VANCOUVER, Wash. – The glittering, serpentine structures that power wearable electronics can be created with the same technology used to print rock concert t-shirts, new research shows.
Credit: Washington State University
VANCOUVER, Wash. – The glittering, serpentine structures that power wearable electronics can be created with the same technology used to print rock concert t-shirts, new research shows.
The study, led by Washington State University researchers, demonstrates that electrodes can be made using just screen printing, creating a stretchable, durable circuit pattern that can be transferred to fabric and worn directly on human skin. Such wearable electronics can be used for health monitoring in hospitals or at home.
“We wanted to make flexible, wearable electronics in a way that is much easier, more convenient and lower cost,” said corresponding author Jong-Hoon Kim, associate professor at the WSU Vancouver’s School of Engineering and Computer Science. “That’s why we focused on screen printing: it’s easy to use. It has a simple setup, and it is suitable for mass production.”
Current commercial manufacturing of wearable electronics requires expensive processes involving clean rooms. While some use screen printing for parts of the process, this new method relies wholly on screen printing, which has advantages for manufacturers and ultimately, consumers.
In the study, published in the ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces journal, Kim and his colleagues detail the electrode screen-printing process and demonstrate how the resulting electrodes can be used for electrocardiogram monitoring, also known as ECG.
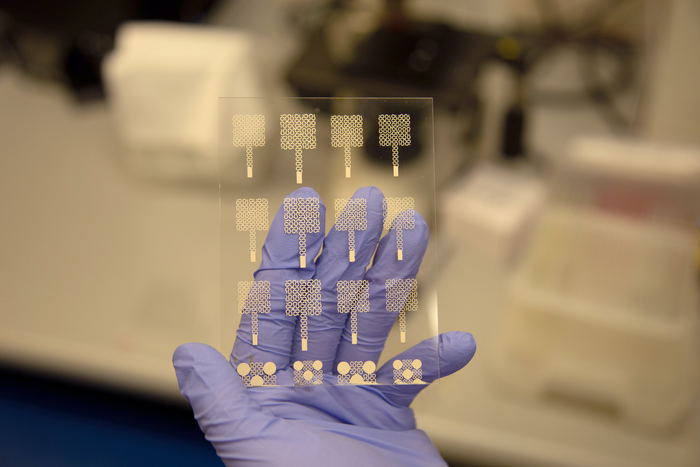
They used a multi-step process to layer polymer and metal inks to create snake-like structures of the electrode. While the resulting thin pattern appears delicate, the electrodes are not fragile. The study showed they could be stretched by 30% and bend to 180 degrees.
Multiple electrodes are printed onto a pre-treated glass slide, which allows them to be easily peeled off and transferred onto fabric or other material. After printing the electrodes, the researchers transferred them onto an adhesive fabric that was then worn directly on the skin by volunteers. The wireless electrodes accurately recorded heart and respiratory rates, sending the data to a mobile phone.
While this study focused on ECG monitoring, the screen-printing process can be used to create electrodes for a range of uses, including those that serve similar functions to smart watches or fitness trackers, Kim said.
Kim’s lab is currently working on expanding this technology to print different electrodes as well as entire electronic chips and even potentially whole circuit boards.
In addition to Kim, co-authors on the study includes researchers from the Georgia Institute of Technology and Pukyong National University in South Korea as well as others from WSU Vancouver. This research received support from the National Science Foundation.
Journal
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
DOI
10.1021/acsami.2c17653
Article Title
RETURN TO ISSUEPREVAPPLICATIONS OF POLY…NEXT Fully Screen-Printed PI/PEG Blends Enabled Patternable Electrodes for Scalable Manufacturing of Skin-Conformal, Stretchable, Wearable Electronics
Article Publication Date
3-Jan-2023




