Credit: RUDN University
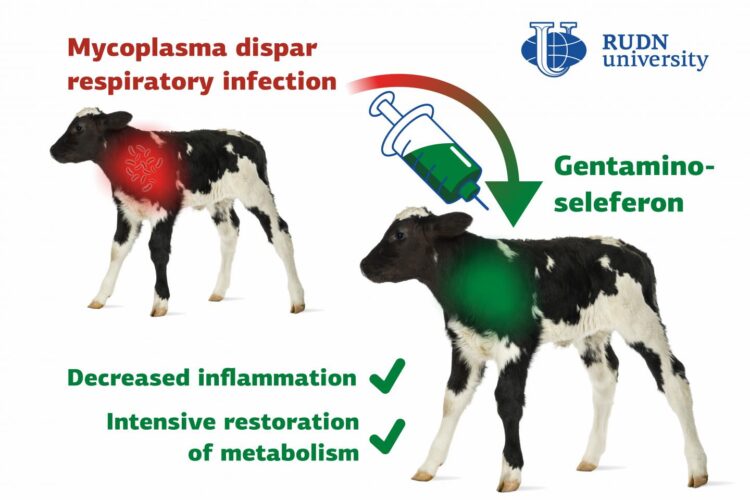
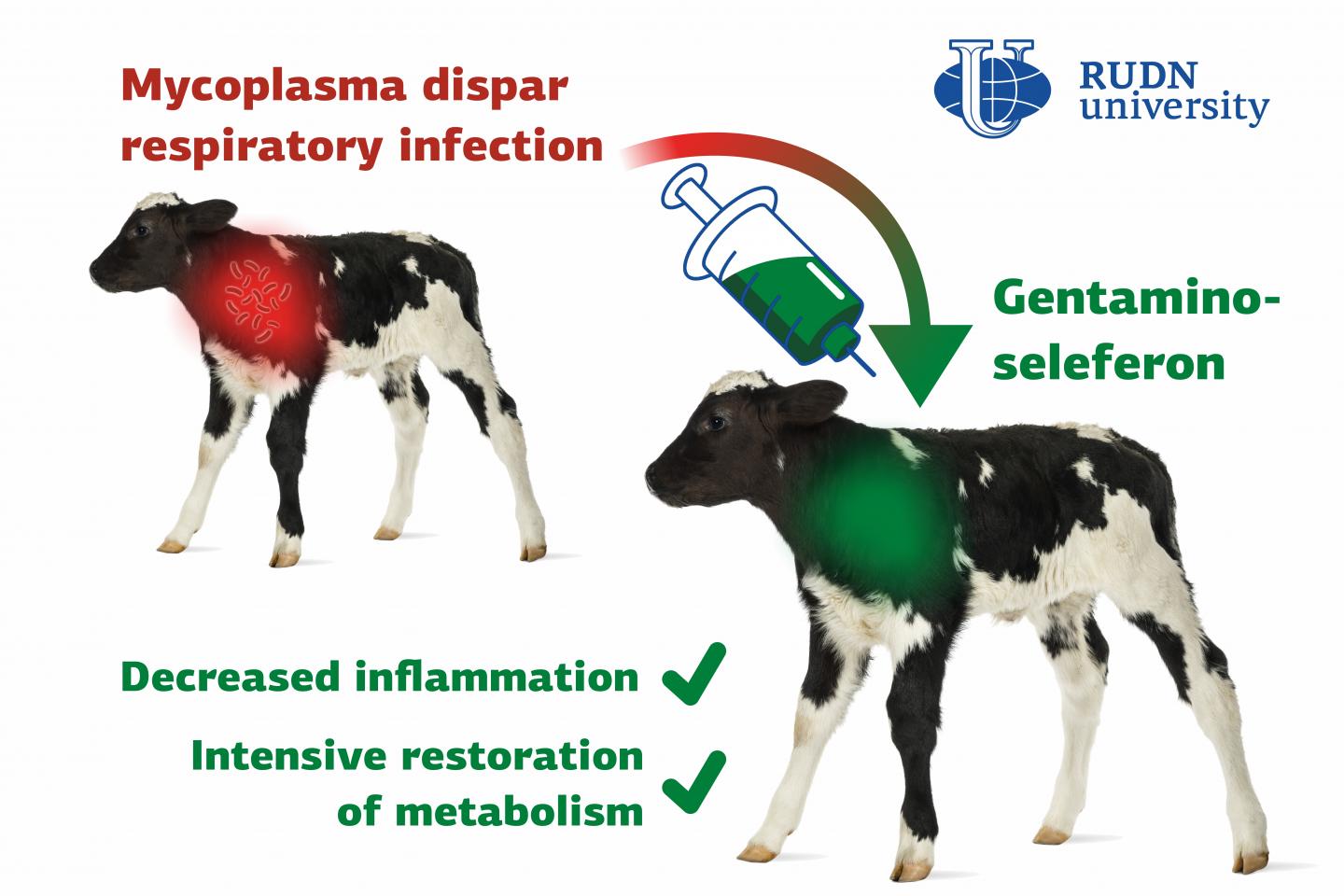
Respiratory tract diseases in young animals of the cattle are a big issue for world agriculture and food safety because a bacterium that causes them is resistant to most antibiotics. A team of veterinarians from RUDN University developed and tested a complex preparation called gentaminoseleferon that could help treat respiratory infection in calves. The results of the study were published in the Veterinary World journal.
Bacteria of the genus Mycoplasma cause many infectious diseases in animals, including atypical pneumonia, other respiratory tract conditions, reproductive pathologies, arthritis, keratoconjunctivitis, mastitis, and so on. The genus includes about 200 species of bacteria, and all of them are dangerous for animals. While the action of many antibiotics is focused on the destruction of bacterial cell walls, Mycoplasma cells don’t have it which makes Mycoplasma diseases difficult to treat. A team of veterinarians from RUDN University tested a new drug against Mycoplasma dispar that often causes pneumonia in calves.
“Respiratory diseases of young cattle cause economic damage on a global scale. They are treated with complex preparations that support natural body resistance, normalize metabolism, and have an anti-inflammatory effect. Our goal was to study the therapeutic efficiency of gentaminoseleferon against respiratory tract diseases in calves, in particular the Mycoplasma dispar infection,” said Mohammad Abed Alhussen and Hamdan Naef, postgraduate students at the Center for Innovative Veterinary Medicine, RUDN University.
