Experiment produces new material that can conduct electricity perfectly
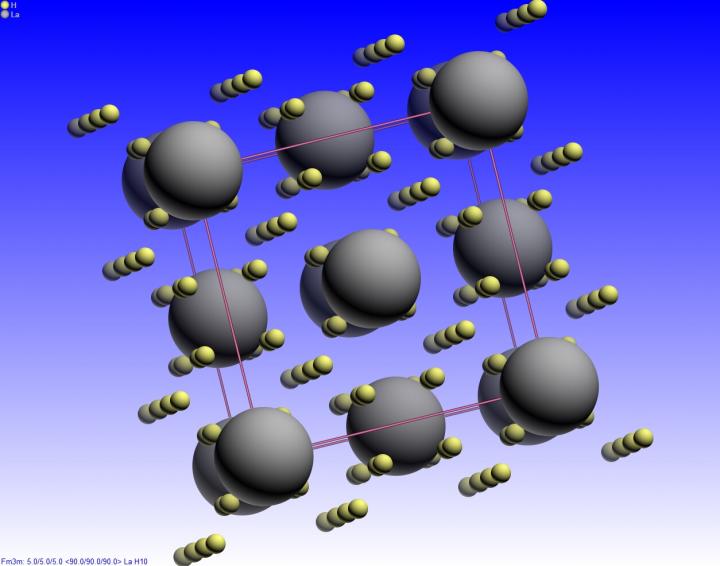
Credit: Courtesy of Drozdov et al.
University of Chicago scientists are part of an international research team that has discovered superconductivity–the ability to conduct electricity perfectly–at the highest temperatures ever recorded.
Using advanced technology at UChicago-affiliated Argonne National Laboratory, the team studied a class of materials in which they observed superconductivity at temperatures of about minus-23 degrees Celsius (minus-9 degrees Fahrenheit)–a jump of about 50 degrees compared to the previous confirmed record.
Though the superconductivity happened under extremely high pressure, the result still represents a big step toward creating superconductivity at room temperature–the ultimate goal for scientists to be able to use this phenomenon for advanced technologies. The results were published May 23 in the journal Nature; Vitali Prakapenka, a research professor at the University of Chicago, and Eran Greenberg, a postdoctoral scholar at the University of Chicago, are co-authors of the research.
Just as a copper wire conducts electricity better than a rubber tube, certain kinds of materials are better at becoming superconductive, a state defined by two main properties: The material offers zero resistance to electrical current and cannot be penetrated by magnetic fields. The potential uses for this are as vast as they are exciting: electrical wires without diminishing currents, extremely fast supercomputers and efficient magnetic levitation trains.
But scientists have previously only been able to create superconducting materials when they are cooled to extremely cold temperatures–initially, minus-240 degrees Celsius and more recently about minus-73 degrees Celsius. Since such cooling is expensive, it has limited their applications in the world at large.
Recent theoretical predictions have shown that a new class of materials of superconducting hydrides could pave the way for higher-temperature superconductivity. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Chemistry in Germany teamed up with University of Chicago researchers to create one of these materials, called lanthanum superhydrides, test its superconductivity, and determine its structure and composition.
The only catch was that the material needed to be placed under extremely high pressure–between 150 and 170 gigapascals, more than one and a half million times the pressure at sea level. Only under these high-pressure conditions did the material–a tiny sample only a few microns across–exhibit superconductivity at the new record temperature.
In fact, the material showed three of the four characteristics needed to prove superconductivity: It dropped its electrical resistance, decreased its critical temperature under an external magnetic field and showed a temperature change when some elements were replaced with different isotopes. The fourth characteristic, called the Meissner effect, in which the material expels any magnetic field, was not detected. That’s because the material is so small that this effect could not be observed, researchers said.
They used the Advanced Photon Source at Argonne National Laboratory, which provides ultra-bright, high-energy X-ray beams that have enabled breakthroughs in everything from better batteries to understanding the Earth’s deep interior, to analyze the material. In the experiment, researchers within University of Chicago’s Center for Advanced Radiation Sources squeezed a tiny sample of the material between two tiny diamonds to exert the pressure needed, then used the beamline’s X-rays to probe its structure and composition.
Because the temperatures used to conduct the experiment is within the normal range of many places in the world, that makes the ultimate goal of room temperature–or at least 0 degrees Celsius–seem within reach.
The team is already continuing to collaborate to find new materials that can create superconductivity under more reasonable conditions.
“Our next goal is to reduce the pressure needed to synthesize samples, to bring the critical temperature closer to ambient, and perhaps even create samples that could be synthesized at high pressures, but still superconduct at normal pressures,” Prakapenka said. “We are continuing to search for new and interesting compounds that will bring us new, and often unexpected, discoveries.”
###
Media Contact
Mary Naset
[email protected]




