This method exposes fake images created by computer algorithms rather than by humans
Credit: © RUB, Lehrstuhl für Systemsicherheit
They look deceptively real, but they are made by computers: so-called deep-fake images are generated by machine learning algorithms, and humans are pretty much unable to distinguish them from real photos. Researchers at the Horst Görtz Institute for IT Security at Ruhr-Universität Bochum and the Cluster of Excellence “Cyber Security in the Age of Large-Scale Adversaries” (Casa) have developed a new method for efficiently identifying deep-fake images. To this end, they analyse the objects in the frequency domain, an established signal processing technique.
The team presented their work at the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) on 15 July 2020, one of the leading conferences in the field of machine learning. Additionally, the researchers make their code freely available online at https:/
Interaction of two algorithms results in new images
Deep-fake images – a portmanteau word from “deep learning” for machine learning and “fake” – are generated with the help of computer models, so-called Generative Adversarial Networks, GANs for short. Two algorithms work together in these networks: the first algorithm creates random images based on certain input data. The second algorithm needs to decide whether the image is a fake or not. If the image is found to be a fake, the second algorithm gives the first algorithm the command to revise the image – until it no longer recognises it as a fake.
In recent years, this technique has helped make deep-fake images more and more authentic. On the website http://www.
For their analysis, the Bochum-based researchers used the data sets that also form the basis of the above-mentioned page “Which face is real”. In this interdisciplinary project, Joel Frank, Thorsten Eisenhofer and Professor Thorsten Holz from the Chair for Systems Security cooperated with Professor Asja Fischer from the Chair of Machine Learning as well as Lea Schönherr and Professor Dorothea Kolossa from the Chair of Digital Signal Processing.
Frequency analysis reveals typical artefacts
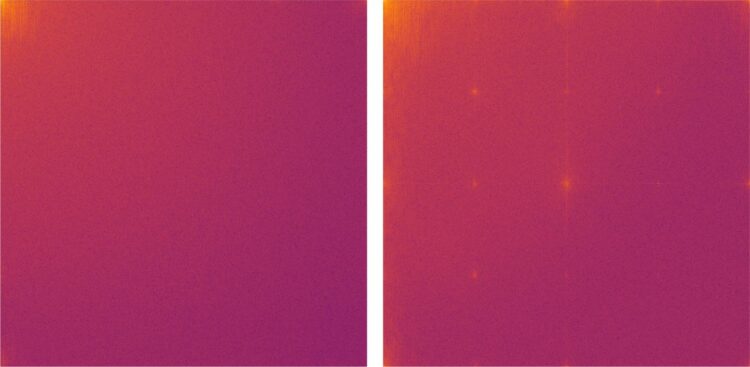
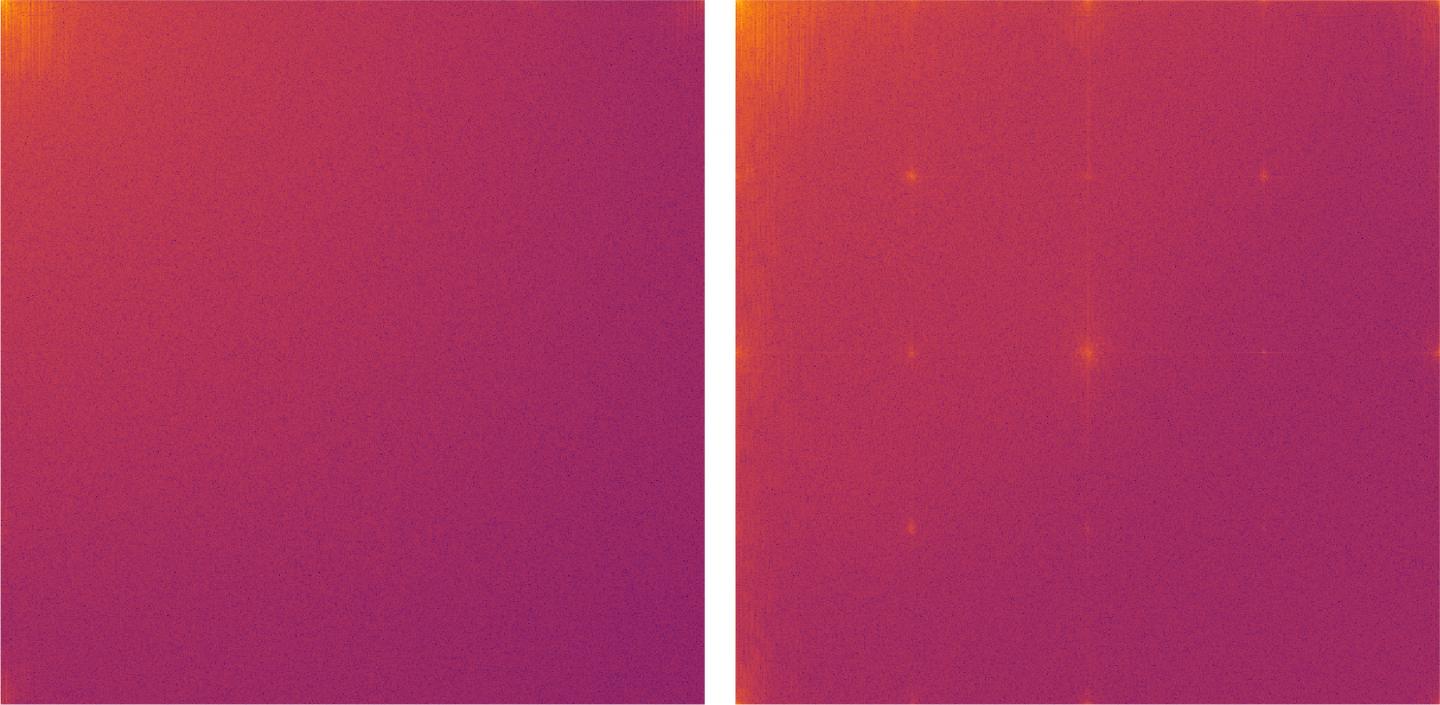
To date, deep-fake images have been analysed using complex statistical methods. The Bochum group chose a different approach by converting the images into the frequency domain using the discrete cosine transform. The generated image is thus expressed as the sum of many different cosine functions. Natural images consist mainly of low-frequency functions.
The analysis has shown that images generated by GANs exhibit artefacts in the high-frequency range. For example, a typical grid structure emerges in the frequency representation of fake images. “Our experiments showed that these artefacts do not only occur in GAN generated images. They are a structural problem of all deep learning algorithms,” explains Joel Frank from the Chair for Systems Security. “We assume that the artefacts described in our study will always tell us whether the image is a deep-fake image created by machine learning,” adds Frank. “Frequency analysis is therefore an effective way to automatically recognise computer-generated images.”
###
Media Contact
Joel Frank
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/