The team conducted a pilot study of the drug on 15 calves that were divided into three groups: the first one was a control group with healthy animals and the second and the third contained calves with early clinical signs of the respiratory infection. Each calf from the second group was intramuscularly injected with 5 to 10 ml sulfetrisan (a drug based on the antibiotics sulfadimethoxine, erythromycin, and trimethoprim that is traditionally used to treat this disease) for seven days. The third group received gentaminoseleferon injections in the dose of 1 ml per 10 kg of mass for the same time. The healthy calves from group one did not receive any treatment. The team took blood samples from all animals 10 days before and after the treatment.
As a result of treatment, the biochemical properties and plasma parameters of the blood of infected calves returned to normal. Moreover, the third group experienced an additional positive effect: the protein content in their blood plasma increased by 2.2% compared to the second group, the level of vitamin A grew by 13.5%, E by 11.9%, C by 15.1%, iron by 9.3%, and zink by 4.1%. While in the course of the illness the bodies of the calves lacked these vitamins and microelements, after the treatment they returned to normal levels.
“These results indicate a prominent decrease of inflammatory processes in the respiratory tract along with active recovery of metabolism, thus confirming the therapeutic efficiency of gentaminoseleferon,” added Mohammad Abed Alhussen and Hamdan Naef from RUDN University.
###
Media Contact
Valeriya Antonova
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.