Researchers learn how a key transcription factor helps regulate the immune system and could be critical to understanding autoimmune disease and cancer immunosuppression
Credit: OIST
Our immune systems defend our bodies against dangerous invaders and help clean up when damage is done. But if our bold protectors are left unsupervised, they sometimes do their jobs too well and end up harming healthy tissues. Researchers at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST) have now described how a specific transcription factor, which modulates gene expression, plays a critical role in keeping the immune system in line in mice.
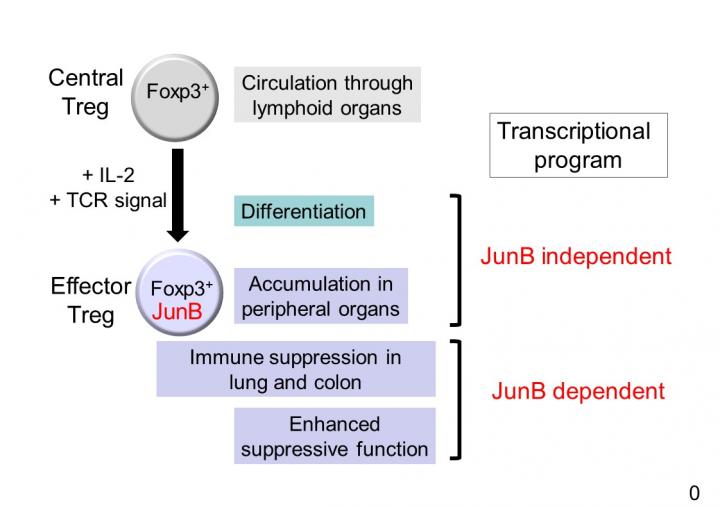
The key transcription factor, known as JunB, helps control the activity of cells whose job it is to suppress immune activity. These cells are called effector regulatory T cells, or eTreg cells for short. The researchers found that JunB helps switch eTreg cells into their “active state” and promotes their immunosuppressive functions. Their results, published on December 17, 2018, in Nature Communications, could give important insight into the development of autoimmune disease and cancer immunosuppression.
“We found that JunB regulates select functions of eTreg cells, specifically in the lung and colon,” said Dr. Shin-ichi Koizumi, co-first author of the study and a postdoctoral scholar in the Immune Signal Unit, led by Prof. Hiroki Ishikawa. “If we can manipulate JunB expression, we may be able to regulate tissue-specific immune responses. This could lead to the development of new therapies for cancer and autoimmune disease.”
Koizumi led the study with his co-author Dr. Daiki Sasaki, another postdoctoral scholar in the unit. The researchers studied mutant mice to learn what would happen if eTreg cells lacked JunB. Without this key layer of regulation, mice appear to develop severe inflammation in their lungs and colons. This suggests that JunB helps prevent autoimmunity in a specific subset of organs, and without its watchful surveillance, the immune system will attack those tissues.
“Interestingly, in contrast to other Treg mutants, inflammation is restricted to these particular organs,” said Prof. Ishikawa. “In the future, JunB expressed by eTregs may itself may be a therapeutic target for colon and lung cancers.”
Tissue Specificity Key for Future Clinical Applications
In a previous study, the researchers reported that JunB helps control the differentiation of T helper cells, another subset of cells that regulate the immune system. They depleted JunB expression in mice for that experiment, as well, and noticed that eTreg cells levels dropped significantly in the colon. They hypothesized that JunB is not only important to T helper cells, but to eTreg cells, too.
Effector Treg cells begin as central Treg cells, or cTreg cells, until they are exposed to antigens — proteins that label foreign substances in the body so the immune system can find them. cTreg cells then differentiate into eTreg cells, and in turn, significantly boost their JunB expression. The researchers found that, without JunB, eTreg cells are unable to accumulate in the colon and thus their numbers fall drastically.
In the lung and spleen, eTreg levels remained normal but the cells’ function was compromised. Those tissues exhibited severe inflammation and autoimmunity because JunB wasn’t present to rein in the host immune response.
Looking forward, the researchers want to learn exactly how JunB interacts with other transcription factors to keep the immune system at bay. With better understanding of the mechanism as a whole, scientists may someday be able to modulate immune responses in specific tissues. At present, treatments often affect immune responses across the entire body and lead to unfortunate side effects. Doctors need a more targeted approach.
“We want to completely elucidate the transcription program in eTreg cells,” said Koizumi. “If we can induce a new transcription program in eTreg cells, we could potentially manipulate immune responses in various tissues and treat a range of cancers and autoimmune-related diseases.”
###
Media Contact
Kaoru Natori
[email protected]
098-966-2389
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




