Credit: Yokohama National University
Researchers from the Yokohama National University have teleported quantum information securely within the confines of a diamond. The study has big implications for quantum information technology – the future of how sensitive information is shared and stored.
The researchers published their results on June 28, 2019 in Communications Physics.
“Quantum teleportation permits the transfer of quantum information into an otherwise inaccessible space,” said Hideo Kosaka, a professor of engineering at Yokohama National University and an author on the study. “It also permits the transfer of information into a quantum memory without revealing or destroying the stored quantum information.”
The inaccessible space, in this case, consisted of carbon atoms in diamond. Made of linked, yet individually contained, carbon atoms, a diamond holds the perfect ingredients for quantum teleportation.
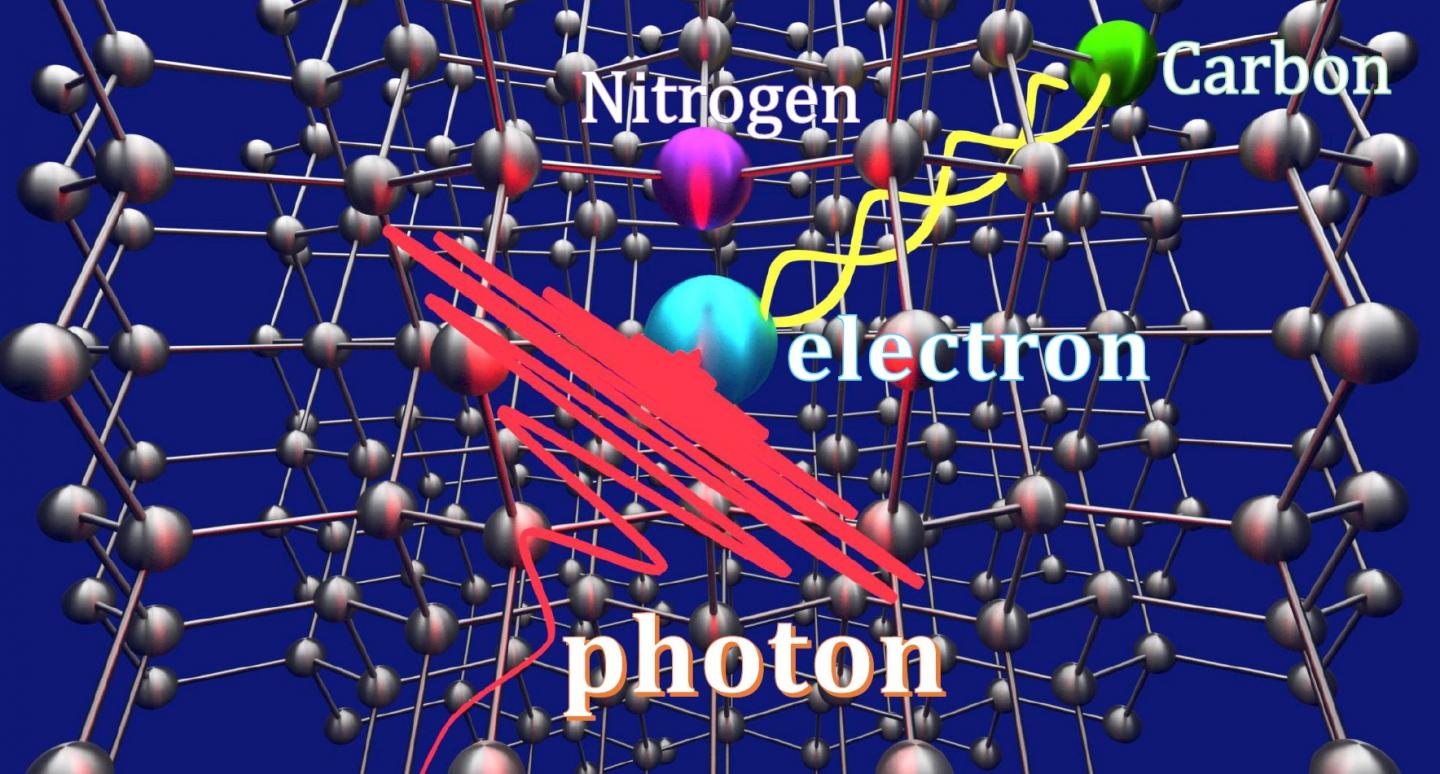
A carbon atom holds six protons and six neutrons in its nucleus, surrounded by six spinning electrons. As the atoms bond into a diamond, they form a notoriously strong lattice. Diamonds can have complex defects, though, when a nitrogen atom exists in one of two adjacent vacancies where carbon atoms should be. This defect is called a nitrogen-vacancy center.
Surrounded by carbon atoms, the nucleus structure of the nitrogen atom creates what Kosaka calls a nanomagnet.
To manipulate an electron and a carbon isotope in the vacancy, Kosaka and the team attached a wire about a quarter the width of a human hair to the surface of a diamond. They applied a microwave and a radio wave to the wire to build an oscillating magnetic field around the diamond. They shaped the microwave to create the optimal, controlled conditions for the transfer of quantum information within the diamond.
Kosaka then used the nitrogen nanomagnet to anchor an electron. Using the microwave and radio waves, Kosaka forced the electron spin to entangle with a carbon nuclear spin – the angular momentum of the electron and the nucleus of a carbon atom. The electron spin breaks down under a magnetic field created by the nanomagnet, allowing it to become susceptible to entanglement. Once the two pieces are entangled, meaning their physical characteristics are so intertwined they cannot be described individually, a photon which holds quantum information is applied and the electron absorbs the photon. The absorption allows the polarization state of the photon to be transferred into the carbon, which is mediated by the entangled electron, demonstrating a teleportation of information at the quantum level.
“The success of the photon storage in the other node establishes the entanglement between two adjacent nodes,” Kosaka said. Called quantum repeaters, the process can take individual chunks of information from node to node, across the quantum field.
“Our ultimate goal is to realize scalable quantum repeaters for long-haul quantum communications and distributed quantum computers for large-scale quantum computation and metrology,” Kosaka said.
###
The rest of the team from Kosaka’s laboratory at Yokohama National University who contributed to this paper are Kazuya Tsurumoto, Ryota Kuroiwa, Hiroki Kano, and Yuhei Sekiguchi.
Yokohama National University (YNU or Yokokoku) is a Japanese national university founded in 1949. YNU provides students with a practical education utilizing the wide expertise of its faculty and facilitates engagement with the global community. YNU’s strength in the academic research of practical application sciences leads to high-impact publications and contributes to international scientific research and the global society. For more information, please see: https:/
Media Contact
Akiko Tsumura
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




