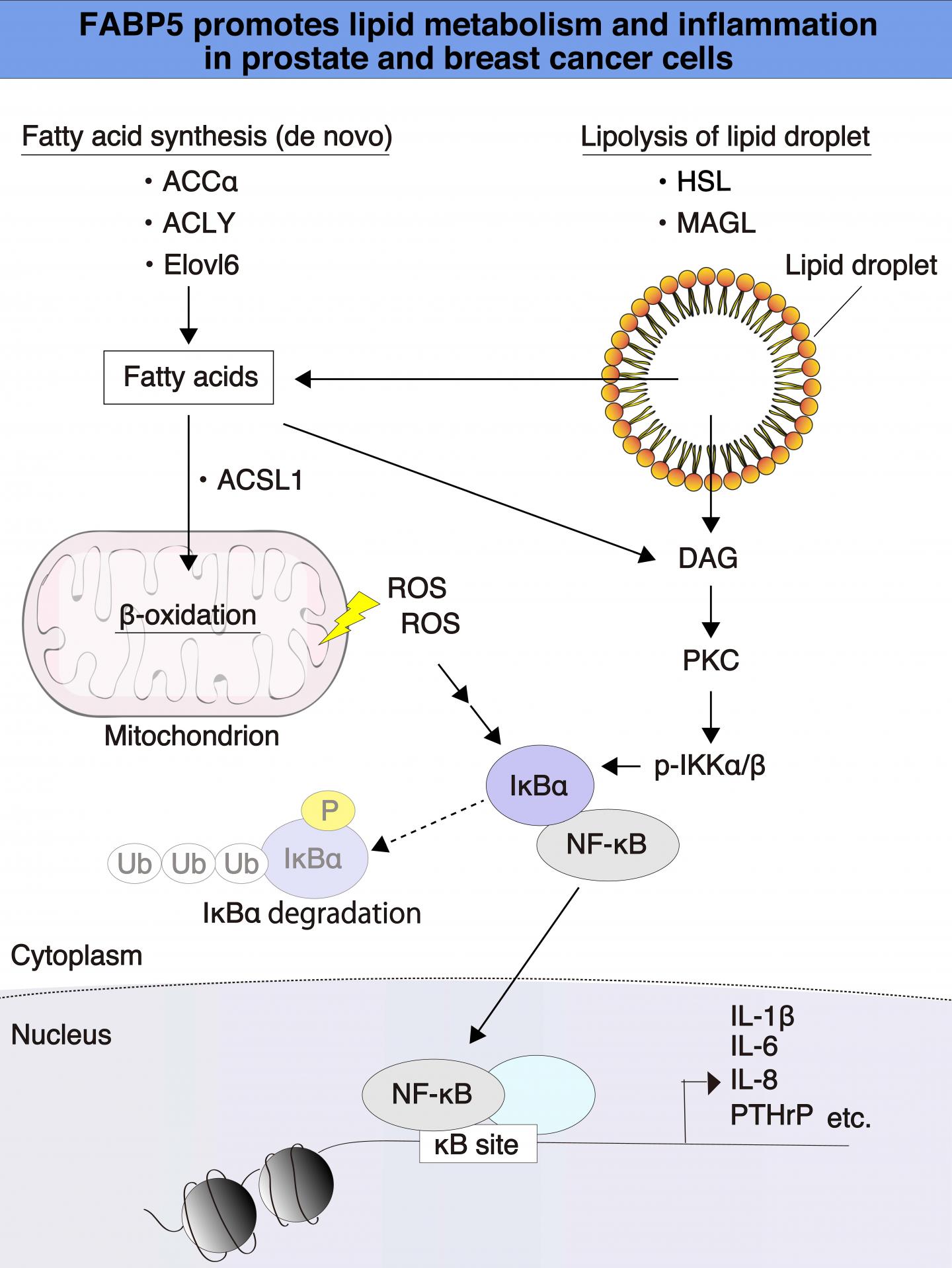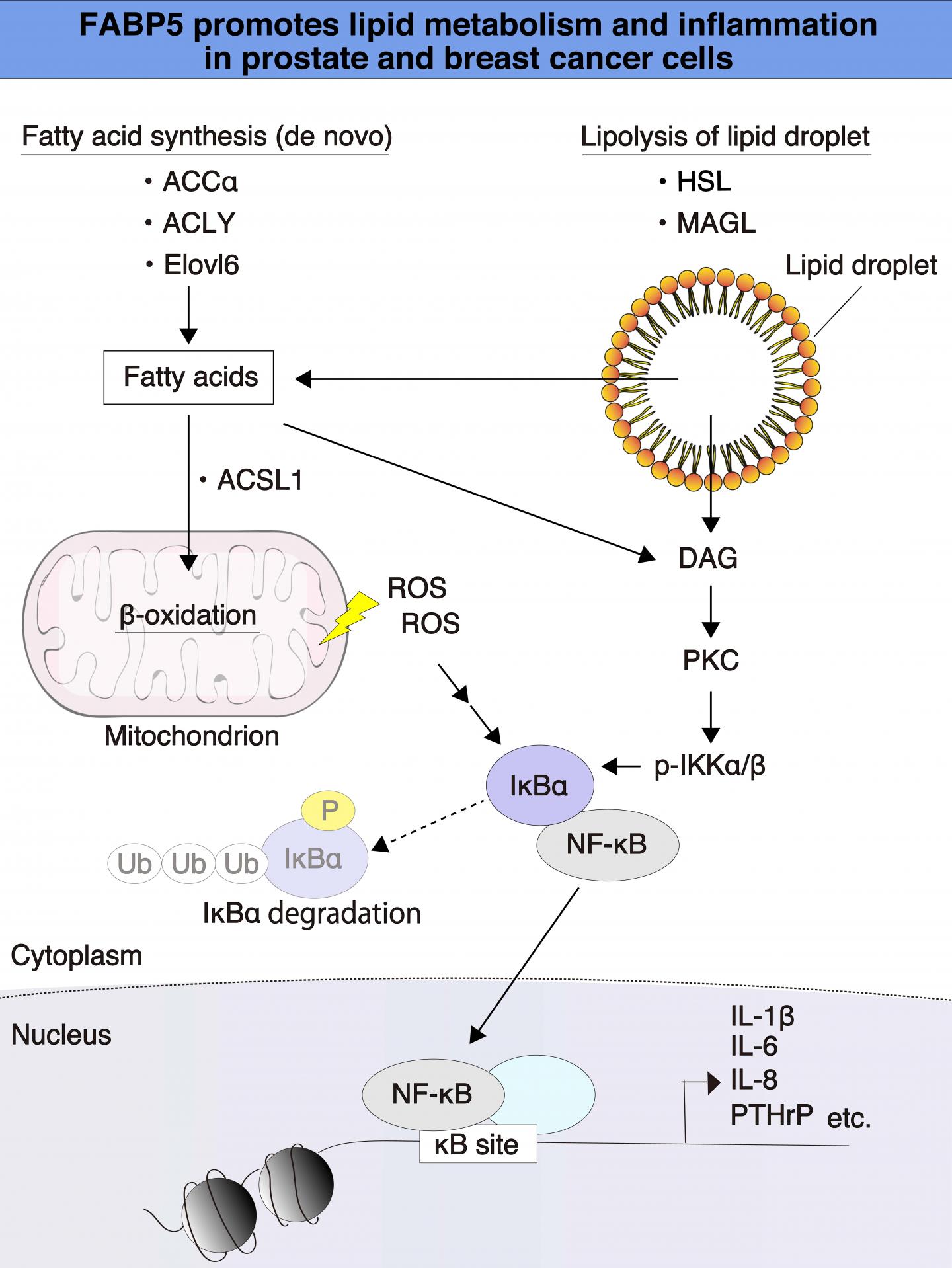
Credit: Hiroshi Fujii Ph.D., the Institute for Biomedical Sciences, Shinshu University
Japanese researchers have revealed for the first time that a specific protein plays a critical role in the development and metastasis of highly aggressive prostate and breast cancer cells.
The study reports that large amounts of the fatty acid-binding protein 5 (FABP5), a kind of transport protein for fatty acids, promotes processes associated with cancer aggressiveness such as cell growth, invasiveness, survival and inflammation in prostate and breast cancer cells. The researchers point out that a better understanding of the molecular pathways of specific cancers is a step in the direction of finding more effective therapeutic targets.
Altered fatty acid metabolism is thought to be a hallmark of cancer. It is known that cancer cells exhibit significantly increased demands for energy, mass, and large molecules to keep multiplying and spreading as part of their metastatic behavior. It has also recently been revealed that alterations of lipid metabolism play pivotal roles in cancer development and metastasis. Furthermore, although cancer cells with high levels of lipid droplets (LDs) are more resistant to chemotherapy, the molecular mechanisms behind this remain unclear. Therefore, it is very important to identify the critical genes involved in metabolic reprogramming and regulation of LDs formation during carcinogenesis to develop novel diagnostic tools and treatments for cancers.
Professor Hiroshi Fujii, Vice-Director of the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Shinshu University and the project lead, adds that he and his team have "demonstrated that there is a specific pathway behind FABP5 inflammation as well as production of immune substances in specific cancer cells. Therefore, FABP5 could be expected to be a target for development of therapeutic reagents and/or a biomarker for prostate and breast cancers in the future."
The process of lipid metabolism includes events such as lipogenesis, lipid storage as well as degradation. Any irregularities in lipid metabolism in cancer cells are frequently detected and used as an indicator for tumor malignancy. Fatty acids, in particular, are involved in several aspects of the formation of tumors.
