Credit: IST Austria
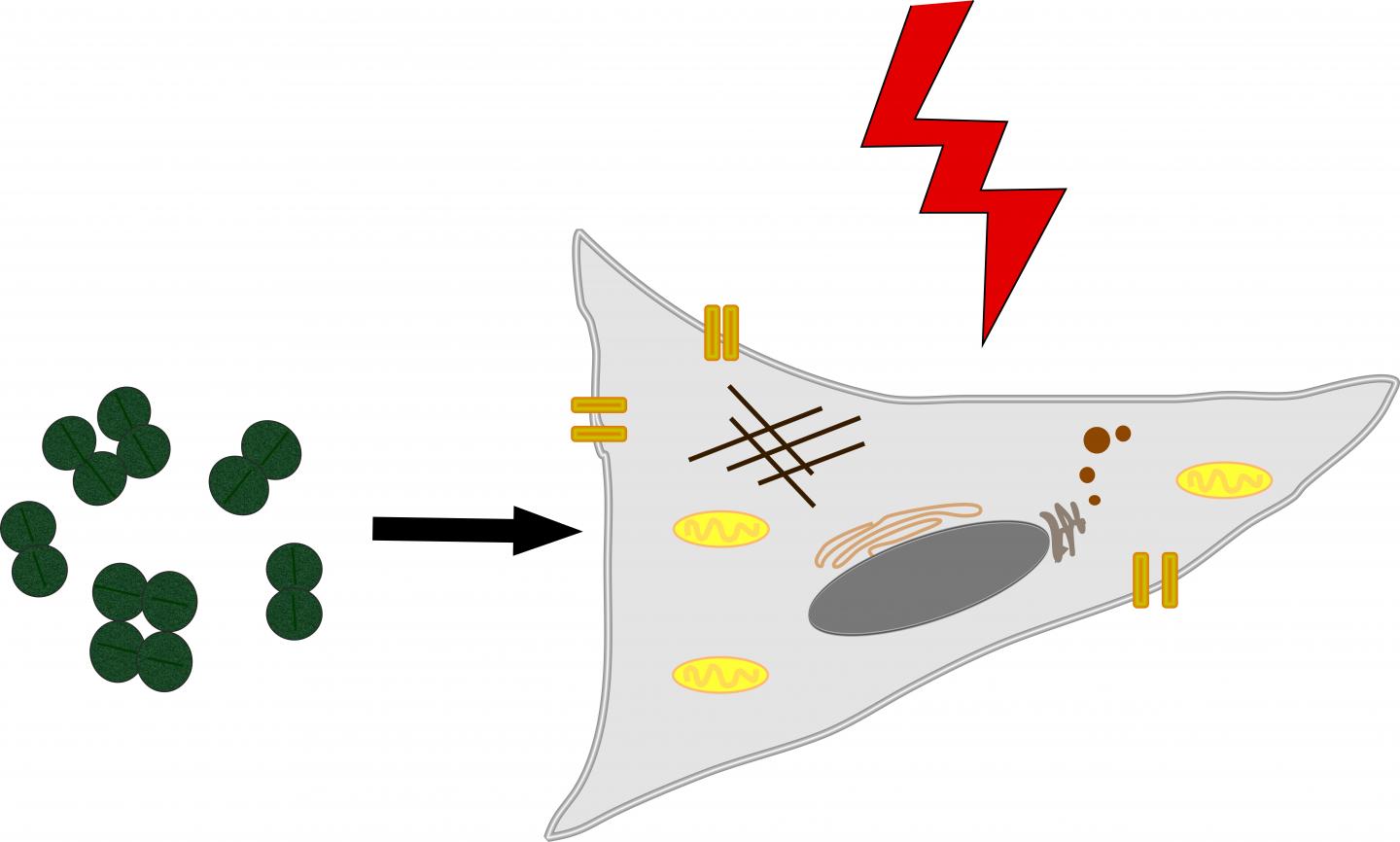
Compared with the blue light mostly used in current approaches, red light has major benefits, particularly with respect to applications in model systems for diseases. Red light can penetrate deep tissues and can be employed without surgery in a non-invasive way; it has minimal cytotoxicity for human and animal tissues and has no effects on fluorescent proteins. Often used for various applications in research labs, florescent proteins tend to be activated or bleached by blue light. Although red light has so many advantages over blue light, there are very few red light-based optogenetic tools currently available.
For the light-sensitive protein, IST Austria Professor Harald Janovjak and his research group chose a photoreceptor which can be activated by red light. This photoreceptor was found in the cyanobacterium Synechocystos which was already first described in 1968. In their study the authors modified the receptor and fused it with a mammalian receptor, which has been found significant for many diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer, Parkinson and diabetes. Later, they successfully demonstrated in experiments that the red-light activation of the fused receptor could activate a signal pathway that plays a crucial role in cell division.
As a rule, cell division is activated by so-called growth factors. They are the reason why two receptors undergo a binding and activation process, marking the start of cell division. The researchers managed to induce the binding and activation process by combining the receptors and using red light. Additionally, they showed that the fused receptor could be activated by red light even across tissue in cells which are used in model studies for diabetes.
Harald Janovjak and his co-authors, including PhD student Eva Reichhart, expect huge improvements in future research: "Specific receptors are less active or numerically limited in such diseases as Alzheimer, Parkinson, and diabetes. In the future, scientists might develop an approach based on gene therapy that could restore the normal signal pathways by using fused receptors — without recourse to surgery."
###
Media Contact
Stefan Bernhardt
[email protected]
@Istaustria
http://Www.ist.ac.at