Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a way to characterize the force generated by contracting myotubes, precursors to skeletal muscle fiber, combining electrostimulation and analysis of wrinkles in the silicone substrate on which they are mounted. Existing methods rely on muscle mass or the expression of certain proteins, both not as strongly correlated with muscle strength. Accurate measurement of myotube strength promises more effective screening of drug targets for treating muscle atrophy.
Credit: Tokyo Metropolitan University
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a way to characterize the force generated by contracting myotubes, precursors to skeletal muscle fiber, combining electrostimulation and analysis of wrinkles in the silicone substrate on which they are mounted. Existing methods rely on muscle mass or the expression of certain proteins, both not as strongly correlated with muscle strength. Accurate measurement of myotube strength promises more effective screening of drug targets for treating muscle atrophy.
Muscular atrophy, the deterioration of muscle tissue, can have a devastating effect on quality of life, and is known to affect lifespans. The effects are felt particularly strongly in aging populations, where there are also significant costs associated with medical interventions and daily care. This makes treating and preventing muscular atrophy a key issue for society.
But the reality is that treatments for muscular atrophy remain very limited. One of the challenges holding researchers back is the lack of an effective screening system for new drug targets, specifically how different compounds impact muscle strength. Myotubes, the cylindrical groups of cells that go on to form muscle fibers, can be isolated in the lab and studied in different biochemical environments, but measuring how strongly they contract remains difficult. That is why existing methods look at indirect measures, such as muscle mass or the proteins they express, but these are not always strongly correlated with how strongly they can pull. In the past, this has even led to seemingly promising drugs making it to clinical trials, only to be found to not lead to improved muscle strength.
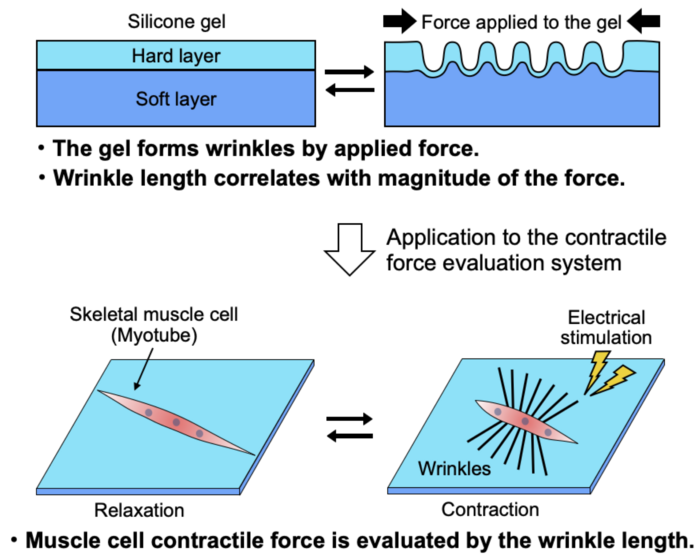
Now, a team of researchers led by Associate Professor Yasuko Manabe of Tokyo Metropolitan University have come up with a simple way of directly measuring how strong myotubes really are. They looked at myotubes mounted on a two-layered elastic silicone substrate, with a hard surface layer on top of a thicker, soft layer. When the myotubes were stimulated with an electric pulse, the team saw that the fibers contracted and deformed the substrate surface, forming a series of wrinkles which were clearly visible under a microscope. Through careful calibration experiments using a flexible needle of known stiffness, they were able to demonstrate that the total length of the wrinkles was directly correlated with the strength of forces deforming the substrate. In the case of myotubes, wrinkle length corresponded to how strongly they were able to contract when stimulated.
Using known atrophic (weaker) and hypertrophic (stronger) myotubes, they found that their new “force index” was much more sensitive to muscle strength than existing measures, such as muscle mass and the expression of the Myosin Heavy Chain (MHC) protein. The method is simple to deploy with standard microscopy and image analysis techniques, with great scope for practical application in the lab. The team believes that this will greatly accelerate drug discovery in the fight against muscular atrophy.
This work was supported by a Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) in the field of Sports Science (Grant Number JP 17H02159), the TMU Strategic Research Fund for innovative research projects and a Tokyo Metropolitan Government Advanced Research Grant (R2-2).
Journal
Scientific Reports
DOI
10.1038/s41598-022-17548-7
Article Title
Establishment of a system evaluating the contractile force of electrically stimulated myotubes from wrinkles formed on elastic substrate
Article Publication Date
15-Aug-2022




