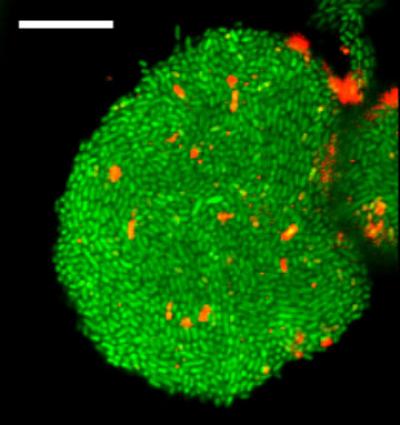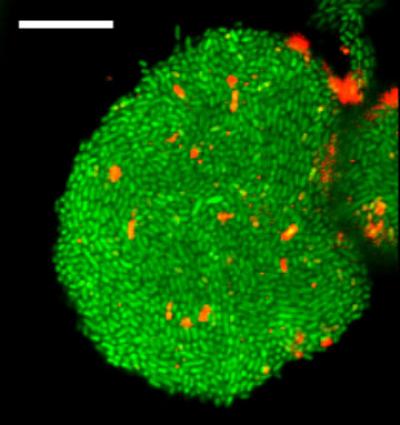
Credit: Levchenko Lab/Yale University
New Haven, Conn. – By severely curtailing the effects of antibiotics, the formation of organized communities of bacterial cells known as biofilms can be deadly during surgeries and in urinary tract infections. Yale researchers have just come a lot closer to understanding how these biofilms develop, and potentially how to stop them.
Biofilms form when bacterial cells gather and develop structures that bond them in a gooey substance. This glue can protect the cells from the outside world and allow them to form complex quasi-organisms. Biofilms can be found almost everywhere, including unwashed shower stalls or the surfaces of lakes. Because the protective shell can keep out potential treatments, biofilms are at their most dangerous when they invade human cells or form on sutures and catheters used in surgeries. In American hospitals alone, thousands of deaths are attributed to biofilm-related surgical site infections and urinary tract infections.
"Biofilms are a huge medical problem because they are something that makes bacterial infections very difficult to deal with," said Andre Levchenko, senior author of the study, which was published Oct. 5 in Nature Communications.
Fighting biofilms has been particularly difficult because it hasn't been well understood how bacteria cells make the transition from behaving individually to existing in collective structures. However, the researchers in the Levchenko lab, working with colleagues at the University of California-San Diego, recently found a key mechanism for biofilm formation that also provides a way to study this process in a controlled and reproducible way.
The investigators designed and built microfluidic devices and novel gels that housed uropathogenic E. coli cells, which are often the cause of urinary tract infections. These devices mimicked the environment inside human cells that host the invading bacteria during infections. The scientists found that the bacterial colonies would grow to the point where they would be squeezed by either the walls of the chamber, the fibers, or the gel. This self-generated stress was itself a trigger of the biofilm formation.
"This was very surprising, but we saw all the things you would expect from a biofilm," said Levchenko, the John C. Malone Professor of Biomedical Engineering and director of the Yale Systems Biology Institute. "The cells produced the biofilm components and suddenly became very antibiotic-resistant. And all of that was accompanied by an indication that the cells were under biological stress and the stress was coming from this mechanical interaction with the environment."
With this discovery, Levchenko said, researchers can use various devices that mimic other cellular environments and explore biofilm formation under countless environments and circumstances. They can also use the devices introduced in this study to produce biofilms rapidly, precisely, and in high numbers in a simple, inexpensive, and reproducible way. This would allow screening drugs that could potentially breach the protective layer of the biofilms and break it down.
"Having a disease model like this is a must when you want to do these kinds of drug-screening experiments," he said. "We can now grow biofilms in specific shapes and specific locations in a completely predictable way."
###
Media Contact
William Weir
[email protected]
203-432-0105
@yale
http://www.yale.edu