Bladder cancer, notorious for being one of the most costly malignancies to manage, often results in patient discomfort and frequent, invasive, and expensive procedures.Traditional treatments, though gradually being replaced by immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), have had varied success rates with limited predictors for individual patient responses.
Credit: Jiaqi Wang, et al.
Bladder cancer, notorious for being one of the most costly malignancies to manage, often results in patient discomfort and frequent, invasive, and expensive procedures.Traditional treatments, though gradually being replaced by immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), have had varied success rates with limited predictors for individual patient responses.
In a study published in the journal Genes & Diseases, researchers from Fudan University, have developed a novel urine-based prognostic model that promises to transform the management and treatment of bladder cancer.
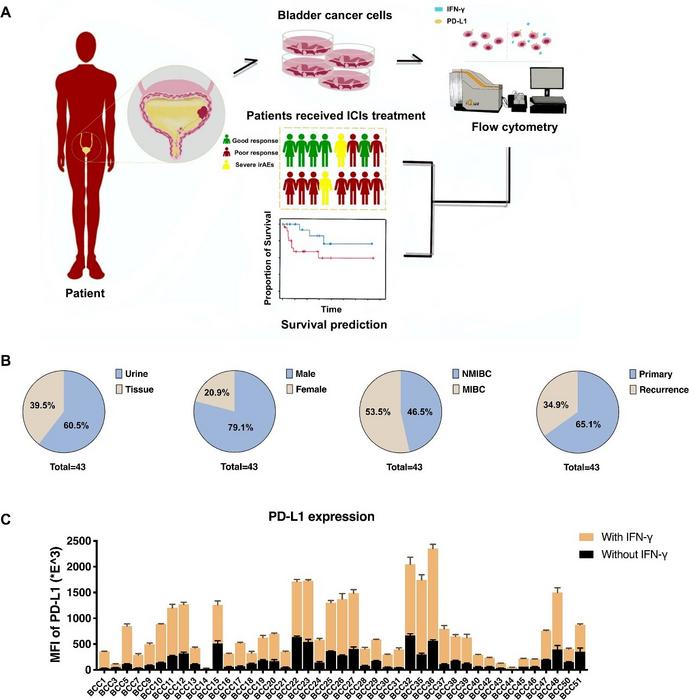
The research team collected urine and tumor samples from 43 bladder cancer patients, examining the expression levels of PD-L1 – a key marker in immune response – on bladder cancer cells (BCCs). And the study focused on the variability of PD-L1 expression and its response to IFN-γ in bladder cancer cells (BCCs) as detected by the BC-PD-L1 platform. From 43 bladder cancer (BLCA) patients, urine and tumor samples were obtained and used for primary cell culturing. Intriguingly, PD-L1 expression, before and after treatment with IFN-γ, varied significantly among the BCCs. Moreover, the degree of PD-L1 upregulation post-IFN-γ treatment showed a negative correlation with baseline PD-L1 expression levels. To ensure BC-PD-L1’s reliability, the study employed RNA sequencing and correlated PD-L1 protein levels with mRNA levels, which validated its ability to detect PD-L1 regardless of its heavy glycosylation – a trait that can potentially obstruct accurate detection. In evaluating the platform’s clinical potential, the study delved into how BC-PD-L1, especially urine-derived BC-PD-L1 (UBC-PD-L1), can predict BLCA patient outcomes. Although prior research on the prognostic significance of PD-L1 in bladder cancer has been mixed, this study’s analysis revealed that higher surface PD-L1 levels were associated with longer disease-free survival and overall survival rates. Intriguingly, RNA sequencing highlighted differences between high and low PD-L1 expressing BCCs. High PD-L1 BCCs showed upregulation of pathways related to the extracellular matrix (ECM) – a key component influencing cancer progression. Additionally, these high PD-L1 BCCs were more immune-active, suggesting a better prognosis. This finding underscores the importance of PD-L1 as a potential biomarker and the BC-PD-L1’s potential role in personalizing bladder cancer treatment strategies.
The study underscores the power of personalized medicine, highlighting the potential of urine-based tests in transforming bladder cancer treatments. Given bladder cancer’s propensity for recurrence and the invasive nature of current diagnostic and treatment methods, this innovation offers a beacon of hope.
###
Contact: Genes & Diseases Editorial Office, [email protected]
The publisher KeAi was established by Elsevier and China Science Publishing & Media Ltd to unfold quality research globally. In 2013, our focus shifted to open access publishing. We now proudly publish more than 100 world-class, open access, English language journals, spanning all scientific disciplines. Many of these are titles we publish in partnership with prestigious societies and academic institutions, such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
Journal
Genes & Diseases
DOI
10.1016/j.gendis.2022.10.022
Article Title
A novel in vitro prognostic model of bladder cancer based on urine-derived living tumor cells



