Since the introduction of the first ruby laser—a solid-state laser that uses the synthetic ruby crystal as its laser medium—in 1960, the use of lasers has expanded significantly in scientific, medical and industrial fields.
Credit: Kaiyu Cui, Tsinghua University
Since the introduction of the first ruby laser—a solid-state laser that uses the synthetic ruby crystal as its laser medium—in 1960, the use of lasers has expanded significantly in scientific, medical and industrial fields.
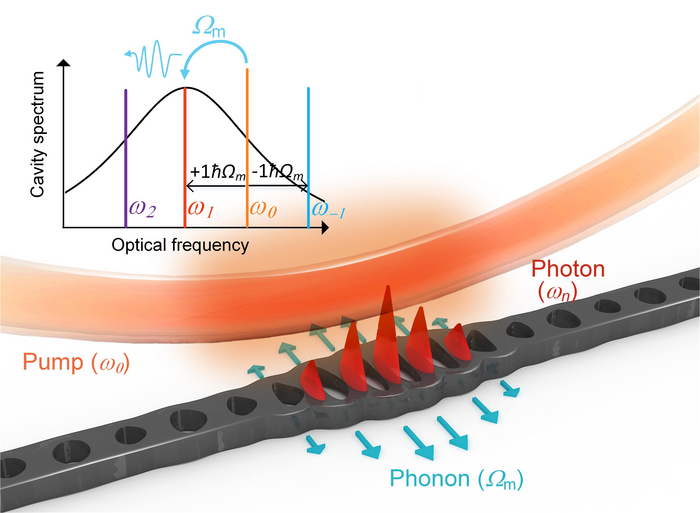
With the advancement of science and technology, lasers with extremely narrow linewidths have become the key to research in frontier scientific fields. The much-anticipated gravitational wave detection program Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) in the US, for instance, has extremely strict requirements for the coherence of lasers. While Brillouin lasers have great potential for such applications because of their linewidth narrowing effect, the lasing threshold of on-chip Brillouin lasers is high due to the intrinsic loss of the Brillouin waveguide and the large mode volume.
To circumvent this issue, a team from the Nano-OptoElectronics Lab led by Professor Yidong Huang at Tsinghua University proposes a similar scattering photon lasing phenomenon occurring in an optomechanical microcavity, which can help realize a new on-chip narrow linewidth laser with a lower lasing threshold.
“The new laser can be achieved from a one-dimensional optomechanical crystal with both photon and phonon excitation within a chip size of just tens of microns by a small pump threshold of only 500 microwatts,” shares Associate Professor Kaiyu Cui, a researcher involved in the study.
The team observed that the linewidth of the new laser was narrowed by four orders of magnitude to 5.4 kHz after phonon lasing at 6.2 GHz. This highly coherent phonon laser has important applications in fields such as high-precision mass sensing, spectral sensing and signal processing. At the same time, the excited photon also exhibits a significant threshold effect, which can be applied in coherent wavelength conversion.
Notably, achieving simultaneous photon and phonon lasing in one-dimensional optomechanical crystals is no easy feat. Periodically aligned nanostructures are needed to confine both light and mechanical waves in a very small volume by a physical mechanism known as defect modes. Only then could the localized photons and phonons within the microcavity undergo strong energy coupling, and in turn enabling coherent lasing at very low pump power.
Nonetheless, the team has successfully fabricated one-dimensional optomechanical crystals on a silicon chip using electron-beam lithography. When the incident pump power exceeded the threshold, significant lasing was observed on the spectrometer. Indeed, the experimental results matched those of theoretical expectations.
The researchers published their latest findings, which could pave the way for silicon-based photonic and phononic lasers to fulfil the urgent need for new laser technologies, in the journal Fundamental Research.
“In optomechanical crystals, nonlinear equations can be used to describe the behavior of photons and phonons. Since nonlinear systems cannot be solved analytically in general, most previous studies have been conducted based on linearized equations,” explains Prof Huang. “Based on our findings, we propose that the nonlinear equations can be analyzed directly by means of limit-cycle theory, which gives the first analytical formulation of the laser linewidth under the effect of phase noise.”
Journal
Fundamental Research
Article Title
Phonon and photon lasing dynamics in optomechanical cavities




