“[…] there has been limited research to date on the effect of cellular ‘ageing’, termed senescence, on amyloidosis.”
Credit: 2023 Whitehead et al.
“[…] there has been limited research to date on the effect of cellular ‘ageing’, termed senescence, on amyloidosis.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 29, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 5, entitled, “Senescence and extracellular vesicles: novel partners in vascular amyloidosis.”
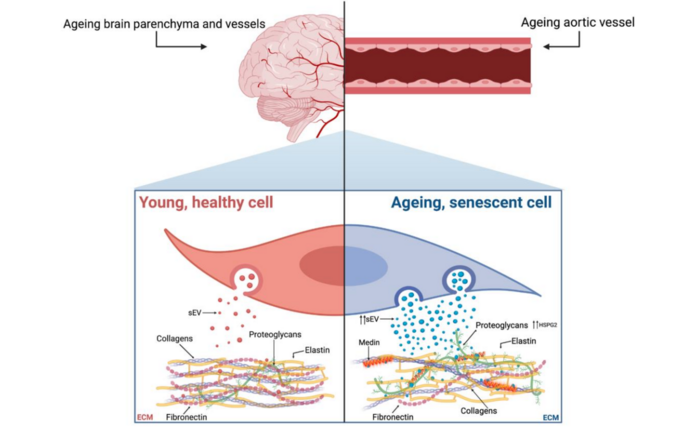
In their editorial, researchers Meredith Whitehead, Marco Antonazzi and Catherine M. Shanahan from King’s College London discussed amyloidosis—a prevalent age-associated pathology caused by the accumulation of fibrous, insoluble protein fibrils in tissues. The most common human amyloid is aortic medial amyloid (AMA), caused by aggregation of a 50-amino acid peptide called medin, which is cleaved by an unknown mechanism from its parent protein, milk fat globulin EGF-factor 8 (MFGE8). Medin is present in the vessel wall of 97% of Caucasians aged over 50- years, yet despite its prevalence in the ageing population there is a very limited understanding of the mechanisms driving AMA.
“Despite several forms of amyloidosis, including AMA and Alzheimer’s disease (AD), being frequently associated with ageing, there has been limited research to date on the effect of cellular ‘ageing’, termed senescence, on amyloidosis.”
The novel data presented in the paper by Whitehead et al. provides evidence that vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC)-derived small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) are key mediators of medin accumulation in the vessel wall. In addition, the authors identify, for the first time, a role for cellular senescence in triggering amyloidosis via changes in sEVs and extracellular matrix (ECM) composition. Thus, this study not only advances our understanding of how AMA is formed but uncovers potential therapeutic targets for mitigating the detrimental effects of amyloidosis on tissue function.
“Further work is now required to understand the relationships between cellular ageing pathways, different forms of amyloidosis and potentially other ageing pathologies with shared mechanisms, such as vascular calcification, that often occur concomitantly within the aged ECM.”
Continue Reading the Full Editorial: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.204571
Corresponding Author: Catherine M. Shanahan
Corresponding Email: [email protected]
Keywords: amyloid, smooth muscle cells, senescence, extracellular vesicles, medin
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.204571
About Aging-US:
Launched in 2009, Aging publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
- SoundCloud
- YouTube
- LabTube
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact [email protected].
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
Journal
Aging-US
DOI
10.18632/aging.204571
Method of Research
Commentary/editorial
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
Senescence and extracellular vesicles: novel partners in vascular amyloidosis
Article Publication Date
1-Mar-2023




