New research on transcriptional pausing, which helps control gene expression in cells, will aid our understanding of the enzyme RNA polymerase – a key player in the process and active target for antibacterial drugs
Credit: Robert Landick
Researchers have provided new insight on the mechanism underlying the control of gene expression in all living organisms, according to a study published today in eLife.
The findings, first reported on bioRxiv, could ultimately improve our understanding of how certain antibacterial drugs work against the enzyme RNA polymerase (RNAP) in treating conditions such as Clostridium difficile infections and tuberculosis.
Gene expression occurs when the information contained in DNA is used to produce functional gene products such as proteins and other molecules. The process has two stages. In the first stage, called transcription, RNAP reads the information in a strand on DNA, which is then copied into a new molecule of messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA). In the second stage, the molecule then moves on to be processed or translated.
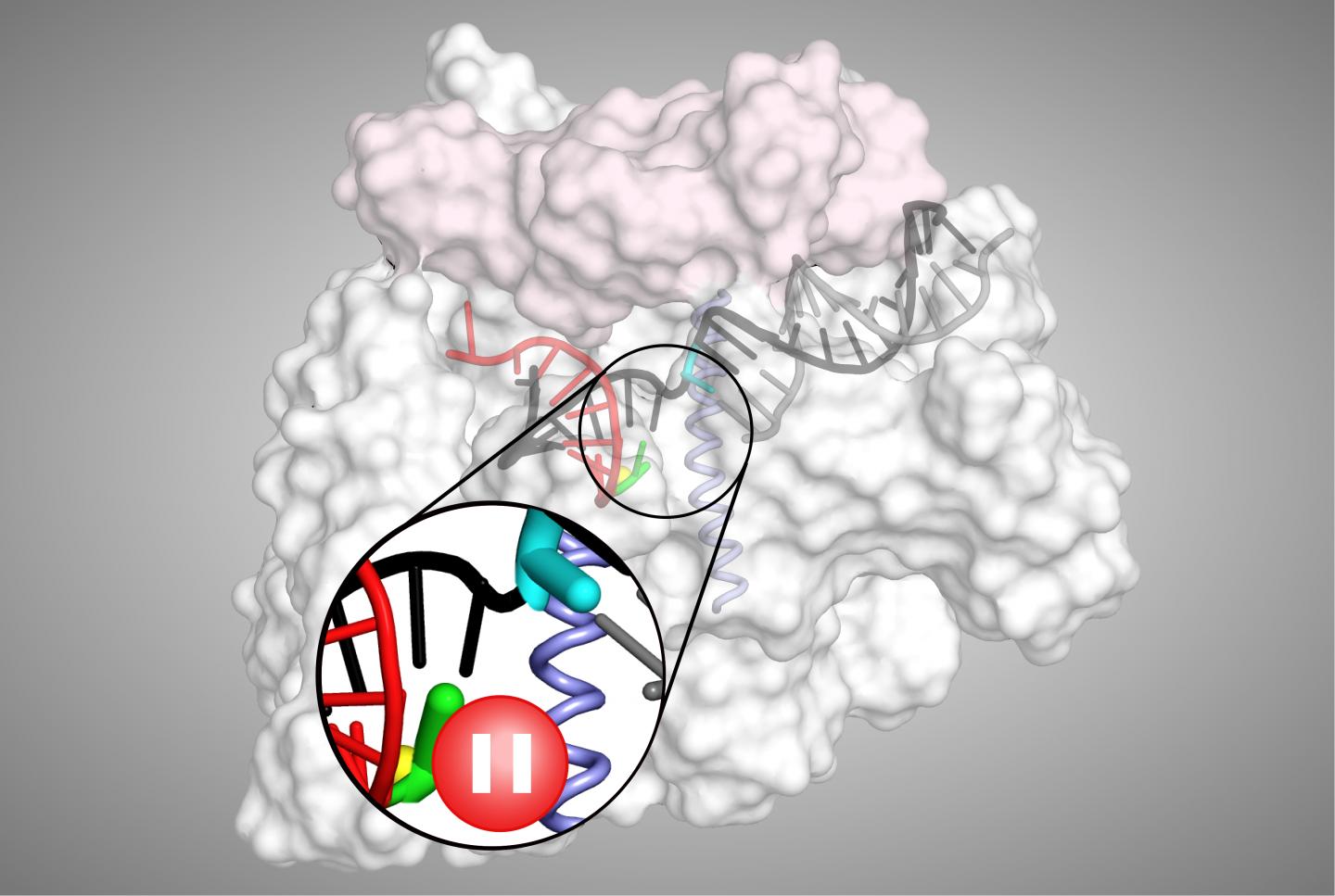
However, to help control gene expression levels, transcriptional pausing by RNAP can occur between the two stages, providing a kind of ‘roadblock’ where transcription may be terminated or modulated.
“A consensus pause sequence that acts on RNAPs in all organisms, from bacteria to mammals, halts the enzyme in an elemental paused state from which longer-lived pauses can arise,” explains senior author Robert Landick, Charles Yanofsky Professor of Biochemistry & Bacteriology at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, US. “As the fundamental mechanism of this elemental pause is not well defined, we decided to explore this using a variety of biochemical and biophysical approaches.”
The team’s analyses first revealed that the elemental pause process involves several biological players, which together create a barrier to prevent escape from paused states. The process also causes a modest conformational shift that makes RNAP ‘stumble’ in feeding DNA into its reaction centre, temporarily stopping it from making RNA.
“We also found that transcriptional pausing makes RNAP loosen its grip and backtrack on the DNA while paused,” says Landick. “Together, these results provide a framework to understand how the process is controlled by certain conditions and regulators within cells.”
He adds that these insights could aid future efforts to design synthetic genes, for example to direct the pausing behaviour of RNAP in a way that yields desired outputs from genes. It could also help our understanding of how certain drugs, known as RNAP inhibitors, target the enzyme.
“For now, we would like to try and generate structures of paused transcription complexes obtained at a series of time intervals,” Landick concludes. “This would allow us to see exactly how parts of the enzyme move as it enters and leaves the paused state.”
###
Reference
The paper ‘The elemental mechanism of transcriptional pausing’ can be freely accessed online at https:/
This study was first published on bioRxiv, at https:/
Media contact
Emily Packer, Senior Press Officer
eLife
[email protected]
01223 855373
About eLife
eLife aims to help scientists accelerate discovery by operating a platform for research communication that encourages and recognises the most responsible behaviours in science. We publish important research in all areas of the life and biomedical sciences, including Biochemistry and Chemical Biology, and Chromosomes and Gene Expression, which is selected and evaluated by working scientists and made freely available online without delay. eLife also invests in innovation through open-source tool development to accelerate research communication and discovery. Our work is guided by the communities we serve. eLife is supported by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, the Max Planck Society, the Wellcome Trust and the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation. Learn more at https:/
To read the latest Biochemistry and Chemical Biology research published in eLife, visit https:/
To read the latest Chromosomes and Gene Expression research published in eLife, see https:/
Media Contact
Emily Packer
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




