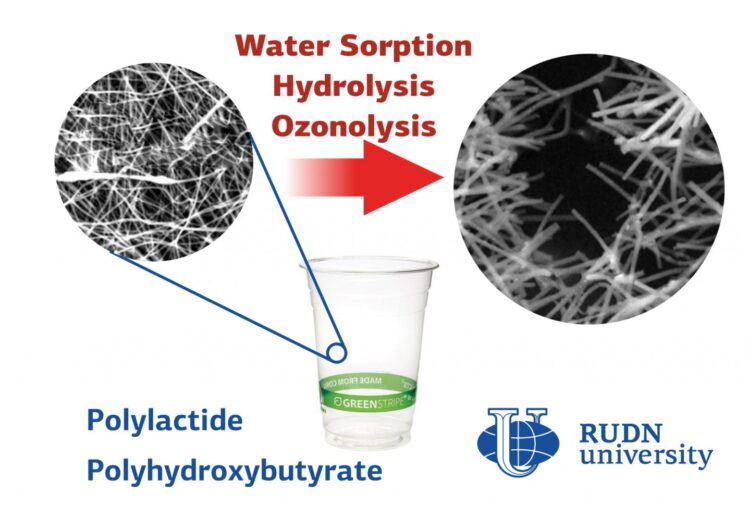
RUDN University biologist studied the aggressive impact of environmental factors (water, salts, and ozone) on ultrathin nanofibers of biopolymers. The results will help choosing suitable bioplastic depending on the use; for example, for medical implants, biodegradable packaging or filters for water cleaning. The results are published in the journal Polymers.
Bioplastics are an alternative to ordinary plastics. They are obtained from waste of plant and food industry. The safe composition allows using them as filters for gases and liquids, as “sponges” for cleaning reservoirs and medical implants. Depending on the field of use, bioplastics are exposed to different environmental factors — light, water, temperature, and the physiological environment. It is still not known how the external environment affects the nanostructure of bioplastics products. The RUDN University biologist found out how the environment affects the nanofibers of two plastics of organic origin: polylactide and polyhydroxybutyrate.
“We obtained the electrospun ultrathin fibers based on thermoelastic biopolyesters. Both of them produced from the naturally abundant renewable resources, namely, polylactide and polyhydroxybutyrate. But our main aim was not to obtain the fibers themselves, but to determine whether their properties are preserved under the impact of aggressive environmental factors”, Alexandre Vetcher, PhD, Deputy Director of the Scientific-educational centre “Nanotechnologies” of RUDN University
Biologists obtained six types of fibers from polyhydroxybutyrate powder and polylactide granules by electrospinning method. The polymer solution was placed in a high-voltage electrostatic field, which “pulled” the solution into thin jets. After cooling, they turned into fibers. Six types of finished fibers differed in the content of polymers in the composition-pure polylactide and polyhydroxybutyrate and their blends in different ratios.
RUDN University biologists have studied the impact of water, physiological environment (internal environment of the body) and ozone on the resulting nanofibers. It turned out that the water vapor absorption depends on the polymer structure. The higher the proportion of polylactide, the more water the fibres absorb: up to 1% of the sample weight. Scientists used a phosphate buffer to simulate the internal environment of a living organism. Polylactide fibers lost more than 50% of their mass in solution over 21 days, and samples with a high polyhydroxybutyrate content lost less than 15%. Also, polymers with a high content of polylactide absorbed ozone molecules more quickly when treated with a stream of this gas and as a result of such intense oxidation they were destroyed. Ozone penetrated the fibers with a 50:50 ratio of the two polymers the fastest.
“We demonstrated that biodegradable nanofibers, which are characterized by a crystalline structure, are more resistant to decomposition by water and ozone. Now it is necessary to test these materials for resistance to UV light and microorganisms in order to determine the optimal applications for each type of fiber”, Alexandre Vetcher, PhD, Deputy Director of the Scientific-educational centre “Nanotechnologies” of RUDN University.
###
Media Contact
Valeriya Antonova
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.