Credit: KIB
Determining the major drivers of species diversification and phenotypic innovation across the Tree of Life is one of the grand challeges in evolutionary biology.
Facilitated by the Germplasm Bank of Wild Species of the Kunming Institute of Botany (KIB) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), Prof. YI Tingshuang and Prof. LI Dezhu of KIB led a novel study on gymnosperm diversification with a team of international researchers.
This study provides critical insight on the processes underlying diversification and phenotypic evolution in gymnosperms, with important broader implications for the major drivers of both micro- and macroevolution in plants.
The results were published today online in Nature Plants in an article entitled “Gene duplications and phylogenomic conflict underlie major pulses of phenotypic evolution in gymnosperms.”
In green plants, it is well understood that whole-genome duplication (WGD, or polyploidization) is an important evolutionary force. However, scientists have not clearly understood the role of WGD in shaping broad-scale evolutionary patterns in plants, especially when WGD is combined with adaptive radiation and other processes arising from climate change or new ecological opportunities.
Likewise, extant gymnosperm lineages clearly exhibit a complex history of ancient radiations, major extinctions, extraordinary stasis, and recent diversification. However, the correlates and causes of major phases of gymnosperm evolution have also not been well understood.
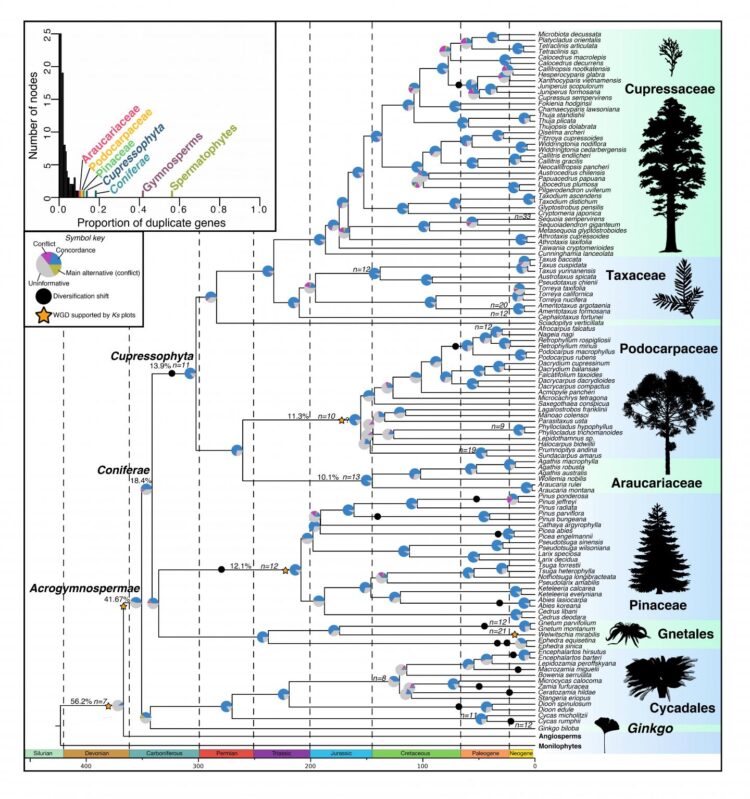
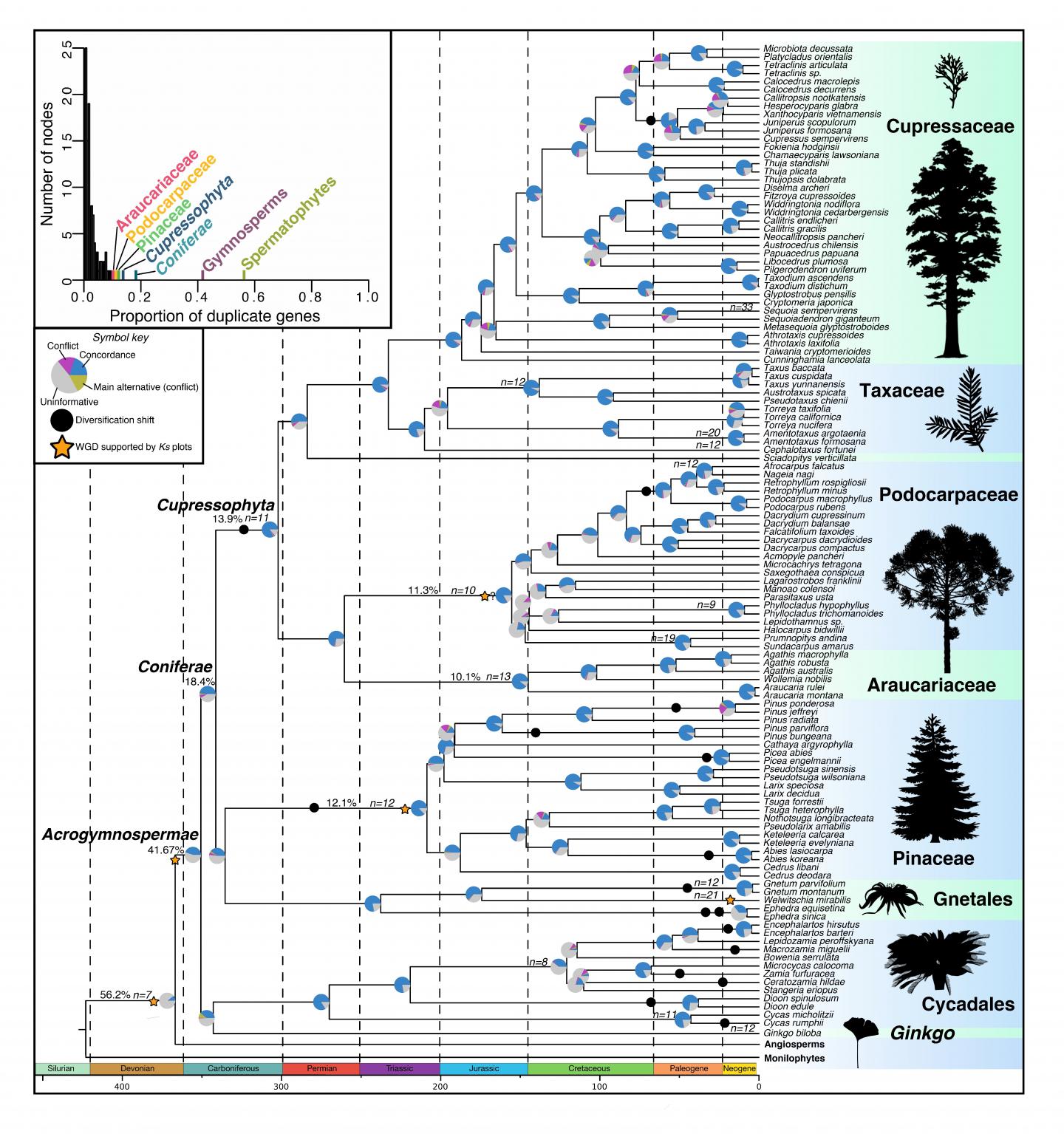
Using a novel transcriptome dataset as well as a diversity of comparative datasets, the researchers examined the relationship between various facets of genomic evolution, including gene and genome duplication, genome size, and chromosome number, and macroevolutionary patterns of phenotypic innovation, species diversification, and climatic occupancy in gymnosperms.
The scientists showed that spikes of gene duplication typically coincide with major spikes of phenotypic innovation, representing one of the first demonstrations of a direct relationship between gene duplication and phenotypic innovation on a macroevolutionary scale.
They also found that most shifts in gymnosperm diversification, since the rise of angiosperms, were decoupled from WGD events and instead are associated with increased rates of climatic occupancy evolution in cooler and/or more arid climatic conditions.
This suggests that ecological opportunity, especially in the late Cenozoic, along with environmental heterogeneity have driven a resurgence of gymnosperm diversification.
###
This work was funded by the Strategic Priority Research Program of CAS and the large-scale scientific facilities of CAS.
Media Contact
YANG Mei
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.