Credit: Mustafar et al., eNeuro (2018)
Rats take a fundamentally different approach toward solving a simple visual discrimination task than tree shrews, monkeys, and humans, according to a comparative study of the four mammal species published in eNeuro. The work could have important implications for the translation of research in animal models to humans.
Scientists have developed powerful technologies that allow for precise manipulation of the rodent nervous system, which is similar to that of humans, making them crucial laboratory animals in neuroscience. Although it is thought that learning in mice and rats can overcome initial species differences on a task, few studies have directly tested this idea.
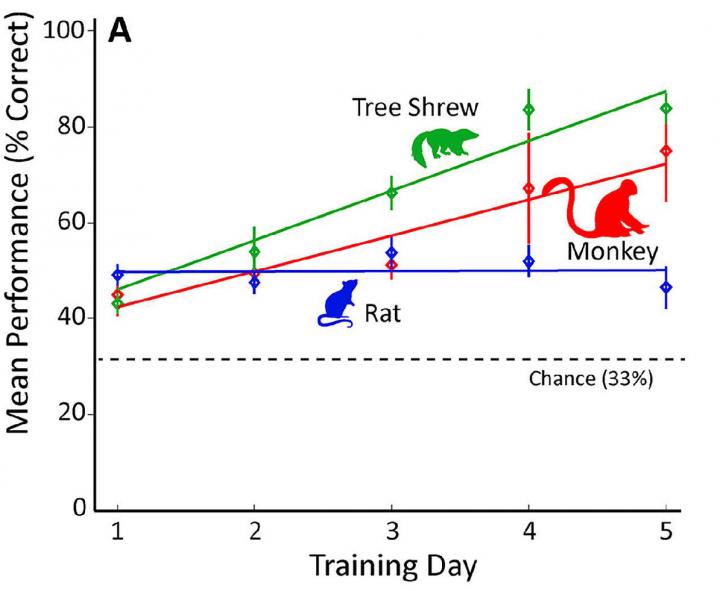
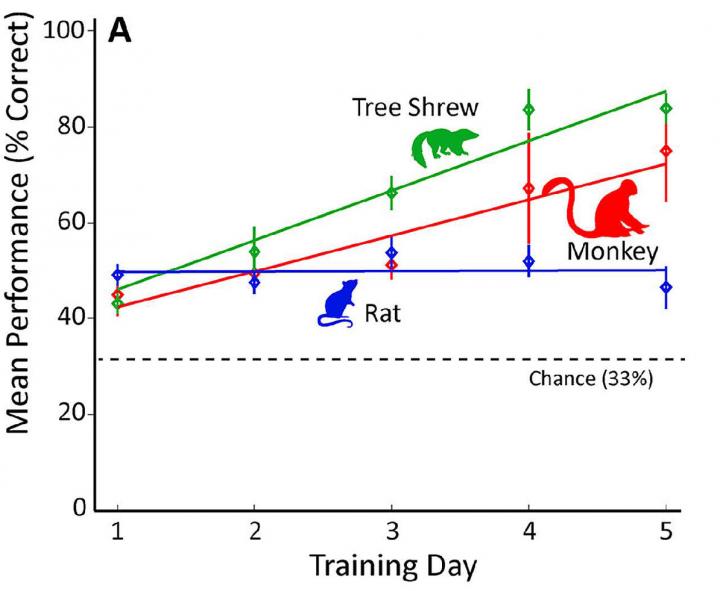
Gregor Rainer and colleagues addressed this gap in knowledge by comparing the ability of two species more closely related to humans — macaques (Macaca fascicularis) and tree shrews (Tupaia belangeri) — to discriminate a flickering light from two distracting stimuli. While the macaques and tree shrews used similar visual learning strategies and their performance improved over time, rats (Rattus norvegicus) were instead focused on where they had previously received a food reward and their performance did not improve. These findings suggest that rats use their brains differently than the other species in the context of this particular task.
###
Article: Divergent solutions to visual problem solving across mammalian species
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0167-18.2018
Corresponding author: Gregor Rainer (University of Fribourg, Switzerland), [email protected]
About eNeuro
eNeuro, the Society for Neuroscience's open-access journal launched in 2014, publishes rigorous neuroscience research with double-blind peer review that masks the identity of both the authors and reviewers, minimizing the potential for implicit biases. eNeuro is distinguished by a broader scope and balanced perspective achieved by publishing negative results, failure to replicate or replication studies. New research, computational neuroscience, theories and methods are also published.
About The Society for Neuroscience
The Society for Neuroscience is the world's largest organization of scientists and physicians devoted to understanding the brain and nervous system. The nonprofit organization, founded in 1969, now has nearly 37,000 members in more than 90 countries and over 130 chapters worldwide.
Media Contact
David Barnstone
[email protected]
202-962-4000
@SfNJournals
http://www.sfn.org
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0167-18.2018