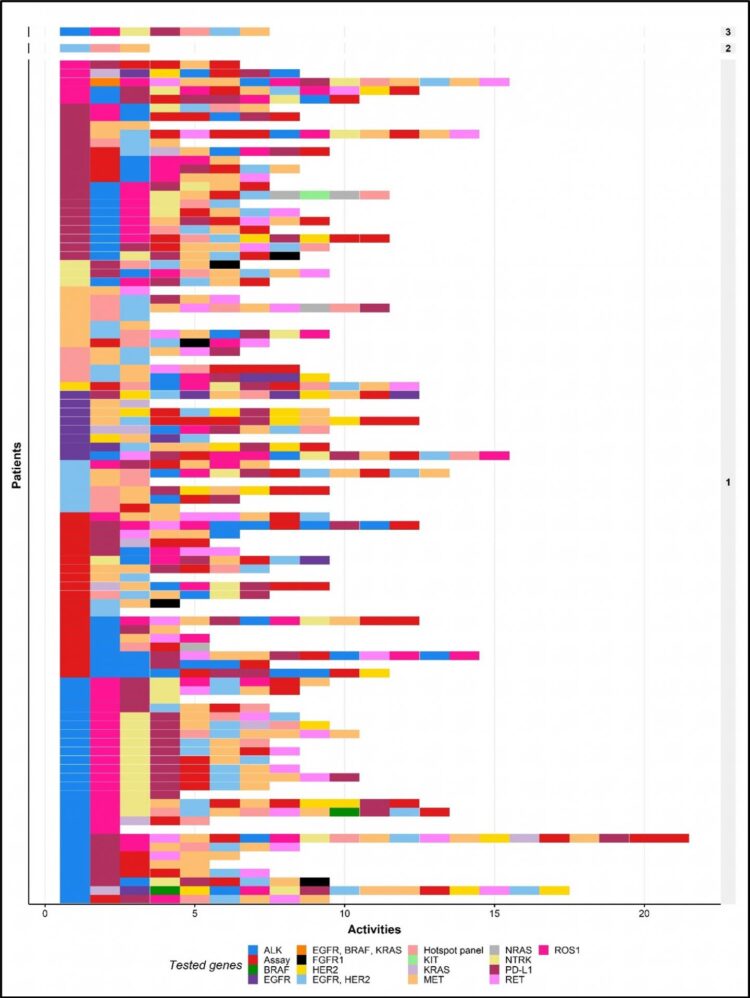
The investigators had access to the complete biomarker testing history of 102 stage IV NSCLC patients who had been referred to a comprehensive cancer center in the Netherlands. Patients are referred to such a facility when they have a complex case, enroll in a clinical trial, or have exhausted treatment options at the referring hospital. Eligible patients were identified using linked pathology data from the referring hospitals to ensure analysis of their complete diagnostic pathways. Process mining allows for the discovery of the actual ordering of care processes and for the evaluation of the characteristics of testing, such as turnaround times and costs.
This study is the first to provide a comprehensive report that includes tested genes, utilized techniques, costs, and turnaround times on the entire sequence of tests received by patients with stage IV NSCLC.
Ninety-nine unique biomarker-test combinations were found in 102 patients; almost none underwent the same tests in the same order. The most common biomarkers were typically tested in the first few tests, and emerging biomarkers were typically tested later. The number of tests per patient also showed substantial variation. Tests were completed at different times in each patient, and in most patients more than one test was completed.
The mean cost per patient of biomarker testing was US$2258.52 / €1881.23. The number of patients for whom biomarker testing would be equally or less expensive if their entire test sequence had been replaced by whole-genome sequencing ranged from 2 to 29, depending on the assumed cost.
“We have shown that it is currently unlikely that replacing the current practice of molecular testing in lung cancer with whole-genome sequencing will be cost saving,” notes first author Michiel van de Ven, PhD candidate, TechMed Center, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands. “Yet, for whole-genome sequencing to be routinely used there are other aspects where it adds value, such as the discovery of other driver mutations not routinely tested for and the potential to streamline diagnostic workflows.”
Multiple biomarker tests for NSCLC can result in unnecessary delays in treatment. The substantial variation of biomarker tests in patients suggests the possibility of inequities in access to the tests and subsequently in access to targeted therapy or immunotherapy. “Whole-genome sequencing may reduce the complexity of the diagnostic pathway, but it has not yet been explored in detail. It could be an exciting avenue for future research,” concludes Professor IJzerman.
###
Media Contact
Eileen Leahy
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.