Credit: Simpson et al. 2021 (please hyperlink to paper)
A team of researchers from the Africa Climate and Development Initiative (ACDI) led a global team of 21 climate risk scholars to better understand and inform decision making around climate change risks in Africa and globally by examining how the drivers of risk interact.
Their work extends on existing risk frameworks with the hope that this research could help decision makers, managers and researchers understand the inherent complexity of climate change.
“Understanding the interactions among risks holds potential to change the way we respond to the risks. This is important because policy makers may worry about the risk of implementing a response as much, or more so, than the risk the response aims to reduce. This can lead to inaction at the very time when we need to be most active and investing heavily in our response to climate change,” said Dr Nick Simpson, lead author of the paper published in One Earth, and postdoctoral fellow at the ACDI based at the University of Cape Town (UCT).
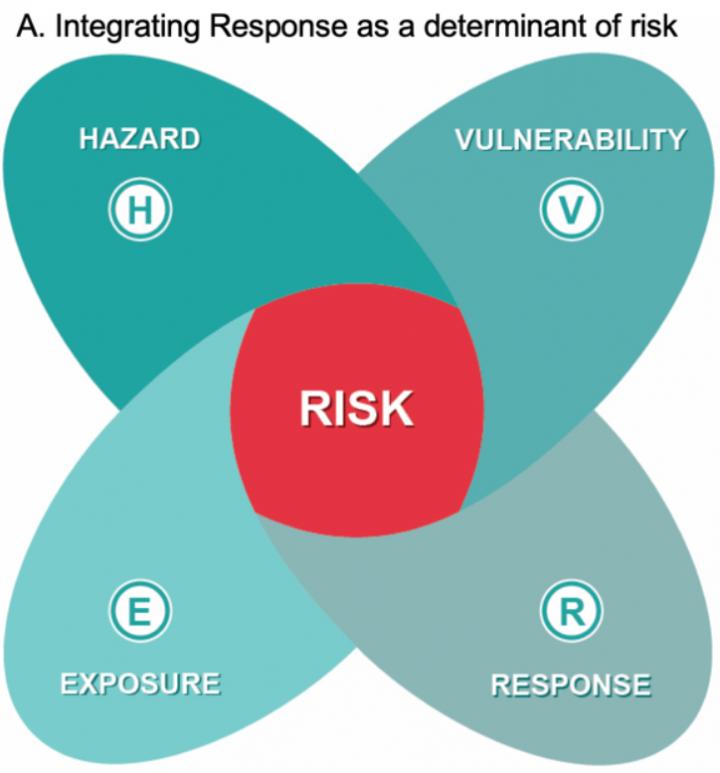
Two important responses to climate change – adaptation and mitigation – are often not considered as part of climate risk assessment. In the article, the team, extends the existing risk framework used by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) by including response options, identifying multiple interactions of drivers of risk, and risk interactions in risk assessment.
Across the suite of terms that have been applied to climate change risk for human and natural systems, there is a commonality: an interaction or aggregation of the determinants of risk (hazard, exposure, vulnerability), and of multiple risks. The researchers expand on this by explicitly recognising that a response to climate change can also be a driver of risk as shown in the diagram below.
For example, biological responses to heatwaves can create faster than normal soil moisture depletion known as a ‘false spring’ as a response to unusual early season growth increasing risk of wildfire and compound conditions of extreme heat (hazard), duration of heatwave (exposure) and increased fuel load (vulnerability).
Yet, response has been generally considered separately or secondarily to interactions between hazards, exposures and vulnerabilities. As a result, response is considered for how it can manage or reduce risk rather than how it might also create risk. But response should be at the centre of climate risk assessment and management.
Simpson highlighted the importance of this innovation: “If human and biological response to climate change was better integrated with conceptualisation of risk, its assessment would be more policy relevant and better reflect real-world decision making around risk,” he said.
The framework goes on to identify two more categories of complex climate change risk and highlights the importance of also considering the interactions of the multiple drivers of risk and interactions between risks themselves. This is particularly important in the African context where there is unique vulnerability and exposure challenges for particular populations and is well illustrated by the interactions of risks during the Cape Town drought.
Effective responses to the drought were delayed due to the political risk of declaring a disaster and a lack of feasible water supply alternatives. Responses became increasingly urgent in early 2018 as the potential of a ‘Day Zero’ event became possible, the point at which a city of four million people might run out of water. The risk of ‘Day Zero’ was anticipated to cascade to affect risks to health, economic output and security and responses by different groups interacted to generate risks to municipal finance.
Considering interactions among these multiple risk and risk drivers is important as it shifts risk assessment from a concentration on individual climate hazards or interactions of hazards as a single ‘event’, such as a drought or flood, to situate that climate hazard within a set of multiple events interacting continuously with evolving social and economic conditions.
Access the full study: Simpson, N.P., et al. (2021). Assessing and responding to complex climate change risks, One Earth. DOI https:/
###
Media Contact
Aamirah Sonday
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




