Credit: GAO Mingbin
MTO process, which was first commercialized in 2010, is a catalytic process converting methanol, which is typically made from coal, natural gas, biomass, and CO2, over SAPO-34 zeolite catalyst. It’s becoming one of the main streams for producing light olefins, including ethylene and propylene, from non-oil resources.
One of the major challenges in MTO is the rapid deactivation of zeolite catalyst due to the coke deposition.
In industrial practices, a fluidized bed reactor-regenerator configuration is normally used in order to maintain the continuous operation, in which air or oxygen is usually input to burn off the deposited coke to restore the catalyst activity in the regenerator. This involves the transformation of coke species to CO2, with a substantial fraction of carbon resource being converted to low-value greenhouse gas.
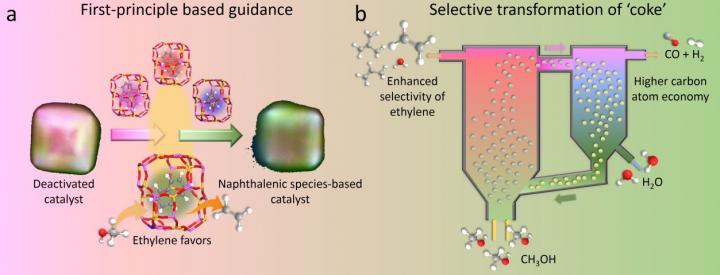
A research group led by Prof. YE Mao and Prof. LIU Zhongmin from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences regenerated deactivated catalyst in industrially important methanol-to-olefins (MTO) process by directly transforming the coke deposited on the zeolite catalyst to active intermediates rather than burning off to carbon oxide.
This work was published in Nature Communications on Jan. 4.
It was previously shown that MTO follows the hydrocarbon pool mechanism, i.e. the light olefins are favorably formed with the participation of active intermediate species, or called hydrocarbon pool species (HCPs), during the reaction. The HCPs will evolve into coke species that deactivate catalyst.
By using the density functional theory (DFT) calculations and multiple spectroscopy techniques, this team showed that naphthalenic cations, amongst HCPs, were highly stable within SAPO-34 zeolites at high temperature, and steam cracking could directionally transform the coke species in SAPO-34 zeolites to naphthalenic species at high temperature.
This technology not only recovers the catalyst activity but also promotes the formation of light olefins owing to the synergic effect imposed by naphthalenic species.
Furthermore, the researchers verified this technology in the fluidized bed reactor-regenerator pilot plant in DICP with industrial-alike continuous operations, achieving an unexpectedly high light olefins selectivity of 85% in MTO reaction and 88% valuable CO and H2 with negligible CO2 in regeneration.
This technology opens a new venue to control the selectivity of products via regeneration in industrial catalytic processes.
###
Media Contact
Jean Wang
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