The research team used several methods to reveal how FABP5 expression levels affect the genes that are involved in crucial processes of aggressive prostate and breast cancer cells.
The authors also add that, "Understanding the alterations of lipid metabolism in cancer cells has important implications for exploring a new therapeutic strategy for treatment of cancer. For example, cholesterol ester and fatty acids (FAs) are required as an energy source and for production of cellular signaling molecules and the formation of membrane components during cancer cell proliferation and metastasis."
The study was published in BBA – Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids in June 2018. The researchers used standard molecular biology methods to obtain their results and show that certain genes are upregulated (or "turned on") by FABP5 expression. These genes are changed in several crucial processes during multiplication and division of aggressive cancer cells.
The authors state that while in the current study they have revealed that FABP5 might regulate lipid quality and/or quantity, but that the details of molecular mechanisms of metabolic reprogramming of lipids mediated by FABP5 are yet to be fully understood.
Professor Fujii adds that, "Studies on analyses of lipid droplet contents should be needed to reveal alterations of lipid profiling induced by FABP5 in cancer cells in the future."
###
About Shinshu University
Shinshu University is a national university in Japan founded in 1949 and working on providing solutions for building a sustainable society through interdisciplinary research fields: material science (carbon nanotubes, fiber, composites), biomedical science (for intractable diseases, preventive medicine), and mountain science. We aim to boost research and innovation capability through collaborative projects with distinguished researchers from the world. For more information, please see: http://www.shinshu-u.ac.jp/english/
Media Contact
Nobuko Imanishi
[email protected]
81-263-372-097
http://www.shinshu-u.ac.jp/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2018.06.010