Credit: SIAT
Plasmonic surface lattice resonances (SLRs) supported by metal nanoparticle arrays have many merits such as strong field enhancements extended over large volumes, as well as long lifetimes, narrow linewidths, angle-dependent dispersion, and a wide range of wavelength tunability.
In order to improve the performance of SLR-based nanophotonic devices such as nanolasers, nonlinear optical devices, and optical sensors, much effort has been put into improving SLR quality factors.
A research group led by Dr. LI Guangyuan from the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has found that nanohemisphere arrays can significantly improve the quality factors of SLRs.
The group’s study, entitled “Exceptionally narrow plasmonic surface lattice resonances in gold nanohemisphere array,” was published in the Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics on August 24.
In previous studies, SLRs were supported mainly by periodic metal nanorods. According to a recent review, the quality factors of such SLRs are ~150 for visible light, ~300 for telecom wavelengths, and ~500 for the midinfrared regime, respectively.
Although the lattice shape is vital for quality factors, studies involving various geometries did not lead to an anticipated remarkable narrowing of localized surface plasmon resonances (LSPRs) associated with these particles.
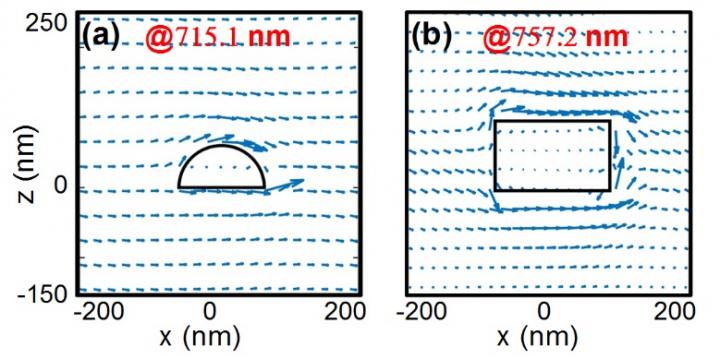
In this study, the researchers investigated SLRs supported by a 2D periodic nanohemisphere array embedded in a symmetric dielectric environment. Their simulation results showed that out-of-plane SLRs can have an ultra-narrow resonant linewidth (~0.9 nm) at visible wavelengths around 715 nm.
This result corresponded to an exceptionally high quality factor of 794, which was an order of magnitude larger than that of widely adopted nanorods.
In addition, the team also showed how to achieve high quality factors based on detuning between the Rayleigh anomaly and the LSPR of an isolated nanoparticle.
“The energy flux propagates along the surface and bypasses the nanoparticle, which mimics a stream bypassing a stone,” said Dr. LI Guangyuan. “We all know that a round stone introduces weaker perturbations. This inspired us to replace nanorods with nanohemispheres.”
The researchers are now continuing to fabricate 2D nanohemisphere array patterns with controlled feature size and shape, which is challenging but feasible.
They believe that SLRs supported by a 2D nanohemisphere array, featuring much higher quality factors than nanorods, will be attractive in diverse applications, including nanolasers, nonlinear optics, and ultrasensitive sensing.
###
Media Contact
ZHANG Xiaomin
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




