Credit: IOZ
The red panda (Ailurus fulgens) is an endangered mammal endemic to the Himalaya and Hengduan Mountains, and its distribution spans China, Myanmar, Bhutan, India and Nepal. Prior to 1902, all red pandas were classified as one species. However, in 1902, scientists established two subspecies, based on their morphological differences: the Himalayan subspecies (A. f. fulgens) and the Chinese subspecies (A. f. styani).
More recent research on their morphological differences and geographical distribution, however, led the taxonomist Colin Groves to reclassify the two subspecies as two distinct species: the Himalayan red panda (A. fulgens) and the Chinese red panda (A. styani). Despite this change, the evolutionary histories of Himalayan and Chinese red pandas have remained unclear and controversy has persisted about whether they should be classified as two distinct species or not.
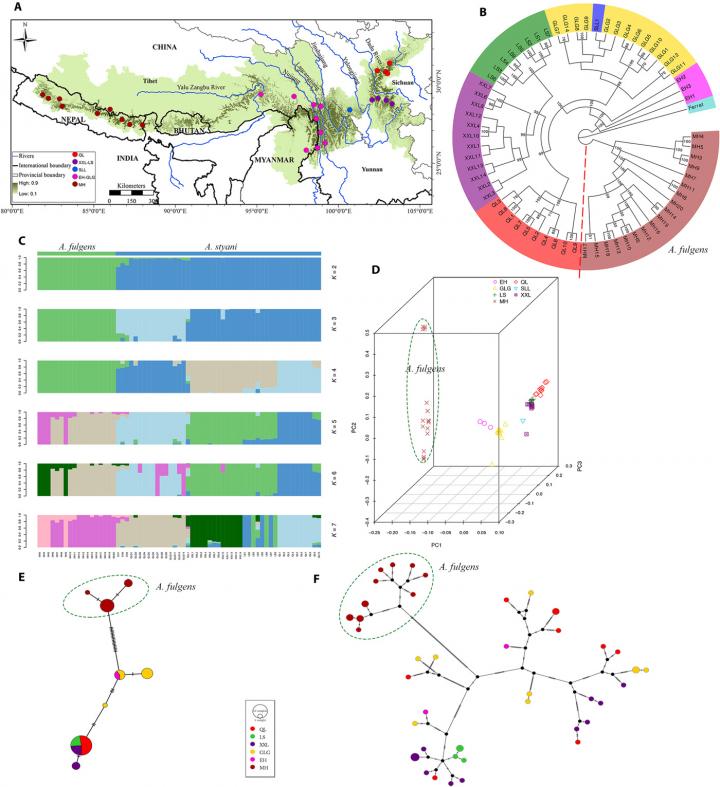
In order to help clarify these questions, a research team led by Prof. WEI Fuwen from the Institute of Zoology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, used population genomics methods to analyze the genome resequencing data of 65 wild red pandas (including both Himalayan and Chinese red pandas) from seven geographical populations; mitochondrial genomes of 49 red pandas; and Y chromosome single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) data from 49 male individuals.
All results from these three types of markers found substantial genetic divergence between the two species, and no sharing was found for the haplotypes of mitochondrial genome and Y chromosome SNPs.
These findings clearly support Groves’ classification of red pandas into two phylogenetic species. Further analysis also found that the Yalu Zangbu River, rather than the Nujiang River, is most likely the geographical boundary between the two species. This explains previous observations that the discriminating morphological characteristics were inconsistent with their geographical distributions.
Furthermore, the research team reconstructed the demographic and divergence histories of the two species based on the genome resequencing data. The results revealed clearly different demographic histories for the two species: The Chinese red panda had experienced two population bottlenecks and one large population expansion, whereas the Himalayan red panda had experienced three bottlenecks and one very small expansion. These two species started to diverge after the serious population bottleneck caused by the Penultimate Glaciation (0.3 to 0.13 Mya).
In contrast to the Chinese red panda, the Himalayan red panda has less genetic diversity, higher linkage disequilibrium and a higher genetic load, thus highlighting the urgency of protecting this endangered species. These findings have important conservation implications for wild red panda conservation, pedigree construction and interbreeding avoidance for captive red pandas.
###
The study, entitled “Genomic evidence for two phylogenetic species and long-term population bottlenecks in red pandas,” was published online in Science Advances on Feb. 27.
This study was supported by the grants from Chinese Academy of Sciences, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China, and etc.
Media Contact
HU Yibo
[email protected]
Original Source
http://english.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




