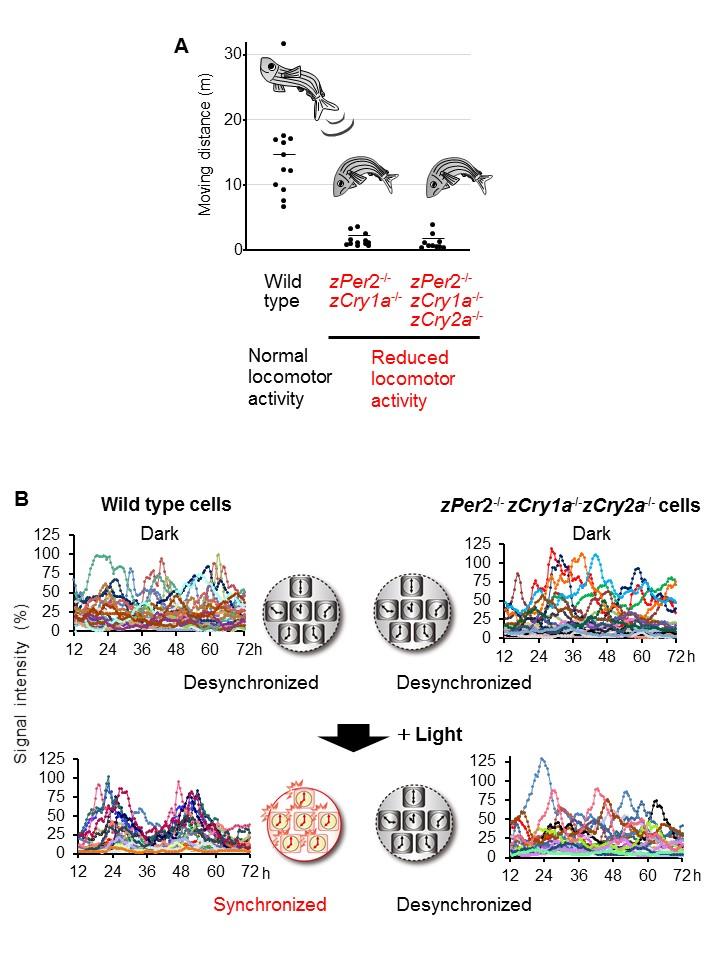
(?)Luminescent traces from individual wild type and zPer2-/- zCry1a-/- zCry2a-/- cultured…
view more
Tokyo, Japan – Animals have distinct behavioral patterns depending on the time of day, with diurnal animals being active during the day and sleeping at night, and vice versa in nocturnal ones. Although genes called clock genes are known to be involved in translating the 24-hour fluctuating rhythm of light exposure into appropriate physiological responses, much remains unclear about how this is achieved.
By focusing on the widely used research tool zebrafish, researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) and colleagues across Japan have shed light on how three clock genes function in responding to light. By abolishing the activity of these genes in zebrafish, this work shows that these genes determine the daily behavioral rhythms of moving and resting, as well as the total time spent being active.
In this study recently reported in the journal Scientific Reports, the team selected zebrafish given the number with which they produce offspring, their simplicity in comparison to mammals, and their simple behavioral rhythms that can be easily quantified and studied. They focused on the genes Cry1a, Per2, and Cry2a in this species, analyzing their functions by knocking out one, two, or all three of them using specific enzymes that can cut DNA
The group then compared normal, unaltered zebrafish with their single-, double-, and triple-knockout counterparts under conditions of complete darkness, 3 hours of light exposure, and 12 hours of light exposure. The latter of these reflected typical conditions when exposed to the fluctuations of light over the course of a day and night.
“In our comparisons of the various zebrafish groups, we found differences in the effects of double knockout of the genes Per2 and Cry1a under 3 hours and 12 hours of light exposure,” corresponding author Hiroshi Nishina says. “The fish showed lower total activity and abnormal locomotion and resting behaviors with 3 hours of light, but these latter abnormalities were improved in the group with 12 hours of exposure, suggesting different regulatory mechanisms between circadian rhythm and locomotor activity.
The team then applied microarray analysis to look more closely at the other specific genes whose expression was affected by knockout of the clock genes. They found that the gene knockout and associated behavioral abnormalities were linked to altered expression of genes involved in metabolism. The findings suggest that the clock genes are connected to the supply of energy to the organism, with their absence reducing this supply and as a result causing lower locomotion and more resting by the zebrafish.
“Our work reveals the importance of the light-inducible clock genes in maximizing physiological efficiency considering a particular organism’s lifestyle,” Jun Hirayama says. “It boosts basic research in this field and could even help in treating sleep disorders related to these genes.”
###
The article “The clock components Period2, Cryptochrome1a, and Cryptochrome2a function in establishing light-dependent behavioral rhythms and/or total activity levels in zebrafish” is published in Scientific Reports at doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37879-8
Media Contact
Hiroshi NISHINA
[email protected]
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




