RUDN University chemist with his colleagues from Portugal has developed two types of coating based on new coordination polymers with silver. Both compounds were successfully tested against four common pathogens. The results are published in ACS Publications (ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces).
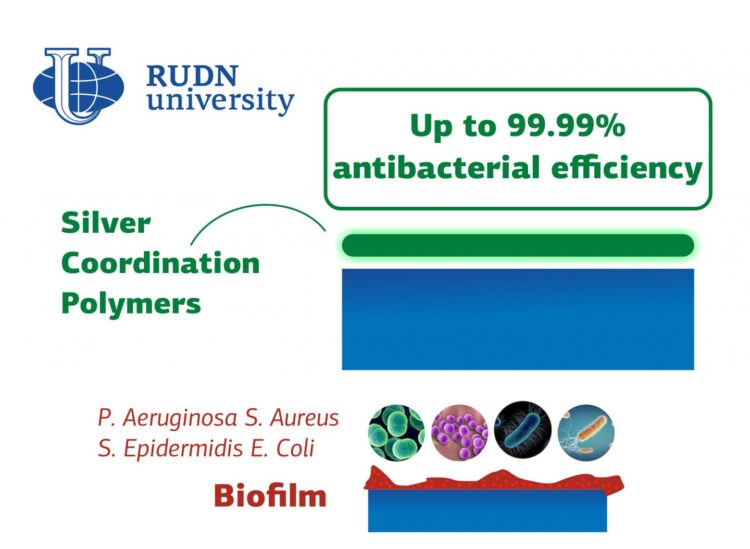
Due to the rapid mutation, harmful microorganisms constantly adapt to new antibiotics and antiseptics. It is especially difficult to destroy bacteria when they form a biofilm. They stick together and create a community ready to fight antimicrobial agents back. Coordination polymers (scaffolds made of metal ions and organic ligands) can solve this problem. They prevent pathogens from forming biofilms and replicating on the surfaces. RUDN University chemists have created two coordination polymers with silver ions with almost 100% antibacterial activity.
“We developed a synthesis protocol and described the characteristics and structural features of two new silver-based bioactive coordination polymers. We immobilized these compounds acrylated epoxidized soybean oil and created a hybrid material for antimicrobial use”, Alexander Kirillov, PhD, an associate of the Joint Institute for Chemical Studies at RUDN.
Coordination polymers consist of cyclic structures. Their central element is an atom or an ion. Scientists used silver nitrate and pyromellitic or trimesic acid to synthetise silver-based polymers. The polymers were obtained by self-assembly, it means that cyclic components themselves interacted to form a pattern which was then added to the substrate made of soybean oil. Chemists have created three types of films with different concentrations of the coordination polymer-0.05%, 0.1% and 0.5%.
RUDN chemists have tested whether the bacteria can form biofilms on surfaces that are coated with new polymers. For the experiment, they used four pathogens that can form biofilms in the human body and cause diseases. Staphylococcus epidermidis causes sepsis, endocarditis, conjunctivitis, Staphylococcus aureus causes purulent inflammatory processes in almost all organs and tissues, Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the agent of nosocomial infections in humans, and the mostly harmless Escherichia coli can sometimes cause severe food poisoning. The new polymers appeared to be active against all four bacteria. The effectiveness of protection depended on the concentration. One of the coatings proved to be more promising — a film with 0.05% of the active polymer destroyed 99.99% of the bacteria of all four species.
“Our work opens up antibiofilm applications of CP-doped biopolymers, providing new perspectives and very promising results for the design of functional biomaterials”, Alexander Kirillov, PhD, an associate of the Joint Institute for Chemical Studies at RUDN.
###
Media Contact
Valeriya Antonova
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.