Special diffraction gratings with gold plates instead of microlenses can accelerate the generation of images in nanoscopes
Credit: Tomsk Polytechnic University
Scientists from Tomsk Polytechnic University together with colleagues proposed using special diffraction gratings with gold plates instead of microlenses used in the classic configuration to obtain images in nanoscopes. Microlenses transmit images by small pieces (pixels), whereas diffraction gratings allow you to see the whole object. Such innovation can help to accelerate the generation of images from nanoscopes without losing any magnification power. The results of the study are presented in the journal Annalen der Physik.
Optical microscopes are considered the simplest. However, for a long time it was believed that they are not powerful enough compared to, for example, electronic microscopes. Everything changed with the advent of nanoscopes in 2011. Images are obtained using small spheres or rectangular particles of quartz glass and enlarged further with a conventional microscope lens. Through nanoscopes it is possible to see objects the size of which is 50 nm, which exceeds the capabilities of a conventional optical microscope by 20 times. They can also be used to study living viruses, as compared to electronic microscopes lacking this function because the flow of electrons just kills them, and the inside of cells. This feature makes nanoscopes extremely promising for biological research. Therefore, scientists around the world are working to improve their resolution and design.
However, images in nanoscopes is formed by ‘pieces’, i.e. each microsphere detects its part of an object at a particular point. Therefore, it is necessary to make a whole matrix of a large number of microspheres or to move a microsphere, which takes some time.
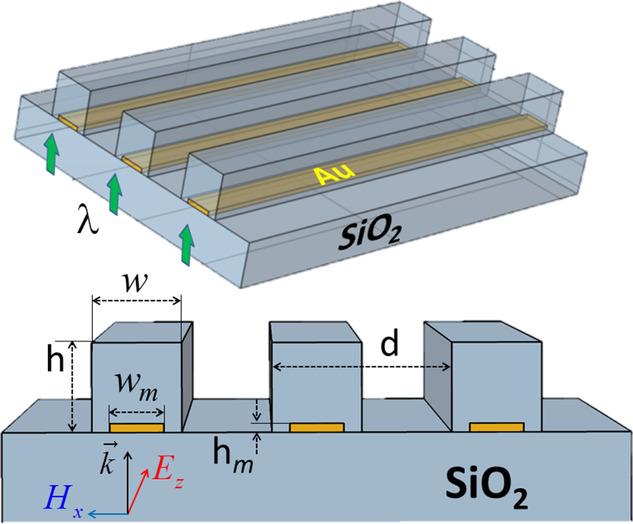
As a solution, TPU scientists proposed using a rectangular mesoscale phase diffraction grating (a grating with a period comparable to the wavelength of the radiation used). This is an optical device that is a surface with a large number of parallel microscopic strokes or protrusions.
The project supervisor, Igor Minin, DSc in technical sciences, SRF at the TPU Division of Electronic Engineering says:
‘A conventional diffraction grating out of dielectric ensures poor resolution in nanoscopes. Therefore, we propose to add a small gold plate to each of the strokes. In fact, a paradox emerges: metal does not transmit light but the resolution nevertheless increases. Why? Here several effects work simultaneously.
These are the effect of abnormal amplitude apodization, the Fabry-Perot resonance, and the Fano resonance. Together they help to improve resolution compared to a conventional diffraction grating up to 0.3 λ. This is about the same solution as that of nanoscopes with spherical particles.’
Now, the researchers are tasked to verify the simulation data during experiments.
###
The article was published in Annalen der Physik in collaboration with the scientists from Tomsk State University and V.E. Zuev Institute of Atmospheric Optics SB RAS.
Media Contact
Kristina Nabokova
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




