Credit: ©Science China Press
Incoherent photonic generation and processing of microwave signals avoid cumbersome and costly pulsed lasers by using an incoherent broadband light source. This methodology has attracted great interest for a wide range of important applications, such as implementation of microwave photonics filter, arbitrary waveform generation and Fourier transformation. The main limitation of a conventional incoherent photonic signal processing technique is the extremely low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the output signal. The low SNR is a result of the spontaneous emission of a purely incoherent light source such as amplified spontaneous emission (ASE). Therefore, signal manipulation and measurement cannot be achieved in a single shot using a conventional incoherent-light microwave signal processing system. Thousands of times average is typically required to mitigate the white noise that is intrinsically present at the output of an incoherent microwave signal processing system, restricting application of the system to processing periodically repeating signals.
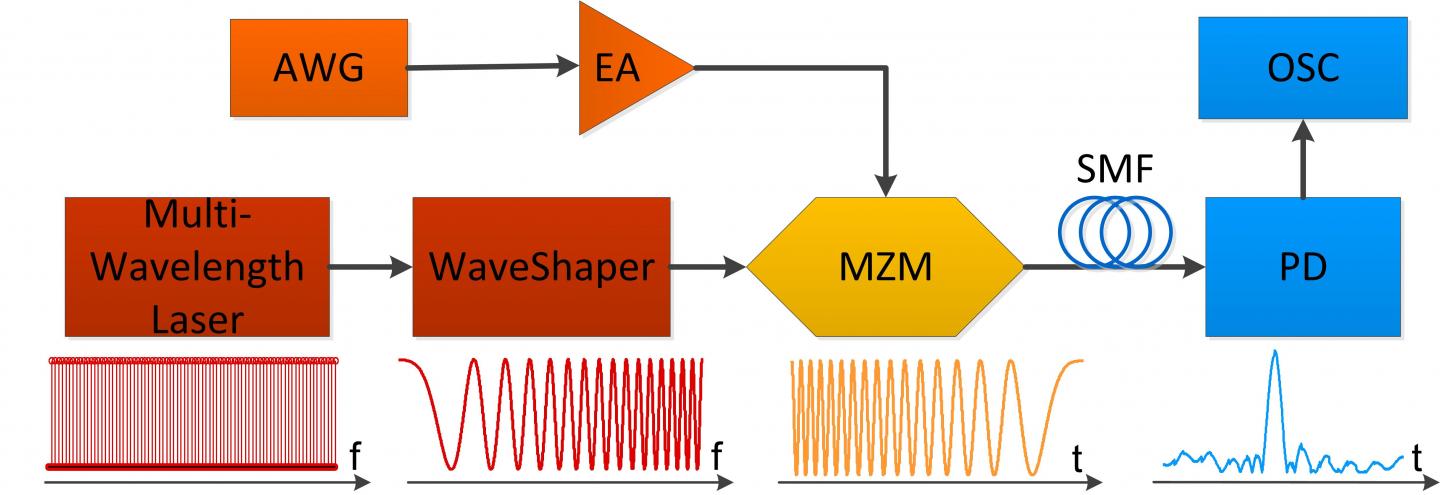
Recently, Prof. Ming Li and his research team in Institute of Semiconductor, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Institut National de la Recherche Scientifique-Énergie, Matériaux et Télécommunications (Canada) report a reconfigurable and single-shot incoherent optical signal processing system for chirped microwave signal compression. In the proposed scheme, they use a multi-wavelength laser (MWL) as the incoherent light source, rather than a continuous spectrum. Due to the use of the MWL, the SNR of the output signal gets improved significantly such that operation in a single-shot is possible. Moreover, the design enables realization of a fiber-based microwave dispersive line with an extremely large chromatic dispersion (i.e., a few ns2, equivalent to several thousand kilometers of conventional single-mode fiber). Such an accomplishment is achieved using a design called time-spectrum convolution (TSC) system. The effective dispersion of microwave signal through this TSC system is orders of magnitude higher than the actual physical optical dispersion used in the system. Furthermore, the induced dispersion on the microwave signal is tunable by adjusting the programmable optical filter or by changing the optical dispersive medium, such that the proposed scheme is fully reconfigurable. Different chirped microwave signals with GHz-bandwidth are successfully compressed and the robustness of the proposed system when input RF signals are largely distorted is also discussed.
###
Reference
Ming Li , Shuqian Sun, Antonio Malacarne, Sophie LaRochelle, Jianping Yao, Ninghua Zhu, Jose Azana. Reconfigurable single-shot incoherent optical signal processing system for chirped microwave signal compression. Science Bulletin, 2017, 62(4):242-248
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2095927317300397
Science China Press
http://www.scichina.com/
Media Contact
Ming Li
[email protected]
http://zh.scichina.com/english/
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag