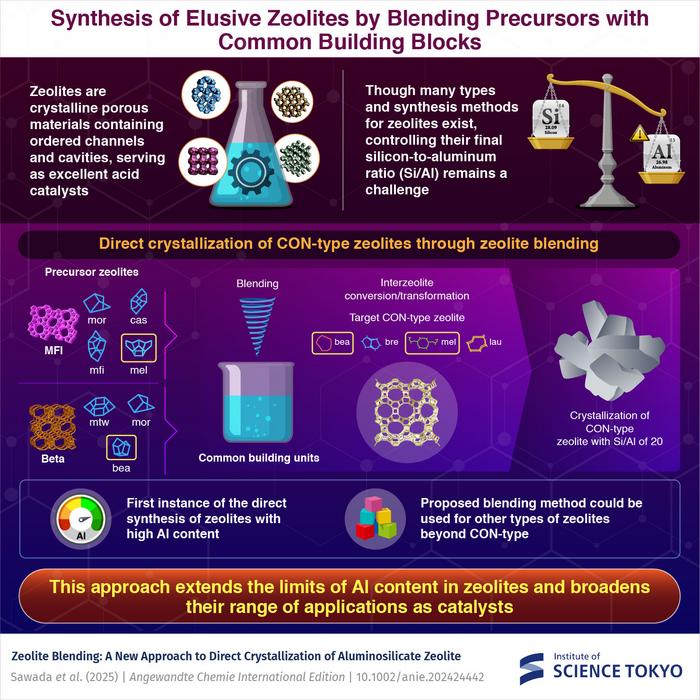
A novel and groundbreaking technique, termed ‘zeolite blending,’ has emerged, revolutionizing the synthesis of zeolites by enabling the production of CON-type zeolites with exceptionally high aluminum content. This significant advancement, reported by scientists from the prestigious Institute of Science Tokyo, addresses a long-standing barrier in zeolite manufacturing that has hindered the precise control of aluminum incorporation in their crystal frameworks. This innovation is particularly transformative for catalytic applications across multiple industrial sectors, which rely on optimized zeolite structures for enhanced performance.
Zeolites, which are crystalline microporous materials characterized by their distinct arrangement of cavities and channels, play a crucial role in catalysis due to their unique structural properties. The manipulation of aluminum ions within the silica framework of zeolites directly influences their acidity and, consequently, their catalytic efficiency. Herein lies the challenge, as traditional methods have struggled with accurately achieving low silicon-to-aluminum (Si/Al) ratios—particularly below a threshold of 100 in CON-type zeolites through direct synthesis.
Through the extensive research conducted by a team led by Professor Toshiyuki Yokoi, a pioneering approach employing multiple zeolite precursors was developed. This methodology not only revolutionizes the aluminum incorporation into the zeolite framework but also broadens the compositional range of zeolite structures. By leveraging the interzeolite conversion/transformation technique, researchers focused on the composite building units (CBUs) shared between precursor zeolites and the desired structural framework. This targeted approach enables the development of zeolite structures showcasing previously unattainable aluminum contents.
Initially, the research team validated their methodology using single zeolite precursors, achieving remarkable success with a Si/Al ratio of around 40 in CON-type zeolites, which surpassed traditional production capabilities. However, the optimal breakthrough was recognized when researchers integrated different zeolite precursor types, specifically utilizing Beta zeolite as a key foundational material complemented by MFI-type zeolite to significantly enhance aluminum incorporation.
This blending strategy facilitated the strategic arrangement of essential building blocks from diverse zeolite frameworks, laying the groundwork for the crystallization of CON-type zeolites endowed with finer aluminum distribution and smaller particle sizes. These characteristics render the newly produced zeolites especially advantageous for catalytic processes, particularly the methanol-to-olefin reaction—a process vital for deriving essential petrochemicals from renewable feedstock sources.
What makes this discovery particularly compelling is not just the successful synthesis of high-aluminum zeolites with a Si/Al ratio of approximately 20—a milestone never achieved through singular precursor routes—but the vast possibilities that this zeolite blending method presents for future research and development in zeolite materials. The advancement opens new avenues for creating specialty zeolites with desired attributes, thus pushing the boundaries of zeolite composition more extensively than ever before.
Beyond the immediate implications for zeolite synthesis, the nuanced understanding gained through this innovative approach allows researchers to investigate the physicochemical properties of precursor materials, optimizing clarity in how different elements and structures interact within the synthesis process. The potential ramifications of this research extend to several industrial applications, promising not only improved catalytic efficiency but also enhanced sustainability protocols within chemical processes.
Moreover, the implications of this research resonate strongly within the context of environmental remediation and petrochemical transformations, where efficient catalysts stand to considerably reduce energy consumption and material waste. It is through such innovative techniques as zeolite blending that the field can achieve a new paradigm, fostering advancements that align with both scientific inquiry and practical utility in real-world applications.
The research findings have been published online and will appear in an upcoming issue of Angewandte Chemie International Edition. This timely communication highlights the need for ongoing exploration into alternative synthesis routes and encourages collaborative efforts to uncover the full spectrum of possibilities embedded within zeolite materials science.
As zeolite utilization expands in industries ranging from petrochemical processing to environmental cleanup, the commitment to exploring and optimizing zeolite frameworks will only continue to grow. Scientists and engineers are now poised to leverage these scientific breakthroughs, significantly enhancing the efficiency and efficacy of zeolite-based catalytic systems in meeting contemporary challenges in chemical production and environmental sustainability.
In summary, the zeolite blending technique marks a significant milestone within the field of materials science, demonstrating the formidable impact that innovative synthesis methods can have. Consequently, it encourages a reassessment of existing assumptions within zeolite research paradigms, propelling the scientific community toward novel explorations with high potential for societal and industrial impact.
Subject of Research:
Article Title: Zeolite Blending: A New Approach to Direct Crystallization of Aluminosilicate Zeolite
News Publication Date: 10-Feb-2025
Web References: Angewandte Chemie International Edition
References: DOI: 10.1002/anie.202424442
Image Credits: Credit: Institute of Science Tokyo
Keywords
Zeolites
Catalyst Development
Aluminum Content Control
Chemical Synthesis
Sustainable Development
Environmental Remediation
Tags: advanced zeolite synthesis methodsaluminum ion manipulation in zeolitescleaner fuel production technologiesenvironmental impact of zeolitesgreener industrial practiceshigh aluminum content zeolitesinnovative zeolite manufacturing processesInstitute of Science Tokyo researchlow Si/Al ratio zeolitessustainable catalytic applicationszeolite blending techniquezeolite structural properties