Credit: Su, Xinyi
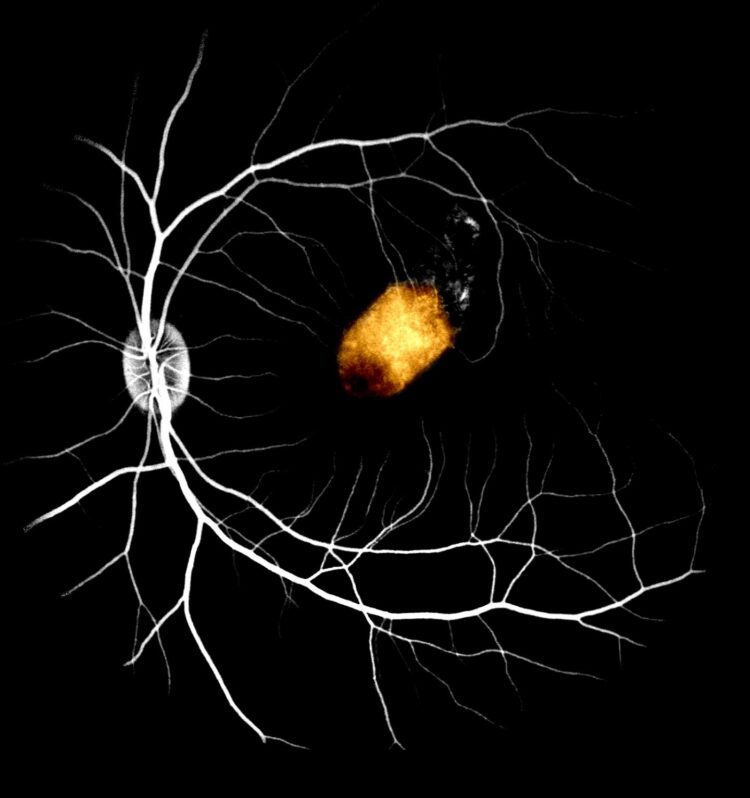
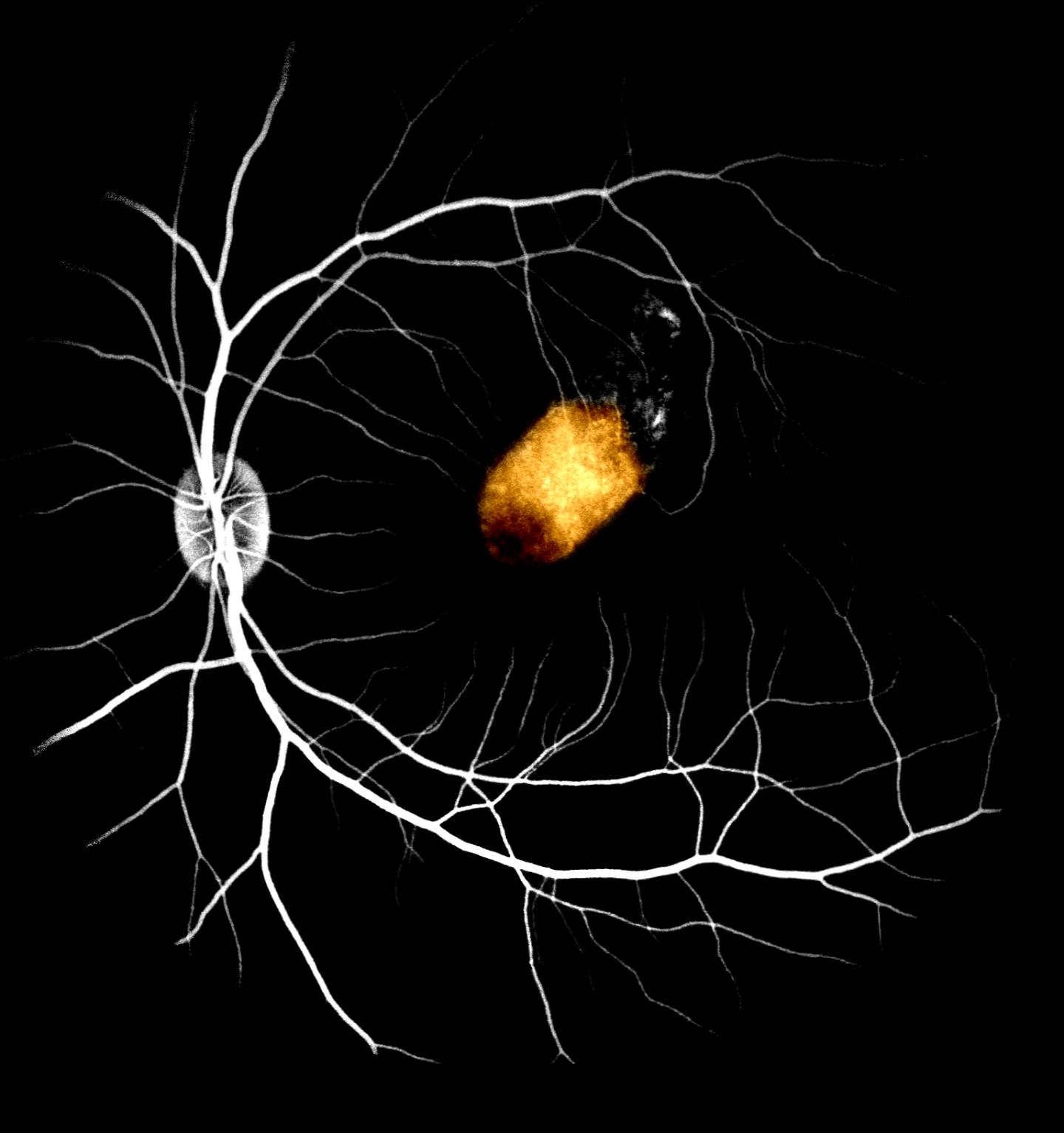
Retinal cells derived from adult human eye stem cells survived when transplanted into the eyes of monkeys, an important early step in the validation of this approach for treating blindness, according to a study by Liu, et al recently published in Stem Cell Reports. The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), a layer of pigmented cells in the retina, is essential for sustaining normal vision. Blindness due to RPE dysfunction, such as macular degeneration, affects about 200 million people worldwide.
To restore this population of cells, researchers extracted retinal stem cells from donated cadaver adult eyes, grew them into RPE cells and transplanted them into the eyes of monkeys. These unique cells have the potential to serve as an unlimited resource of human RPE, with the possibility of donor compatibility matching.
The study is the first time the safety and feasibility of adult retinal stem cell-derived RPE transplants in non-human primates was assessed. Researchers found that RPE patches transplanted into the monkey’s eye stably integrated for at least three months with no serious side effects. What is more, the stem cell-derived RPE partially took over the function of the monkey RPE and was able to support normal photoreceptor function. Importantly, these cells did not cause retinal scarring.
Altogether, this demonstrates the feasibility of using adult retinal stem cell-derived RPE transplants to replace defective RPE as a possible treatment for macular degeneration. However, further experiments need to be conducted. This includes evidence to demonstrate adult retinal stem cell-derived RPE can restore vision in diseased non-human primate models, and eventually in regulatory human clinical trials. Nonetheless, this proof-of-principle study is an important early step in validating this approach, which is part of as international collaboration between the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai (New York), Institute of Molecular Cell Biology (A*STAR), Singapore Eye Research, National University of Singapore, and Eye Clinic Sulzbach (Germany).
###
Media Contact
Kym Kilbourne
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.