Credit: LI Nian
Recently, Prof. WANG Zhenyang’s research group from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has prepared macroscopic thick three-dimensional (3D) porous graphene films.
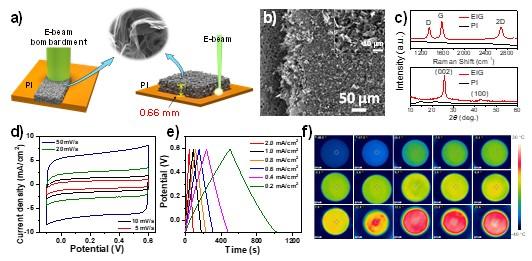
Using high-energy electron beam as the energy source and taking advantages of high kinetic energy and low reflection characteristics of e-beam, the researchers directly induced polyimide precursor into a 3D porous graphene crystal film with a thickness of up to 0.66 mm. Related research results were published in the journal Carbon.
Graphene has been proved to be a new strategic material owing to its numerous exceptional chemical and physical properties. Integrating dimensional (3D) porous graphene network can prevent restacking of graphene sheets and enables easy access and diffusion of ions. However, efficient synthesis of macroscopic thick 3D porous graphene films is still a challenge.
The high instantaneous energy of laser can induce the direct carbonization of the carbon-containing matrix to form high crystalline quality graphene. But the penetration depth of the laser into the carbon-containing matrix is quite low, resulting in insufficient thickness of the prepared graphene film, which limits its application in actual devices. Therefore, exploring a more effective energy source is a key problem that needs to be solved urgently for the industrial application of high-energy beam induced graphene.
In this research, the researchers used high-energy e-beam as a new energy source to realize efficient preparation of macroscopic thick 3D porous graphene crystal films on the polyimide precursor.
Compared with lasers, high-energy e-beam possessed lots of advantages including zero reflection, high kinetic energy, injection effect, and simple focus control, making the e-beam to be a possible better energy source than laser, which could quickly induce carbonization of polyimide precursors to produce graphene.
Hydrogen, oxygen and some other components in polyimide can rapidly escape in the form of gas, resulting in abundant 3D pore structure of graphene.
This study exhibits that the thickness of e-beam-induced graphene (EIG) film is as high as 0.66 mm, and the synthesis rate is 84 cm2/min, which is significantly larger than laser. Furthermore, EIG has been successfully applied to the field of supercapacitor electrodes, which shows excellent electrochemical storage capacity.
With prominent photothermal performance, EIG can also be applied to the field of solar photothermal anti-icing and deicing. The temperatures can be -40 °C, which is ultra-low.
###
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Project of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Anhui Key Research and Development Program.
Media Contact
ZHAO Weiwei
[email protected]
Original Source
http://english.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




