Credit: USTC
Ordered and variable animal behaviours emerge to explore and adapt to the environment. They are generally considered as the combination of a series of stereotyped motor primitives. However, how the nervous system shapes the dynamics of motor sequences remains to be solved.
In a study published in eLife, Prof. WEN Quan from School of Life Sciences, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has proposed the algorithms and circuit mechanisms for the robust and flexible motor states of nematodes during escape responses.
Prof. WEN’s group investigated nematode Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) on the neural circuit mechanisms of how robust and flexible the motor sequences are generated.
C. elegans are ideal subjects for their simple yet fully functional neural system with only 302 neurons, approximately 6400 chemical synapses and 890 electrical synapses. Early in the 1980s, the coupling image of neural networks were reconstituted at the synapse scale by the electron microscope, laying a solid foundation for the research on the neural circuit. Besides, optical manipulation and detection are easily conducted considering C. elegans’ overall transparent bodies.
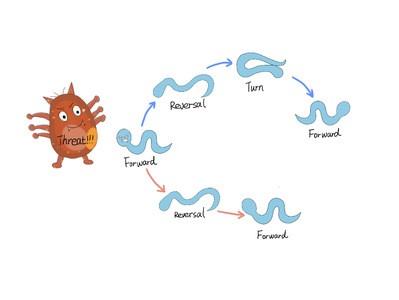
Potential threats like mechanical or thermal stimuli robustly trigger escape responses comprised of stereotyped motor modules including forward movement, backward movement and turning movement. However, the sequence and timing of actions of every module vary from each other.
With the help of optogenetic technology, calcium image and computational models, the researchers discovered that the excitatory feedforward coupling accounts for certain motor sequences robustly triggered by stimuli, while a winner-take-all operation via mutual inhibition between motor modules realizes the flexible alteration of different motor patterns. Also, the plasticity of short-term synapses and the intrinsic noise of the nervous system play an important role in the sequence and timing of motor patterns.
Applying the coupling image of neural networks of C. elegans and molecular biological methods, the researchers further proved that electrical synapses contribute to feedforward coupling, whereas glutamatergic synapses contribute to inhibition between modules through glutamate-gated chloride expressed by downstream neurons.
The study opens more possibilities to understand the mechanisms of motor manipulation of advanced organisms, and sheds new light on the design of the next generation of brain-inspired intelligence.
###
Media Contact
Jane FAN Qiong
[email protected]
Original Source
http://english.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




