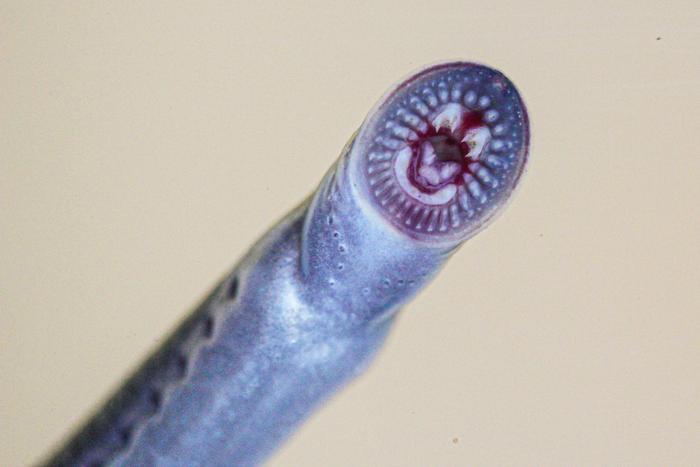
The Australian brook lamprey (Mordacia praecox) is part of a group of primitive jawless fish. It’s up to 15 cm long, with rows of sharp teeth. Surprisingly, it doesn’t use these teeth to suck blood like most lamprey species – it’s non-parasitic.
Credit: David Moffatt
The Australian brook lamprey (Mordacia praecox) is part of a group of primitive jawless fish. It’s up to 15 cm long, with rows of sharp teeth. Surprisingly, it doesn’t use these teeth to suck blood like most lamprey species – it’s non-parasitic.
As larvae, the Australian brook lamprey lives buried in the bottom of streams for around three years, filter-feeding. Its adult phase is about one year long, in which it doesn’t feed at all. Prior to this study – funded in part by the Australian Government through the National Environmental Science Program’s (NESP) Resilient Landscapes Hub – the species was widely believed to only live in a few streams along a 170 km stretch of coastline near the NSW/Victoria border.
The study began after another exciting discovery: Dr Luke Carpenter-Bundhoo from the Australian Rivers Institute at Griffith University found the species living in streams on K’gari (Fraser Island). To unravel the mystery of Queensland lampreys, Dr Carpenter-Bundhoo teamed up with David Moffatt from DESI, who had found isolated populations of lamprey in other Queensland streams.
Together, they confirmed reports of Australian brook lamprey in Queensland, including as far north as Rockhampton! With this enormous extension of its geographic range, Australian brook lamprey becomes the only lamprey species in the world to live in truly tropical waters.
“It’s quite exciting to find an Endangered species so far out of its known range, yet so close to populated areas. We expect these animals naturally occur in Queensland, and have been here for an awfully long time, but have remained hidden due to their cryptic nature,” said Mr Moffatt.
The Australian brook lamprey is thought to be extinct where it was first described, in southern NSW. Its existence is thought to be threatened by sedimentation, wildfires, and human developments.
Perhaps the biggest threat to their conservation is that they’re very difficult to identify – this species truly faces a case of mistaken identity. For most of their life, the non-parasitic Australian brook lamprey is indistinguishable from its more common blood-sucking southern relative, the short-headed lamprey (Mordacia mordax), which has a conservation status of ‘Least Concern’.
Add to this the fact that, globally, only a few people can tell them apart.
In their new Endangered Species Research article, Dr Carpenter-Bundhoo and Mr Moffatt outline the difficulties of implementing a conservation strategy for this fish and propose some solutions.
The species’ conservation is especially important, given projected sea levels rises mean that many of the lowland freshwater coastal streams where Australian brook lamprey live are likely to become saltwater.
With these new findings, scientists will be better equipped to conserve this unusual and Endangered species.
The surveys were partially funded by a NESP project which aims to restore ecosystem health in the Moonaboola (Mary River) catchment area of south-east Queensland and protect threatened species like the Australian lungfish, the Mary River cod and the giant barred frog.
Journal
Endangered Species Research
DOI
10.3354/esr01319
Article Title
Expanding the known range and practical conservation issues of the Endangered Australian brook lamprey Mordacia praecox




