Credit: UC San Diego
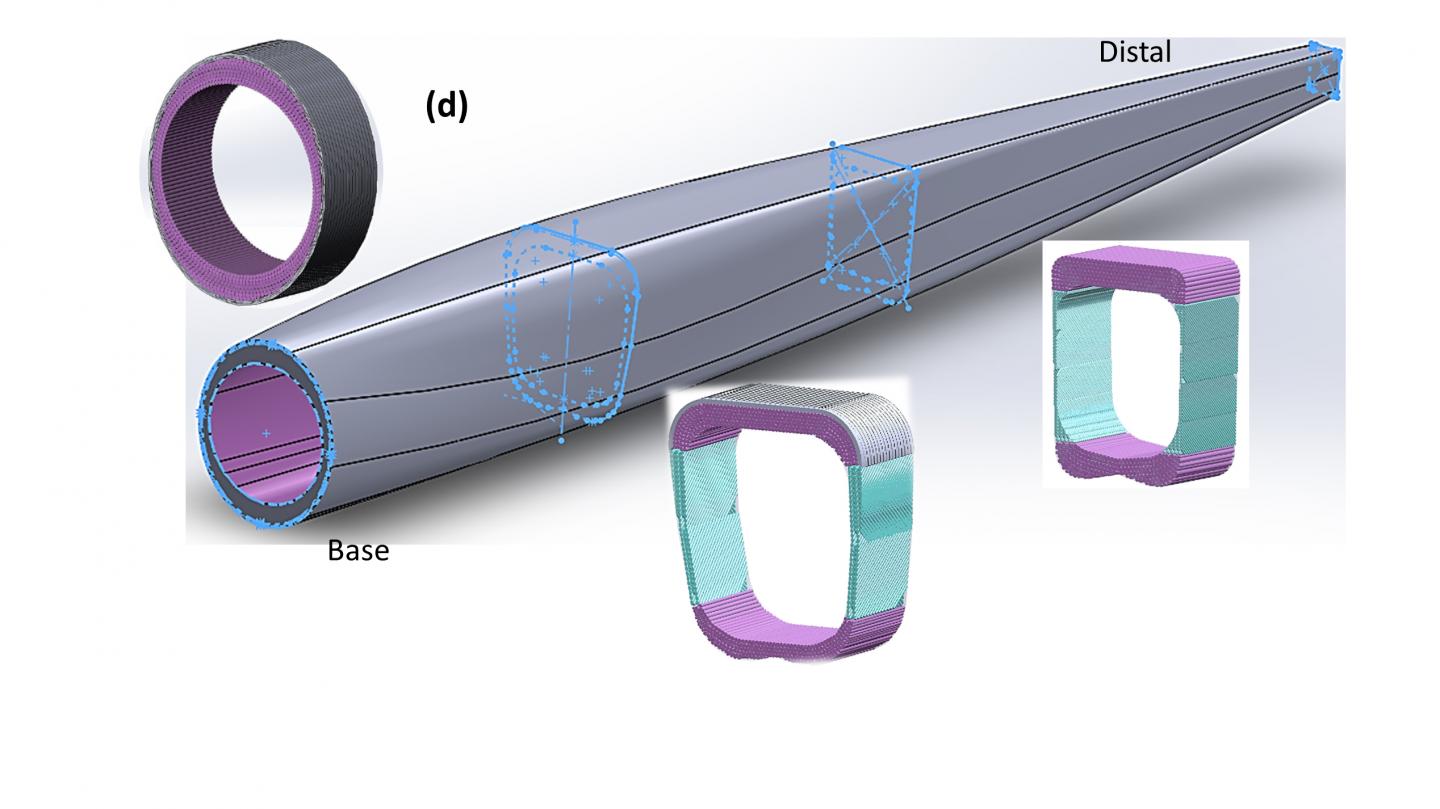
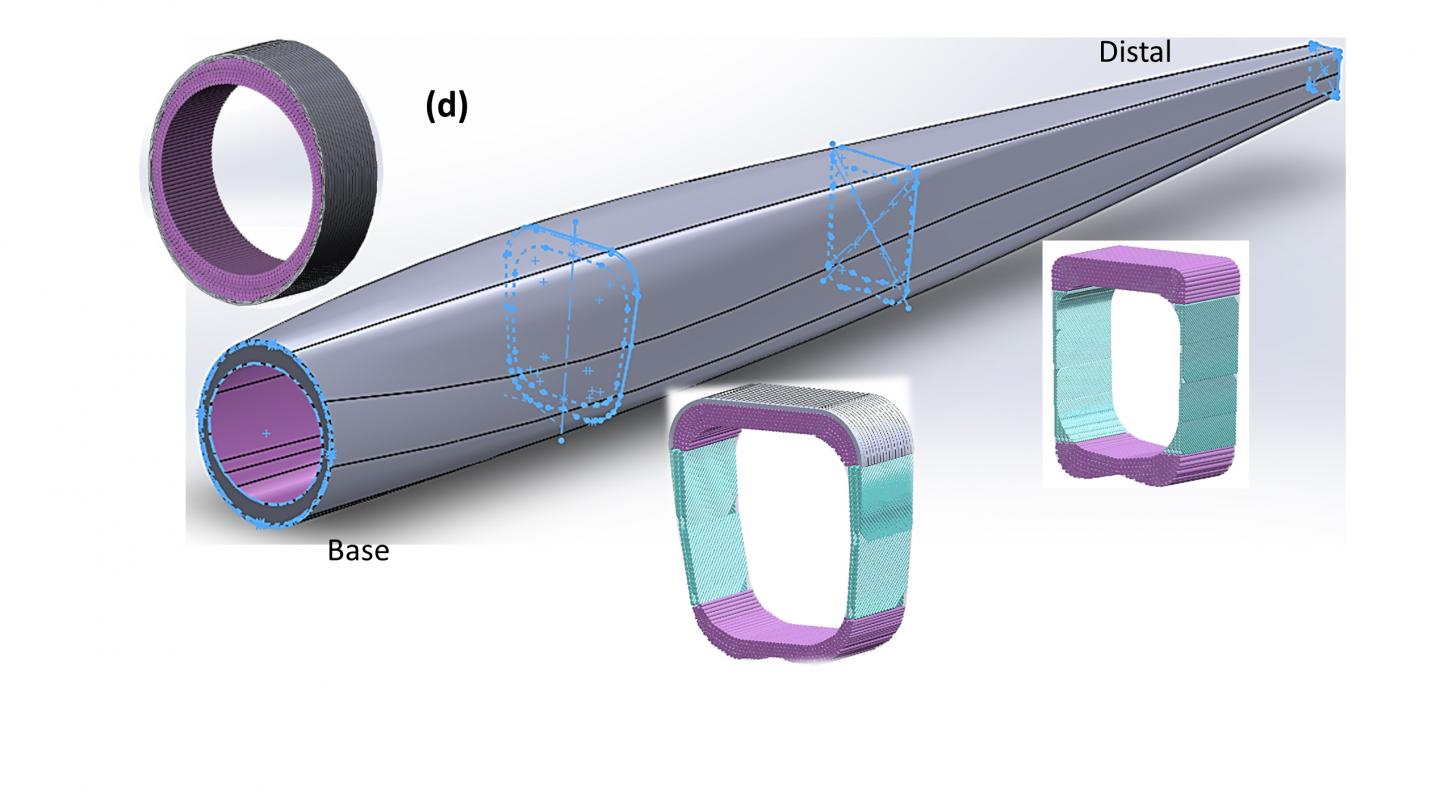
Researchers at the University of California San Diego for the first time have revealed why the shape of the feather shaft changes from round to square when it's put under stress in a paper published in recent issue of Advanced Science. Nature almost always favors roundness. Only under special circumstances does it opt for square shapes. Examples include the cells of plants — which derive their name from the square cells of monks. At a larger, structural level, there are a few rare examples: the seahorse tail, a vine found in the Amazon that has a square cross section, and the feather rachis.
In their study, using fundamental mechanics equations and experiments in modeling materials, researchers show that the square shape provides greater rigidity and higher resistance to ovalization and buckling than a hollow round shape of the same weight. "The most amazing thing is that this reflects textbook mechanics," said Marc Meyers, the paper's senior author and a professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at the Jacobs School of Engineering at UC San Diego. "And obviously, birds haven't studied that subject."
Ovalization can be observed by subjecting a drink straw to progressive bending: the section will gradually change from round to oval, and the stiffness is correspondingly decreased. But the feathers of flying birds, with a round-to-square sectional shape, retain their rigidity intact in spite of bending. By contrast, non-flight feathers, such as flightless ostrich wing feathers and peacock tail feathers, are not subjected to the same constraints and their shafts do not change from round to square. This is because a feather is a highly specialized appendage that enables birds to fly, generating thrust and lift. Its mechanical properties are optimized and weight minimized.
The feather-shaft cortex is a fibrous composite with varying fiber orientations along the length adjusting to local stress requirements: the increasing amount of axial fibers ensure sufficient flexural rigidity, while the crossed fibers provide reasonable flexibility and torsional rigidity.
The features revealed symbolize the unique adaptation of feathers for optimized stiffness and lightness, a natural structure inspiring for advanced engineering designs.
"Nature is indeed wondrous," said Bin Wang, the paper's lead author and a member of Meyers' research group. "And it is such a beauty to look at nature with human knowledge."
Wang and Meyers said that the findings could be used to build stronger, stiffer square foam-filled structures for lightweight vehicles, such as drones and other aircraft. They also said that the findings could be applied to other types of energy-efficient structures.
###
Media Contact
Ioana Patringenaru
[email protected]
858-822-0899
@UCSanDiego
http://www.ucsd.edu
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag