SUTD collaborates with NTU to provide in-depth analysis of 3D in vitro biomimetic skeletal muscle tissue models, highlighting the great potential of bioprinting technology.
Credit: SUTD
Skeletal muscle can be functionally compromised by genetic myopathies, aging, traumatic injuries and tumor ablation. Under some conditions, such as severe traumatic injuries and volumetric muscle loss, the regeneration process is significantly hindered by fibrous scar tissue formation and therefore causing muscle dysfunction.
Even though numerous bioengineering approaches have been explored to construct in vitro skeletal muscle tissues, an in vitro model that is capable of restoring mature muscle, vasculature, and extracellular matrix composition to the damaged tissue has yet to be achieved. Meanwhile, it was found that by incorporating the exogenous factors such as physical, chemical, and electrical cues, tissue engineering scaffolds have achieved remarkable progress in skeletal muscle regeneration.
Researchers from the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) and their research collaborators from the Nanyang Technological University (NTU) developed insightful analyses of these in vitro skeletal muscle tissue models. They also reviewed the state-of-the-art status of these bioengineering approaches in mimicking skeletal muscle tissues. Their paper ‘Bioprinting of 3D in vitro skeletal muscle models: A review’ was published in Materials & Design.
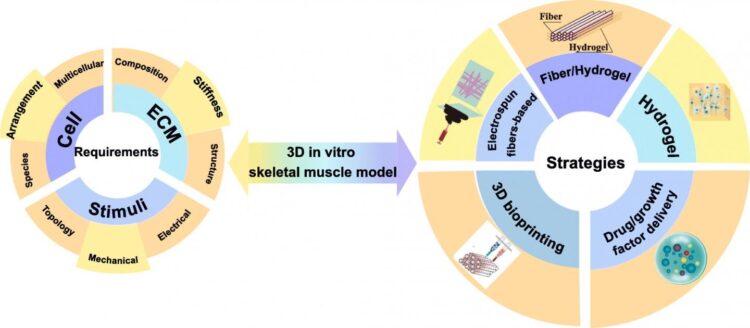
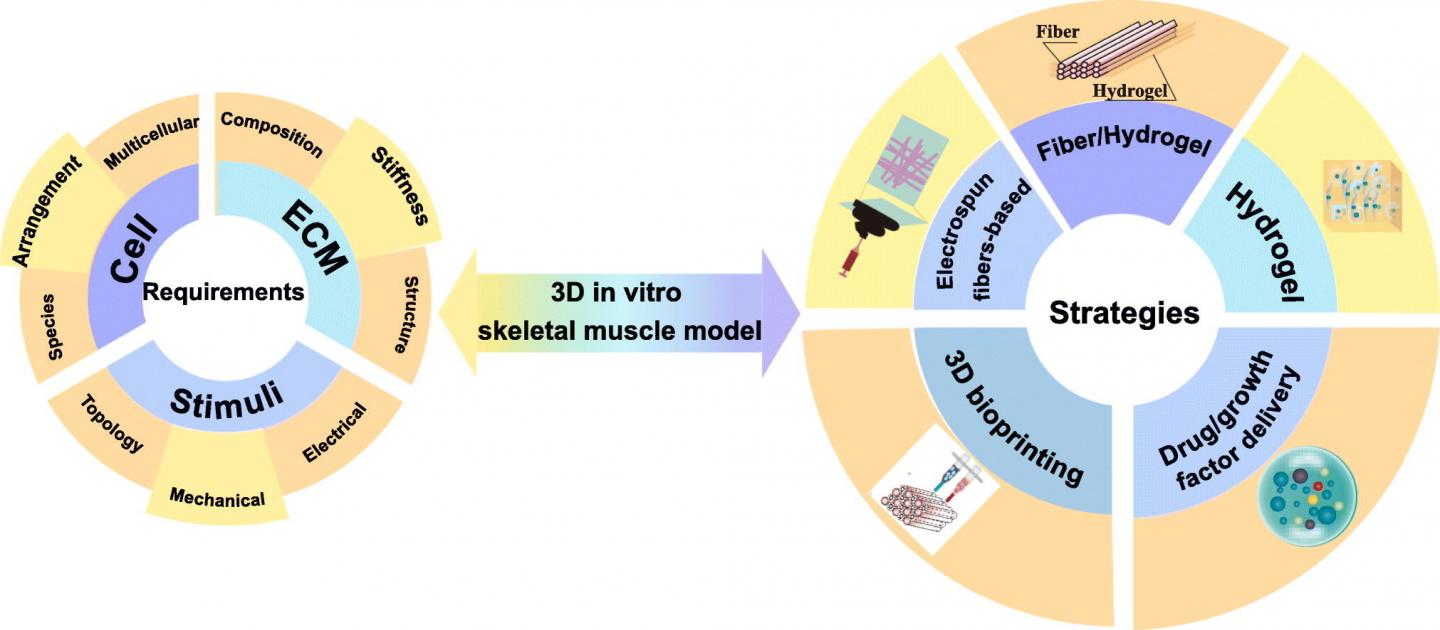
An in-depth analysis of the design considerations related to skeletal muscle models was also presented and various influential parameters including matrix, cells and structures that are associated with myogenesis were discussed. In addition, effects of topological, mechanical, and electrical stimuli were addressed to provide a deeper understanding of the myogenesis. Major bioengineering strategies including electrospinning, hydrogel-based, fiber/hydrogel based, drug delivery and bioprinting have been comprehensively reviewed and compared (refer to image).
The review paper also notes that despite great strides taken in this field, there are still challenges ahead for replicating the native muscle. Besides materials and the multicellular environment, issues such as how to achieve the proper innervation and vascularization have to be addressed in order to rebuild a fully functional muscle.
However, collaborative research efforts in areas such as microfluidic technology, spheroids, programmed control release and electrospinning will pave the way in realizing the full potential of bioprinting.
“In recent years, with bioprinted skeletal muscle demonstrating great flexibility in constructing functional tissue models, almost every organ of the human body can be bioprinted. While our review paper seeks to maximize the potential in 3D skeletal muscle tissue models, we expect our work to also inspire deeper research in eventually replicating native muscle,” said principal investigator Prof Chua Chee Kai from SUTD.
###
Media Contact
Jessica Sasayiah
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.