Random Telegraph Noise (RTN), a type of unwanted electronic noise, has long been a nuisance in electronic systems, causing fluctuations and errors in signal processing. However, a team of researchers from the Center for Integrated Nanostructure Physics within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), South Korea has made an intriguing breakthrough that can potentially harness these fluctuations in semiconductors. Led by Professor LEE Young Hee, the team reported that magnetic fluctuations and their gigantic RTN signals can be generated in a vdW-layered semiconductor by introducing vanadium in tungsten diselenide (V-WSe2) as a minute magnetic dopant.
Credit: Institute for Basic Science
Random Telegraph Noise (RTN), a type of unwanted electronic noise, has long been a nuisance in electronic systems, causing fluctuations and errors in signal processing. However, a team of researchers from the Center for Integrated Nanostructure Physics within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), South Korea has made an intriguing breakthrough that can potentially harness these fluctuations in semiconductors. Led by Professor LEE Young Hee, the team reported that magnetic fluctuations and their gigantic RTN signals can be generated in a vdW-layered semiconductor by introducing vanadium in tungsten diselenide (V-WSe2) as a minute magnetic dopant.
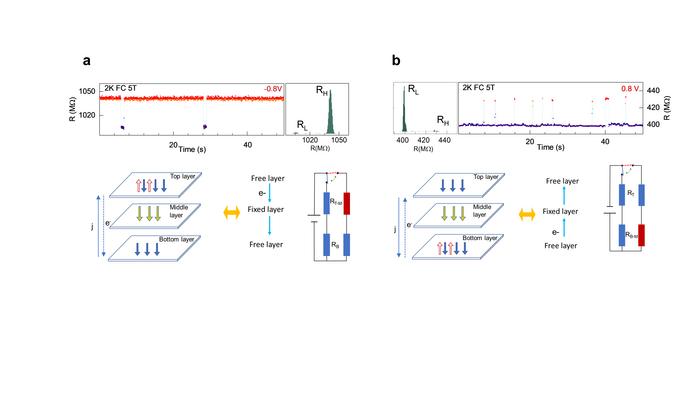
High contact resistance in lateral devices usually limits the manifestation of inherent quantum states and further degrades the device’s performance. To overcome these limitations, the researchers introduced a vertical magnetic tunneling junction device by sandwiching a few layers of V-WSe2, a magnetic material, between the top and bottom graphene electrodes. This device was able to manifest inherent quantum states such as magnetic fluctuations and achieve high-amplitude RTN signals, even with a small vanadium doping concentration of just ~0.2%.
Dr. Lan-Anh T. NGUYEN, the first author of the study said, “The key to success is to realize large magnetic fluctuations in resistance by constructing vertical magnetic tunneling junction devices with low contact resistance.”
Through the resistance measurement experiments using these devices, the researchers observed RTNs with a high amplitude of up to 80% between well-defined two-stable states. In the bistable state, the magnetic fluctuations in resistance prevail with temperature through the competition between intralayer and interlayer coupling among the magnetic domains. They were able to identify this bistable magnetic state through discrete Gaussian peaks in the RTN histogram with distinctive features in the noise power spectrum.
Most importantly the researchers discovered the ability to switch the bistable magnetic state and the cut-off frequency of the RTN simply by changing the voltage polarity. This exciting discovery paves the way for the application of 1/f2 noise spectroscopy in magnetic semiconductors and offers magnetic switching capability in spintronics.
“This is a first step to observe the bistable magnetic state from large resistance fluctuations in magnetic semiconductors and offers the magnetic switching capability with 1/f2 noises by means of simple voltage polarity in spintronics”, explained Professor Lee.
This work was done through interdisciplinary research in collaboration with JOO Min-Kyu at Sookmyung Women’s University and KIM Philip at Harvard University.
Journal
Nature Electronics
DOI
10.1038/s41928-023-01002-1
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Electrically tunable magnetic fluctuations in multilayered vanadium-doped tungsten diselenide
Article Publication Date
10-Aug-2023




