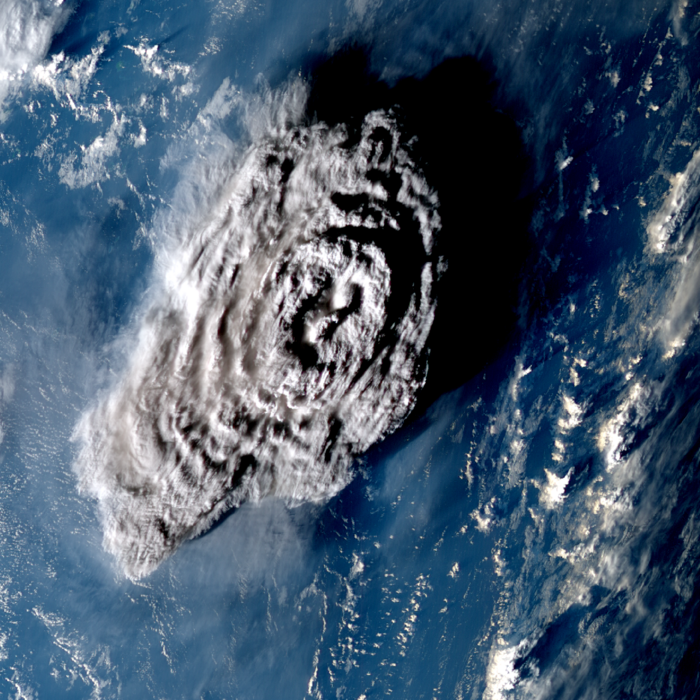
Using images captured by satellites, researchers in the University of Oxford’s Department of Physics and RAL Space have confirmed that the January 2022 eruption of the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai volcano produced the highest-ever recorded plume. The colossal eruption is also the first to have been directly observed to have broken through to the mesosphere layer of the atmosphere. The results have been published today in the journal Science.
Credit: Simon Proud / Uni Oxford, RALSpace NCEO / Japan Meteorological Agency
Using images captured by satellites, researchers in the University of Oxford’s Department of Physics and RAL Space have confirmed that the January 2022 eruption of the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai volcano produced the highest-ever recorded plume. The colossal eruption is also the first to have been directly observed to have broken through to the mesosphere layer of the atmosphere. The results have been published today in the journal Science.
On 15 January 2022, Hunga Tonga–Hunga Haʻapai, a submarine volcano in the Tongan archipelago in the southern Pacific Ocean, violently erupted. The explosion was one of the most powerful ever observed, sending shock waves around the world and triggering devastating tsunamis that left thousands homeless. A towering column of ash and water was ejected into the atmosphere – but until now, scientists lacked an accurate way to measure just how tall this was.
Normally, the height of a volcanic plume can be estimated by measuring the temperature recorded at the top by infrared-based satellites and comparing this to a reference vertical temperature profile. This is because in the troposphere (the first and lowest layer of the Earth’s atmosphere), temperature decreases with height. But if the eruption is so large that the plume penetrates into the next layer of the atmosphere (the stratosphere), this method becomes ambiguous because the temperature begins to increase again with height (due to the ozone layer absorbing solar ultraviolet radiation).
To overcome this problem, the researchers used a novel method based on a phenomenon called ‘the parallax effect’. This is the apparent difference in an object’s position when viewed from multiple lines of sight. You can see this for yourself by closing your right eye, and holding out one hand with the thumb raised upwards. If you then switch eyes, so that your left is closed and your right is open, your thumb will appear to shift slightly against the background. By measuring this apparent change in position and combining this with the known distance between your eyes, you can calculate the distance to your thumb.
The location of the Tonga volcano is covered by three geostationary weather satellites, so the researchers were able to apply the parallax effect to the aerial images these captured. Crucially, during the eruption itself, the satellites recorded images every 10 minutes, enabling the rapid changes in the plume’s trajectory to be documented.
The results showed that the plume reached an altitude of 57 kilometres at its highest extent. This is significantly higher than the previous record-holders: the 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines (40 km at its highest point), and the 1982 eruption of El Chichón in Mexico (31 km). It also makes the plume the first observational evidence of a volcanic eruption injecting material through the stratosphere and directly into the mesosphere, which starts at about 50 km above the Earth’s surface.
Lead author Dr Simon Proud (University of Oxford, RAL Space and the National Centre for Earth Observation), said: ‘It’s an extraordinary result as we have never seen a cloud of any type this tall before. Furthermore, the ability to estimate the height in the way we did (using the parallax method) is only possible now that we have good satellite coverage. It wouldn’t have been possible a decade or so ago.’
The Oxford researchers now intend to construct an automated system to compute the heights of volcano plumes using the parallax method. Co-author Dr Andrew Prata from the Sub-department of Atmospheric, Oceanic & Planetary Physics added: ‘We’d also like to apply this technique to other eruptions and develop a dataset of plume heights that can be used by volcanologists and atmospheric scientists to model the dispersion of volcanic ash in the atmosphere. Further science questions that we would like to understand are: Why did the Tonga plume go so high? What will be the climate impacts of this eruption? And what exactly was the plume composed of?’
Besides the University of Oxford, the study also involved the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory and National Centre for Earth Observation in Harwell, and Munich University of Applied Sciences.
Notes:
The paper ‘The January 2022 eruption of Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai volcano reached the mesosphere’ will be published in Science on 3 November at 14:00 ET /18:00 GMT. To view the manuscript before this, contact the Science editorial board: [email protected]
For media enquiries, contact Dr Caroline Wood, University of Oxford: [email protected]
Journal
Science
DOI
10.1126/science.abo4076
Article Title
The January 2022 eruption of Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai volcano reached the mesosphere
Article Publication Date
3-Nov-2022




