For the first time, researchers have succeeded in predicting how to change the optimum temperature of an enzyme using large computer calculations. A cold-adapted enzyme from an Antarctic bacterium was used as a basis. The study is to be published in the journal Science Advances and is a collaboration between researchers at Uppsala University and the University of Tromsø.
Credit: Johan Åqvist
For the first time, researchers have succeeded in predicting how to change the optimum temperature of an enzyme using large computer calculations. A cold-adapted enzyme from an Antarctic bacterium was used as a basis. The study is to be published in the journal Science Advances and is a collaboration between researchers at Uppsala University and the University of Tromsø.
The type of cold-adapted enzymes used by the researchers for their study can be found in bacteria and fish that live in icy water, for example. Evolution has shaped them to be able to function even at very low temperatures at which other enzymes are normally stone dead. These enzymes also always have a lower optimum temperature and melting point than enzymes from warm-blooded animals and organisms that live at higher temperatures.
The researchers wondered whether computer simulations of the catalysed chemical reaction could predict a small number of mutations in the Antarctic enzyme that could result in an increase in its optimum temperature. The results of the calculation showed that this would be possible if 16 mutations were inserted from the corresponding pig enzyme into the bacterial variant.
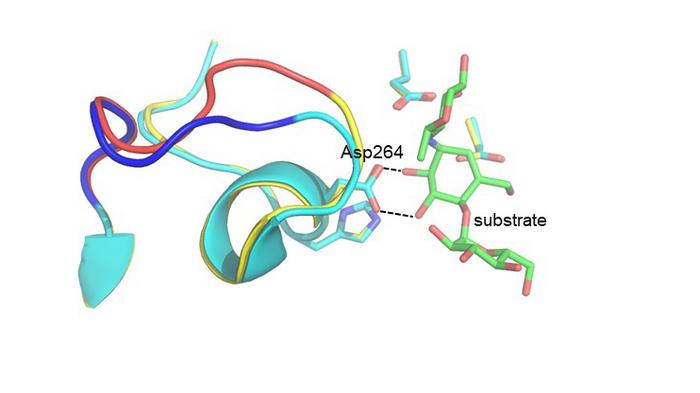
The researchers then produced this hybrid enzyme and measured its catalytic activity as a function of temperature, and it was indeed found that the new variant had a 6 °C higher optimum than the original variant and was faster than both the Antarctic and pig enzymes at 50 °C. They also solved the three-dimensional structure of the hybrid enzyme by X-ray crystallography and showed that the necessary structural changes predicted by the computer calculations had indeed taken place.
Computer-based enzyme design has become a major and hotly pursued research area in recent years. The goal is to create enzymes with new properties and to do so with the help of computer calculations instead of labour-intensive experiments.
“For example, this may involve creating new enzymes that catalyse chemical reactions not found in nature or changing their properties so that they can better cope with heat, cold, high pressure, increased salinity and so on. This area is therefore the subject of great biotechnological interest,” notes Johan Åqvist, Professor of Theoretical Chemistry at Uppsala University.
Journal
Science Advances
DOI
10.1126/sciadv.adi0963
Article Title
Computational design of the temperature optimum of an enzyme reaction
Article Publication Date
28-Jun-2023




