SUTD worked with an international team of researchers to develop glutathione fluorescent probes based on the discovery of Twisted Intramolecular Charge Shuttle (TICS)
Credit: SUTD
Charge transfer and separation is a fundamental process in the energy conversion that powers life on earth. Besides being used in solar cells and photocatalyst, this process is even in photosynthesis as it enables energy conversion by harvesting light and then transferring and converting into chemical energy.
However, deeper understanding of charge transfer and separation at a molecular level continues to be a challenge as this process is very quick – light absorption induced charge transfer and separation takes place over a few femtoseconds to a few picoseconds.
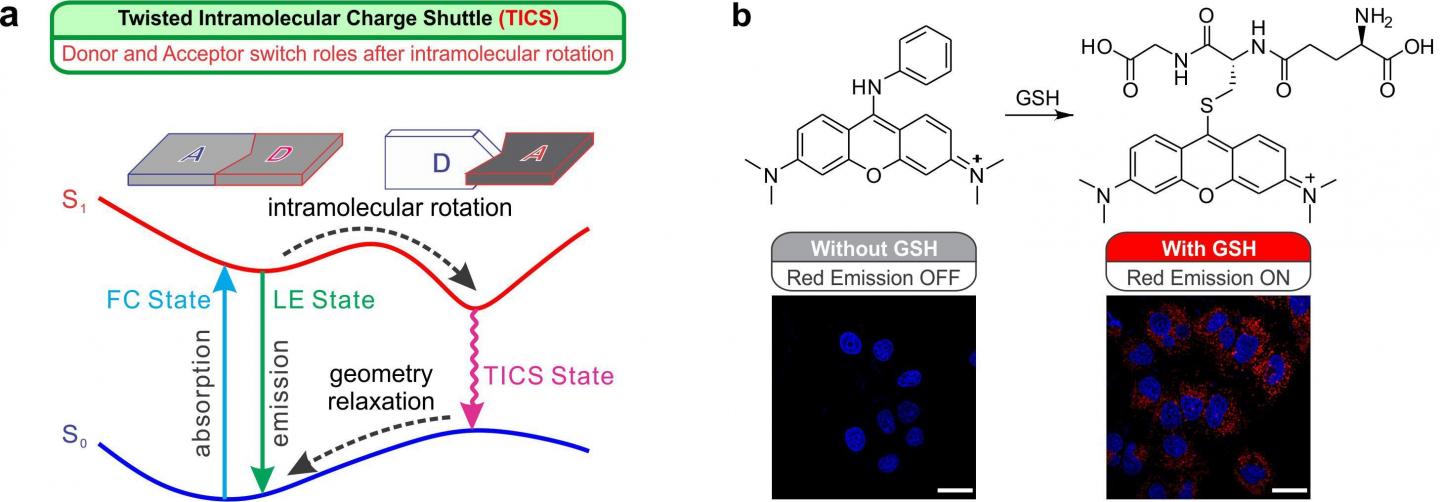
An international team of researchers from the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD), Chinese Academy of Science, Pohang University of Science and Technology and Vanderbilt University, overcame this challenge by using fluorescence in their model systems and studying the change in fluorescence output – intensity, lifetime and wavelength, etc – and discovered a new charge transfer and separation process, Twisted Intramolecular Charge Shuttle (TICS). In TICS molecules, the charge donor and acceptor fragments dynamically switch roles after absorbing light and experiencing a structural twisting, thus exhibit a ‘charge shuttle’ phenomenon.
TICS’ unique bidirectional, role switching process differentiates TICS from a similar process’ unidirectional charge transfer mechanism named the Twisted Intramolecular Charge Transfer (TICT). While TICT has facilitated the development of many functional materials and devices such as bright and photostable fluorophores, dark quenchers, viscosity sensors and polarity sensors, TICS paves a new avenue for chemists to construct unique and useful fluorescent probes in a wide range of chemical families of fluorophores.
For instance, the research team constructed TICS fluorescent probes which can be used to detect glutathione, an antioxidant found in plants and animals that is essential in removing many toxic chemicals in biological cells. Similarly, another type of specifically constructed TICS based probe would be able to detect phosgene, a colourless and highly toxic gas that was used as a chemical weapon agent during World War I, which could potentially be used in terrorist attacks.
SUTD’s Assistant Professor Liu Xiaogang explained how the research team developed TICS based glutathione fluorescent probes and their efforts to transform the dye chemistry from trial-and-error into molecular engineering.
“Research in this area of study has often been based on trial-and-error. At SUTD, where design is a key component in our research strategy, we made sure to take on a design-centric approach in our research process. We first analysed chemical big data and spotted a pattern between molecular structures and fluorescent properties. After understanding this TICS process, we then designed a probe to prove this concept,” said Assistant Professor Liu.
###
The paper, entitled ‘A Photoexcitation Induced Twisted Intramolecular Charge Shuttle (TICS)’, has been published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition, a leading journal in the area of general chemistry.
Media Contact
Jessica Sasayiah
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




