Researchers at EMBL-EBI have resolved a long-standing challenge in stem cell biology by successfully ‘resetting’ human pluripotent stem cells to a fully pristine state, at point of their greatest developmental potential. The study, published in Cell, involved scientists from the UK, Germany and Japan and was led jointly by EMBL-EBI and the University of Cambridge.
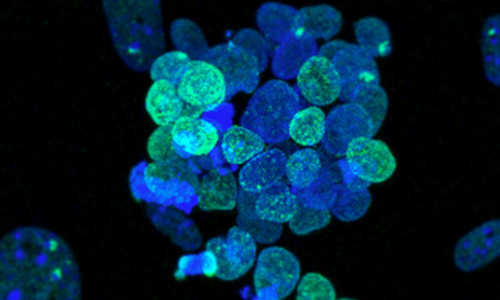
Resetting transcription factor control circuitry toward ground-state pluripotency in Human. Photo Credit: Takashima et al., Cell (2014)
Embryonic stem (ES) cells, which originate in early development, are capable of differentiating into any type of cell. Until now, scientists have only been able to revert ‘adult’ human cells (for example, liver, lung or skin) into pluripotent stem cells with slightly different properties that predispose them to becoming cells of certain types. Authentic ES cells have only been derived from mice and rats.
“Reverting mouse cells to a completely ‘blank slate’ has become routine, but generating equivalent naïve human cell lines has proven far more challenging,” says Dr Paul Bertone, Research Group Leader at EMBL-EBI and a senior author on the study. “Human pluripotent cells resemble a cell type that appears slightly later in mammalian development, after the embryo has implanted in the uterus.”
At this point, subtle changes in gene expression begin to influence the cells, which are then considered ‘primed’ towards a particular lineage. Although pluripotent human cells can be cultured from in vitro fertilised (IVF) embryos, until now there have been no human cells comparable to those obtained from the mouse.
Wiping cell memory
“For years, it was thought that we could be missing the developmental window when naïve human cells could be captured, or that the right growth conditions hadn’t been found,” Paul explains. “But with the advent of iPS cell technologies, it should have been possible to drive specialised human cells back to an earlier state, regardless of their origin – if that state existed in primates.”
Taking a new approach, the scientists used reprogramming methods to express two different genes, NANOG and KLF2, which reset the cells. They then maintained the cells indefinitely by inhibiting specific biological pathways. The resulting cells are capable of differentiating into any adult cell type, and are genetically normal.
The experimental work was conducted hand-in-hand with computational analysis.
“We needed to understand where these cells lie in the spectrum of the human and mouse pluripotent cells that have already been produced,” explains Paul. “We worked with the EMBL Genomics Core Facility to produce comprehensive transcriptional data for all the conditions we explored. We could then compare reset human cells to genuine mouse ES cells, and indeed we found they shared many similarities.”
Together with Professor Wolf Reik at the Babraham Institute, the researchers also showed that DNA methylation (biochemical marks that influence gene expression) was erased over much of the genome, indicating that reset cells are not restricted in the cell types they can produce. In this more permissive state, the cells no longer retain the memory of their previous lineages and revert to a blank slate with unrestricted potential to become any adult cell.
Unlocking the potential of stem cell therapies
The research was performed in collaboration with Professor Austin Smith, Director of the Wellcome Trust-Medical Research Council Stem Cell Institute.
“Our findings suggest that it is possible to rewind the clock to achieve true ground-state pluripotency in human cells,” said Professor Smith. “These cells may represent the real starting point for formation of tissues in the human embryo. We hope that in time they will allow us to unlock the fundamental biology of early development, which is impossible to study directly in people.”
The discovery paves the way for the production of superior patient material for translational medicine. Reset cells mark a significant advance for human stem cell applications, such as drug screening of patient-specific cells, and are expected to provide reliable sources of specialised cell types for regenerative tissue grafts.
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by European Bioinformatics Institute EMBL-EBI.