Credit: Skoltech
Scientists from Skoltech, the Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry of RAS, and the London Institute of Medical Sciences (LMS) have developed an enhanced version of SuperNova, a genetically encoded phototoxic synthesizer, that helps control intracellular processes by light exposure. The research was published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
An important research tool, phototoxic proteins are used as genetically encoded photosensitizers to generate reactive oxygen species under light irradiation. In contrast to common chemical photosensitizers, phototoxic proteins are genetically encoded and expressed by the cell itself, which makes them easy to control and direct to any selected compartment in the cell. Thanks to reactive oxygen species formed by the action of light, phototoxic proteins can create strictly localized oxidative stress, for example, to destroy a selected cell population or disable target proteins ? a feature particularly sought after in the modeling of cellular processes.
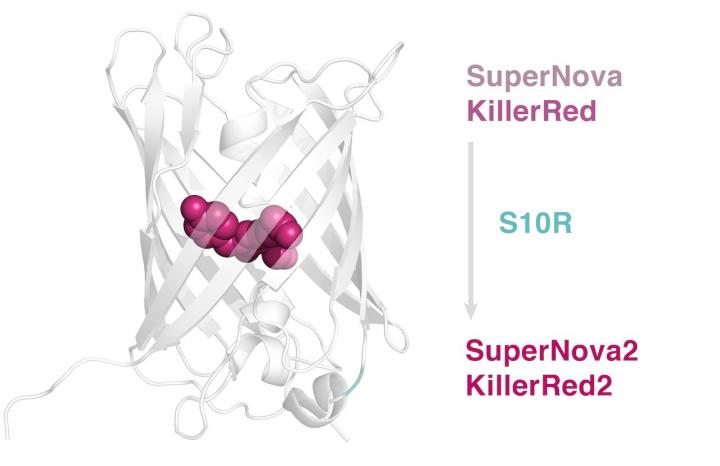
The first phototoxic protein, KillerRed, was described by a team of Russian researchers led by Konstantin Lukyanov, a professor at the Skoltech Center of Life Sciences (CLS), in 2006. KillerRed was further enhanced by Japanese scientists and renamed SuperNova. In their recent study, professor Lukyanov’s team has developed SuperNova2, an improved version of SuperNova, which displays high speed and completeness of maturation and is monomeric, which makes the new protein easily usable and suitable for a broad variety of molecular biology tasks.
“We expect that the genetically encoded photosensitizer SuperNova2 will find use in a wide range of experimental models,” professor Lukyanov comments.
###
Media Contact
Ilyana Zolotareva
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




