Credit: © University of Vienna, created by Thomas Rögelsperger
A novel material that consists of a single sheet of carbon atoms could lead to new designs for optical quantum computers. Physicists from the University of Vienna and the Institute of Photonic Sciences in Barcelona have shown that tailored graphene structures enable single photons to interact with each other. The proposed new architecture for quantum computer is published in the recent issue of npj Quantum Information.
Photons barely interact with the environment, making them a leading candidate for storing and transmitting quantum information. This same feature makes it especially difficult to manipulate information that is encoded in photons. In order to build a photonic quantum computer, one photon must change the state of a second. Such a device is called a quantum logic gate, and millions of logic gates will be needed to build a quantum computer. One way to achieve this is to use a so-called ‘nonlinear material’ wherein two photons interact within the material. Unfortunately, standard nonlinear materials are far too inefficient to build a quantum logic gate.
It was recently realized that nonlinear interactions can be greatly enhanced by using plasmons. In a plasmon, light is bound to electrons on the surface of the material. These electrons can then help the photons to interact much more strongly. However, plasmons in standard materials decay before the needed quantum effects can take place.
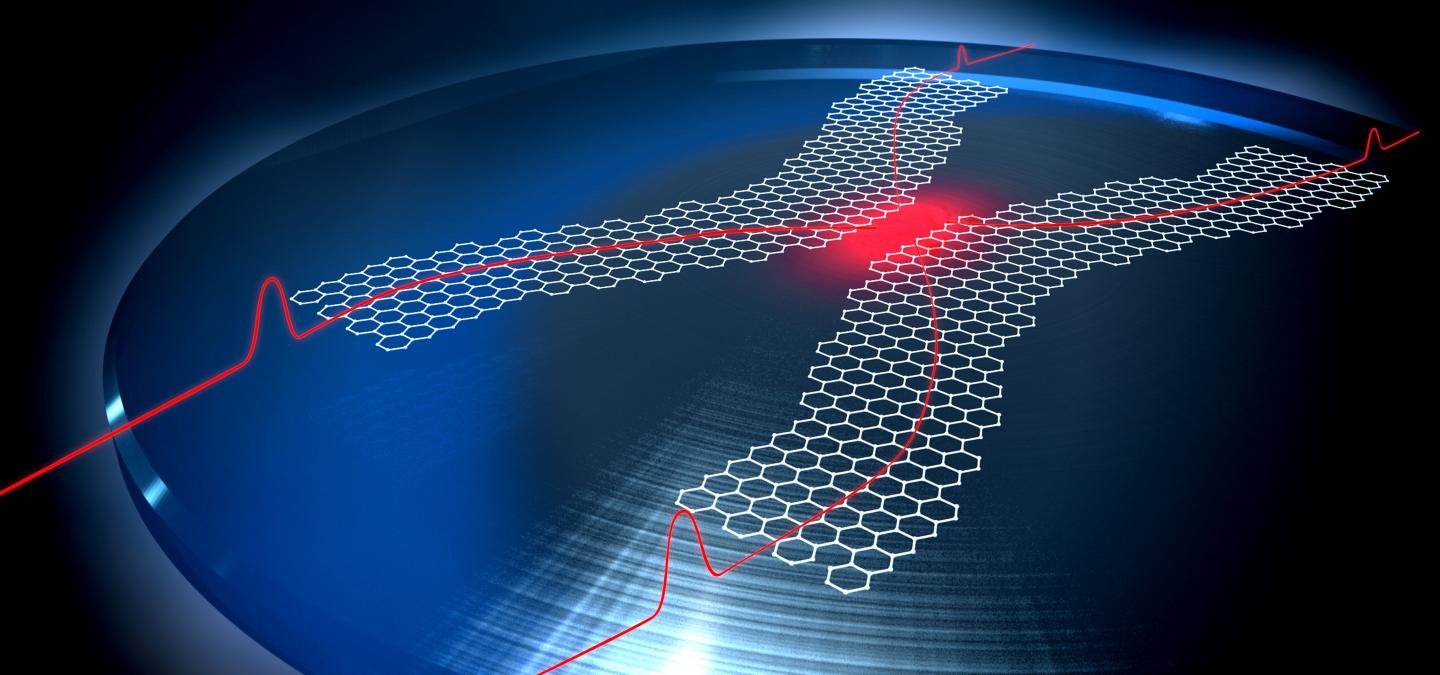
In their new work, the team of scientists led by Prof. Philip Walther at the University of Vienna propose to create plasmons in graphene. This 2D material discovered barely a decade ago consists of a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb structure, and, since its discovery, it has not stopped surprising us. For this particular purpose, the peculiar configuration of the electrons in graphene leads to both an extremely strong nonlinear interaction and plasmons that live for an exceptionally long time.
In their proposed graphene quantum logic gate, the scientists show that if single plasmons are created in nanoribbons made out of graphene, two plasmons in different nanoribbons can interact through their electric fields. Provided that each plasmon stays in its ribbon multiple gates can be applied to the plasmons which is required for quantum computation. “We have shown that the strong nonlinear interaction in graphene makes it impossible for two plasmons to hop into the same ribbon” confirms Irati Alonso Calafell, first-author of this work.
Their proposed scheme makes use of several unique properties of graphene, each of which has been observed individually. The team in Vienna is currently performing experimental measurements on a similar graphene-based system to confirm the feasibility of their gate with current technology. Since the gate is naturally small, and operates at room temperature it should readily lend itself to being scaled up, as is required for many quantum technologies.
###
Publication:
Quantum computing with graphene plasmons, I. Alonso Calafell, J. D. Cox, M. Radonji?, J. R. M. Saavedra, F. J. García de Abajo, L. A. Rozema & P. Walther. npj Quantum Information 5, 37 (2019).
DOI: 10.1038/s41534-019-0150-2
Media Contact
Philip Walther
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




