Credit: B. Minchew/Caltech
For the first time, researchers have closely observed how the ocean's tides can speed up or slow down the speed of glacial movement in Antarctica. The new data will help modelers better predict how glaciers will respond to rising sea levels.
Caltech's Brent Minchew (PhD '16) and Mark Simons, along with their collaborators and in cooperation with the Italian Space Agency (ASI), exploited four COSMO-SkyMed radar-imaging satellites on the Rutford Ice Stream in Antarctica. The satellites gathered near-continuous data for nearly nine months from a variety of angles.
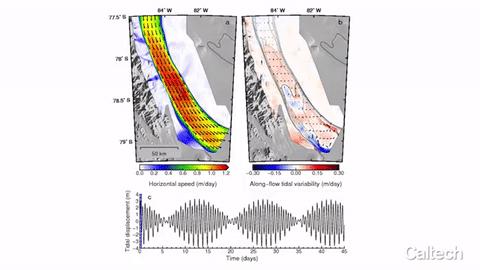
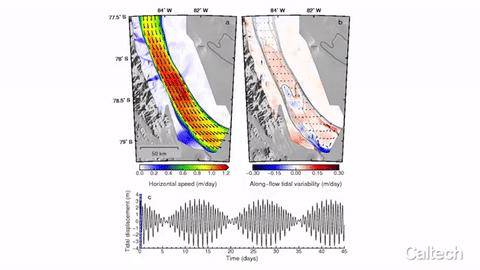
The Rutford Ice Stream is a fast-moving river of ice, approximately 300 kilometers long and 25 kilometers wide, in West Antarctica. It connects glaciers in the Ellsworth Mountains to the Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf, a floating chunk of ice roughly the size of California. Driven by its own weight, the stream of solid ice flows downhill toward the sea at a rate of about one meter per day, though that speed varies by as much as 20 percent with the tides.
The variability is driven by the ice's interactions with the ocean. At low tide, the floating ice sinks far enough to ground out on the sea floor like a foundering ship, causing an ice traffic jam that can be detected up to 100 kilometers upstream. When the tide rises again, the ice lifts off of the sea floor and flows freely once more.
"A rising tide lifts all ships, and it also lifts all ice," says Minchew, a PhD student at Caltech while conducting the research and now a postdoctoral researcher the British Antarctic Survey. Minchew is the lead author of a paper about the study that was published by the Journal of Geophysical Research on November 22.
The ice stream was so sensitive to the change in tides that Simons and Minchew could detect the individual influences of solar and lunar tides.
The planet's solar and lunar tides are caused by the tug of the sun and the moon, respectively, on the earth. High tide occurs simultaneously on the sides of the earth facing toward and away from the sun and the moon because their gravitational pulls create a bulge, or high tide, in the planet.
The lunar and solar tides are not perfectly in sync: the lunar tide cycles from high to low every 12-and-a-half hours, while the solar tide cycles every 12 hours. When those two cycles align perfectly, the sea experiences its strongest tides. When they are most misaligned, the sea experiences its weakest tides.
Previous efforts to explore the effect of the tide on glacial movement relied on placing a GPS device directly on the ice. This technique, however, provides information for only one point of movement.
The Caltech team instead collected pairs of images taken from the same location in space but at different times, thus showing movement not just of a single point but continuous tracking of every single square inch of the surface of the ice streams. (Ice does not move as one solid fixed mass, but rather it flows like an incredibly viscous syrup–its motion is often likened to that of cold honey. As such, the movement of one point provides only the most basic information about the entire glacier.) Further, the variety of viewing angles provided by the constellation of satellites offered three-dimensional information about the ice's movement and revealed, for example, that the floating ice shelf moved more quickly, thus showing that the grounding effect was indeed responsible for changes in the ice's speed.
Studies on glacial movement could yield important data for scientists looking to model how glaciers will respond to the effects of climate change.
"The response of ice flow to changes in sea level and ocean temperature has a direct impact on contemporary sea-level rise," says Simons, professor of geophysics at Caltech. "Quantifying this is critical for understanding how Antarctica will evolve over the next decades and centuries as the climate warms and the marine-terminating glaciers are exposed to warmer ocean water."
With warmer water and high sea levels, glaciers will flow faster into the sea, melting more quickly once they reach the water.
Already, the study has yielded surprising information about the strength of ice and its ability to resist deforming due to glacial stress. As it turns out, ice is weaker along the margins of flowing glacial streams than previously suspected. The same technology and technique could be used to study the motion of glaciers worldwide, Minchew says.
###
Simons and Minchew collaborated with Caltech alumnus Bryan Riel (PhD '14) and Pietro Milillo of the University of Basilicata in Italy, both of whom are now affiliated with JPL.
The paper, titled "Tidally induced variations in vertical and horizontal motion on Rutford Ice Stream, West Antarctica, inferred from remotely sensed observations," can be found online at http://resolver.caltech.edu/CaltechAUTHORS:20161123-141844145. This research was funded by NASA, the National Science Foundation, the Albert Parvin Foundation, and the Achievement Rewards for College Scientists (ARCS) Foundation.
Media Contact
Robert Perkins
[email protected]
626-395-1862
@caltech
http://www.caltech.edu
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag