Credit: Reza Shahbazian-Yassar/UIC
Battery researchers seeking improved electrode materials have focused on "tunneled" structures that make it easier for charge-carrying ions to move in and out of the electrode. Now a team led by a researcher at the University of Illinois at Chicago has used a special electron microscope with atomic-level resolution to show that certain large ions can hold the tunnels open so that the charge-carrying ions can enter and exit the electrode easily and quickly.
The finding is reported in Nature Communications.
"Significant research has been done to increase the energy density and power density of lithium ion battery systems," says Reza Shahbazian-Yassar, associate professor of mechanical and industrial engineering at UIC.
The current generation, he said, is useful enough for portable devices, but the maximum energy and power that can be extracted is limiting.
"So for an electric car, we need to increase the energy and power of the battery — and decrease the cost as well," he said.
His team, which includes coworkers at Argonne National Laboratory, Michigan Technological Institute and the University of Bath in the U.K., has focused on developing a cathode based on manganese dioxide, a very low cost and environmentally-friendly material with high storage capacity.
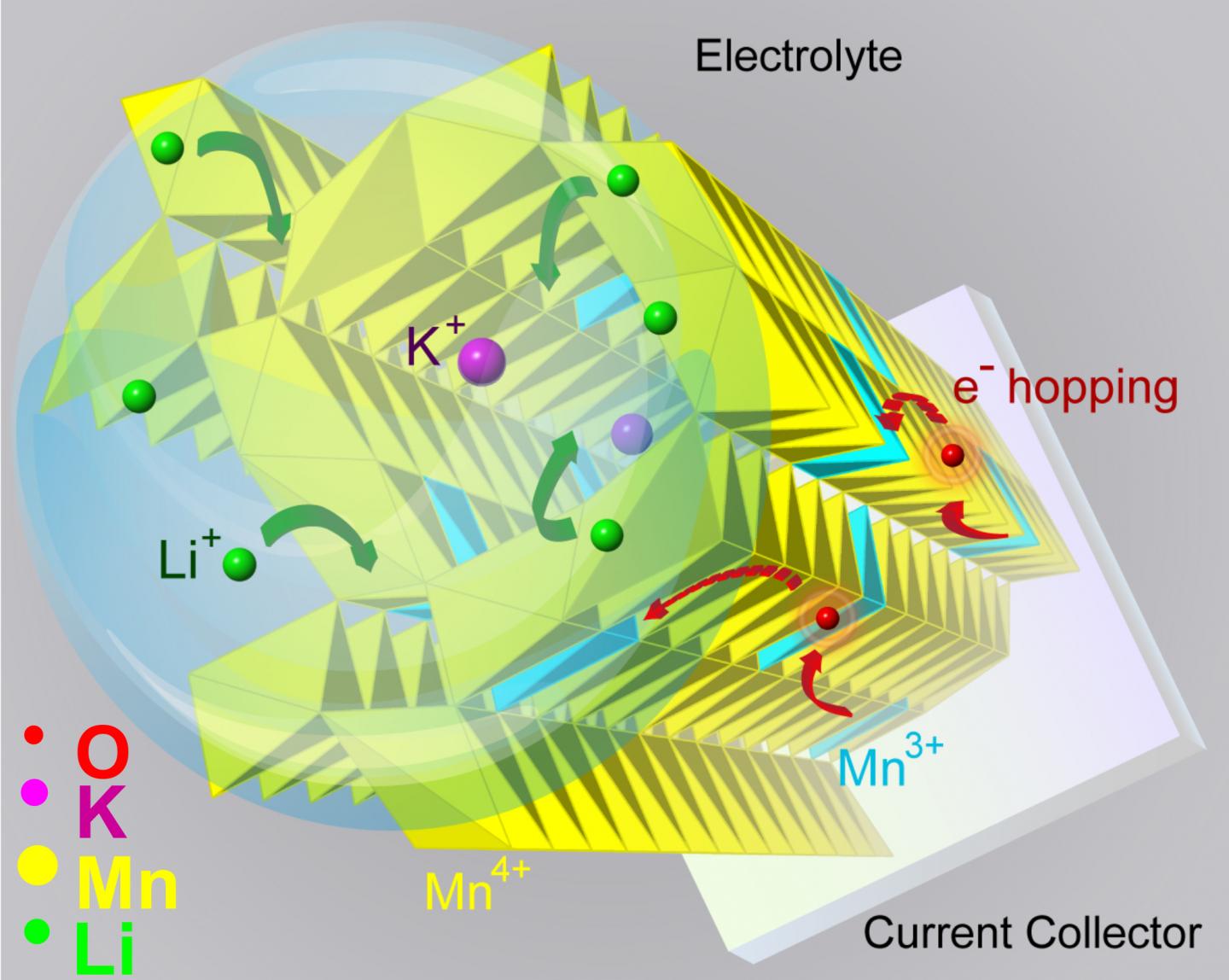
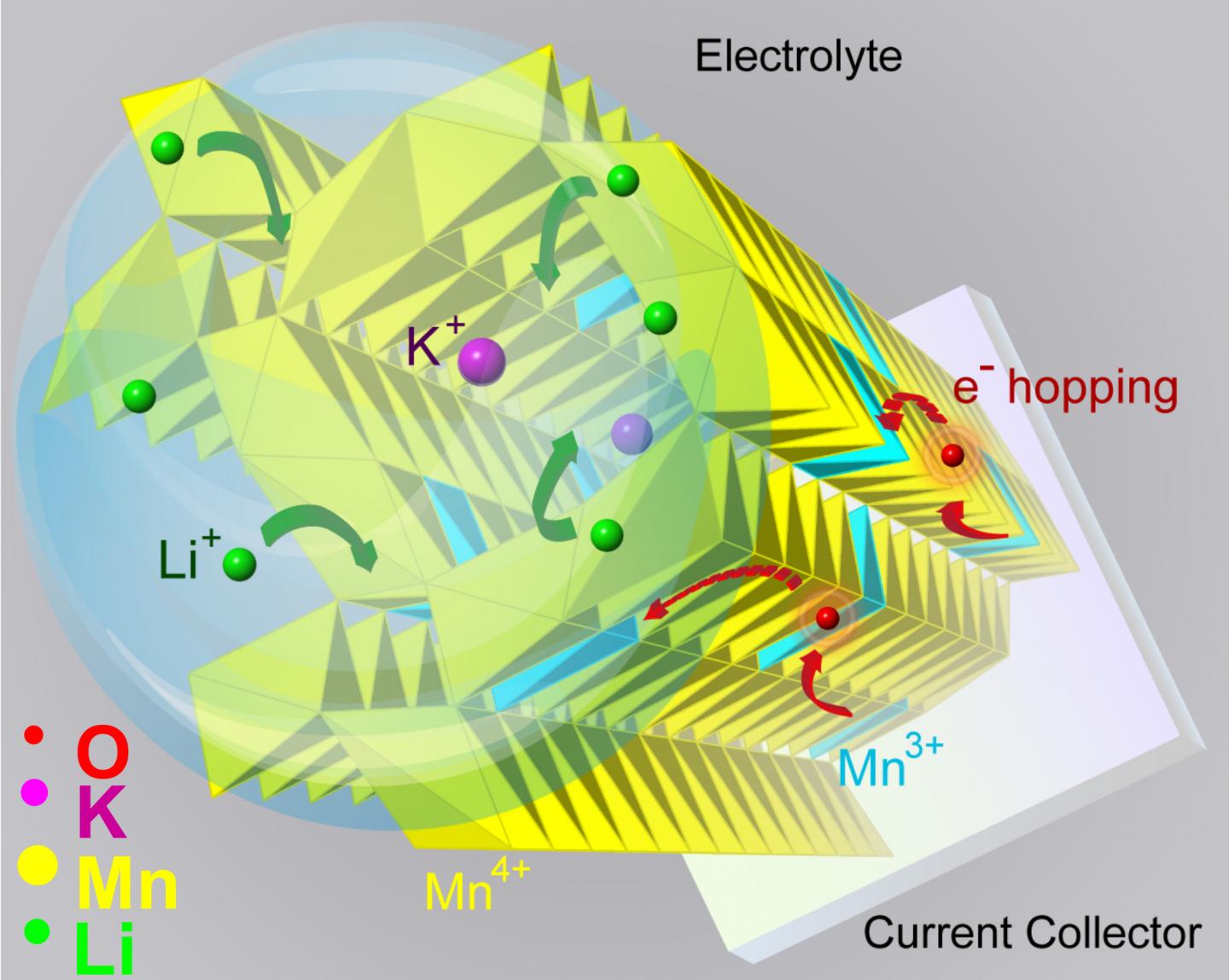
Manganese dioxide has a lattice structure with regularly spaced tunnels that allow charge carriers — like lithium ions — to move in and out freely.
"But for the tunnels to survive for long-lasting function, they need support structures at the atomic scale," Shahbazian-Yassar said. "We call them tunnel stabilizers, and they are generally big, positive ions, like potassium or barium."
But the tunnel stabilizers, being positively charged like the lithium ions, should repel each other.
"If lithium goes in, will the tunnel stabilizer come out?" Shahbazian-Yassar shrugged. "The research community was in disagreement about the role of tunnel stabilizers during the transfer of lithium into tunnels. Does it help, or hurt?"
The new study represents the first use of electron microscopy to visualize the atomic structure of tunnels in a one-dimensional electrode material — which the researchers say had not previously been possible due to the difficulty of preparing samples. It took them two years to establish the procedure to look for tunnels in potassium-doped nanowires of manganese dioxide down to the single-atom level.
Yifei Yuan, a postdoctoral researcher working jointly at Argonne National Laboratory and UIC and the lead author on the study, was then able to use a powerful technique called aberration-corrected scanning transmission electron microscopy to image the tunnels at sub-ångstrom resolution so he could clearly see inside them — and he saw they do change in the presence of a stabilizer ion.
"It's a direct way to see the tunnels," Yuan said. "And we saw that when you add a tunnel stabilizer, the tunnels expand, their electronic structures also change, and such changes allow the lithium ions to move in and out, around the stabilizer."
The finding shows that tunnel stabilizers can help in the transfer of ions into tunnels and the rate of charge and discharge, Shahbazian-Yassar said. The presence of potassium ions in the tunnels improves the electronic conductivity of manganese dioxide and the ability of lithium ions to diffuse quickly in and out of the nanowires.
"With potassium ions staying in the center of the tunnels, the capacity retention improves by half under high cycling current, which means the battery can hold on to its capacity for a longer time," he said.
###
Co-authors on the Nature Communications paper are Kun He, Soroosh Sharifi-Asl, Boao Song and Anmin Nie of UIC; Chun Zhan, Zhenzhen Yang, Xiangyi Luo, Hao Wang, Khalil Amine and Jun Lu of Argonne; Hungru Chen, Stephen M. Wood and M. Saiful Islam of the University of Bath; and Wentao Yao of Michigan Tech.
Funding was provided by the National Science Foundation and the U.S. Department of Energy.
Media Contact
Bill Burton
[email protected]
312-996-2269
@uicnews
http://www.uic.edu
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag